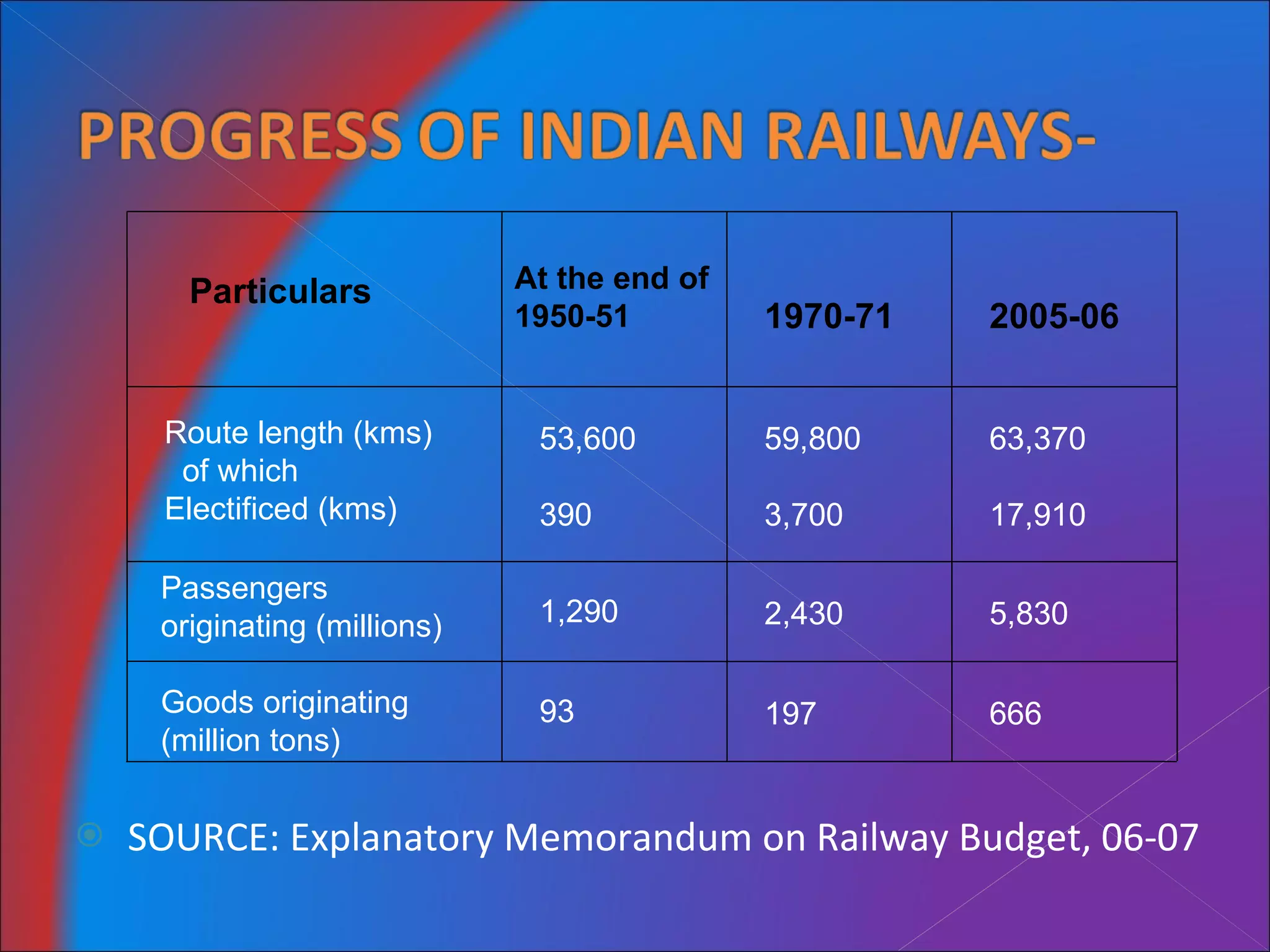
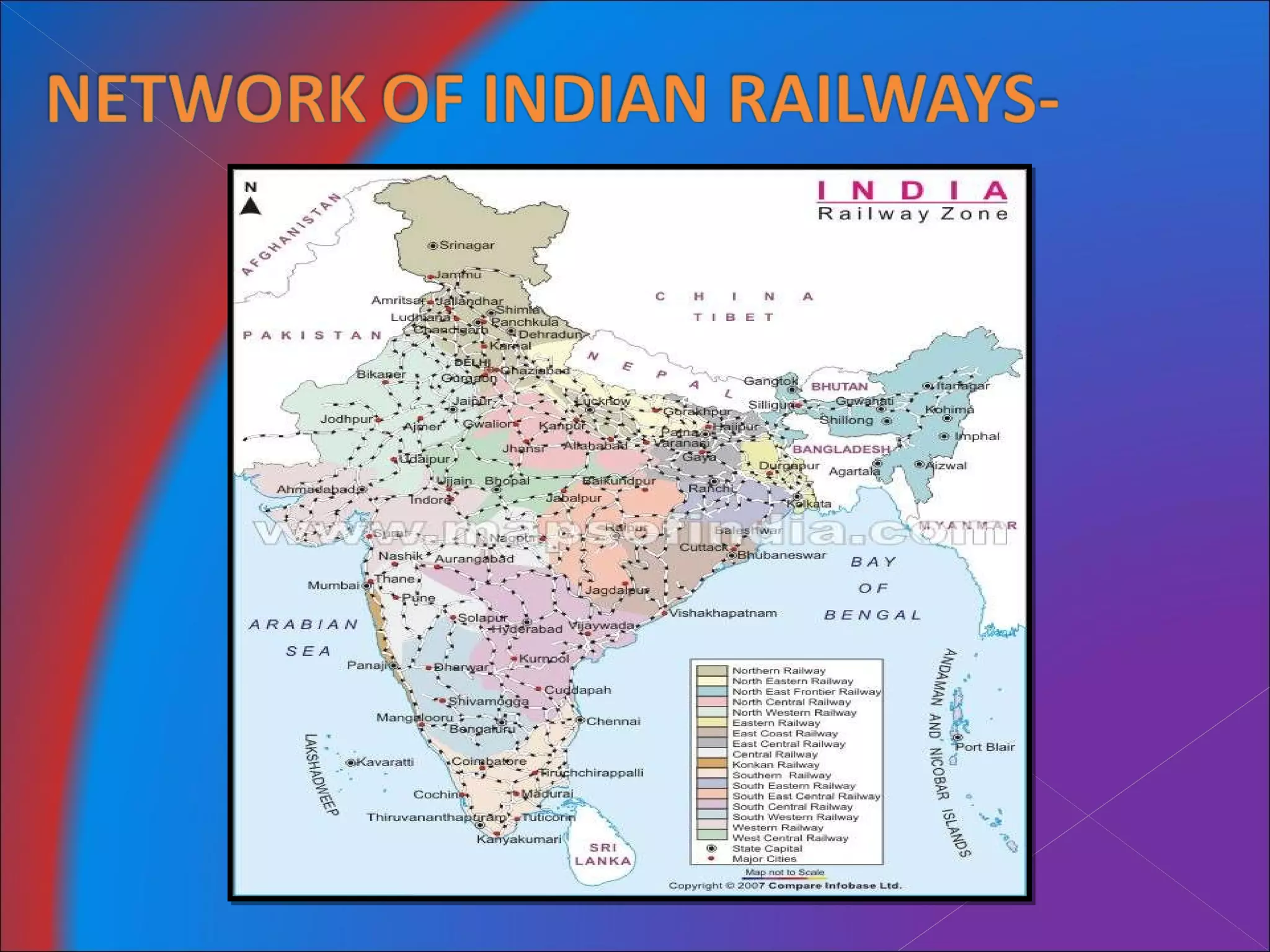
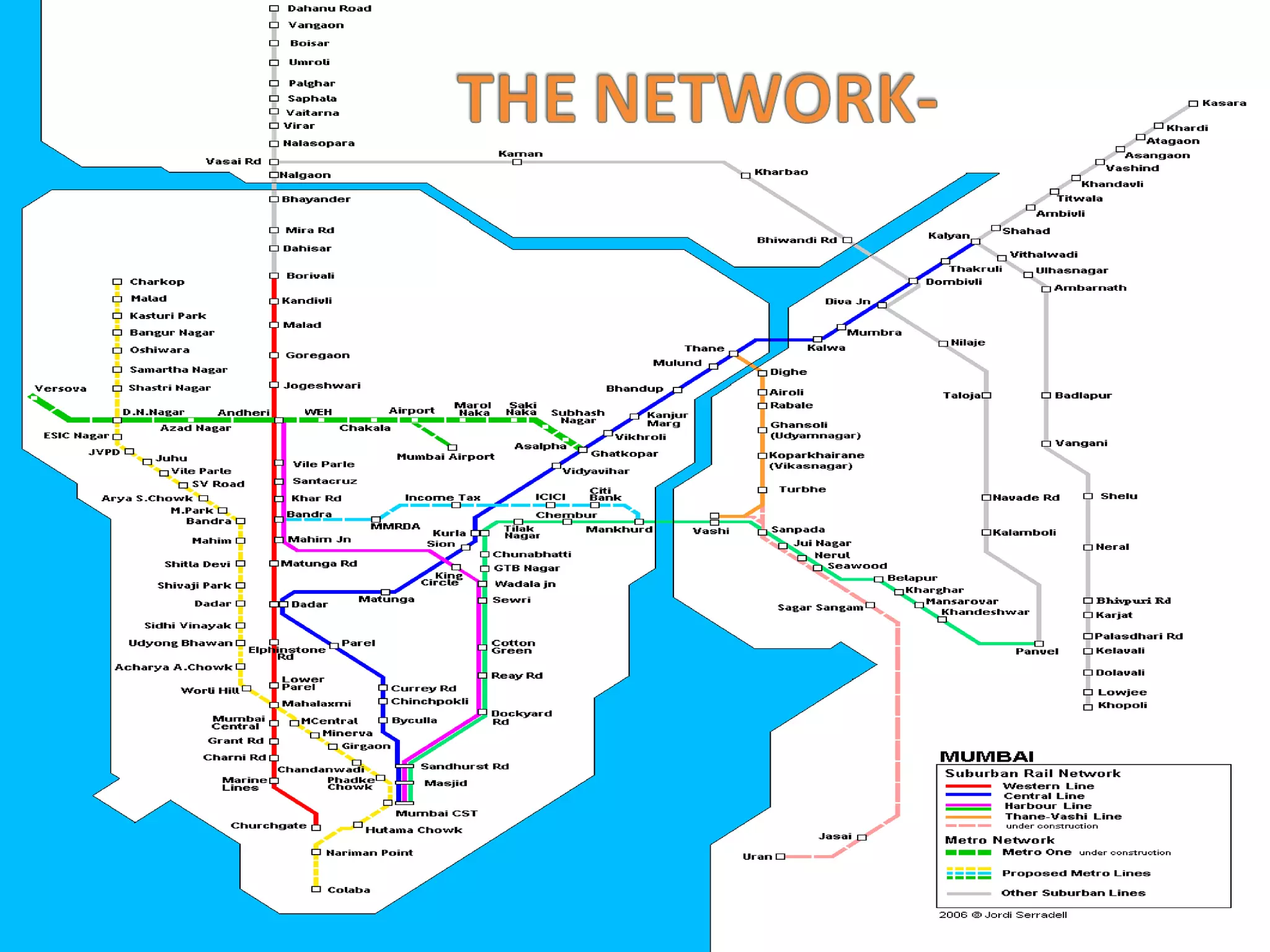
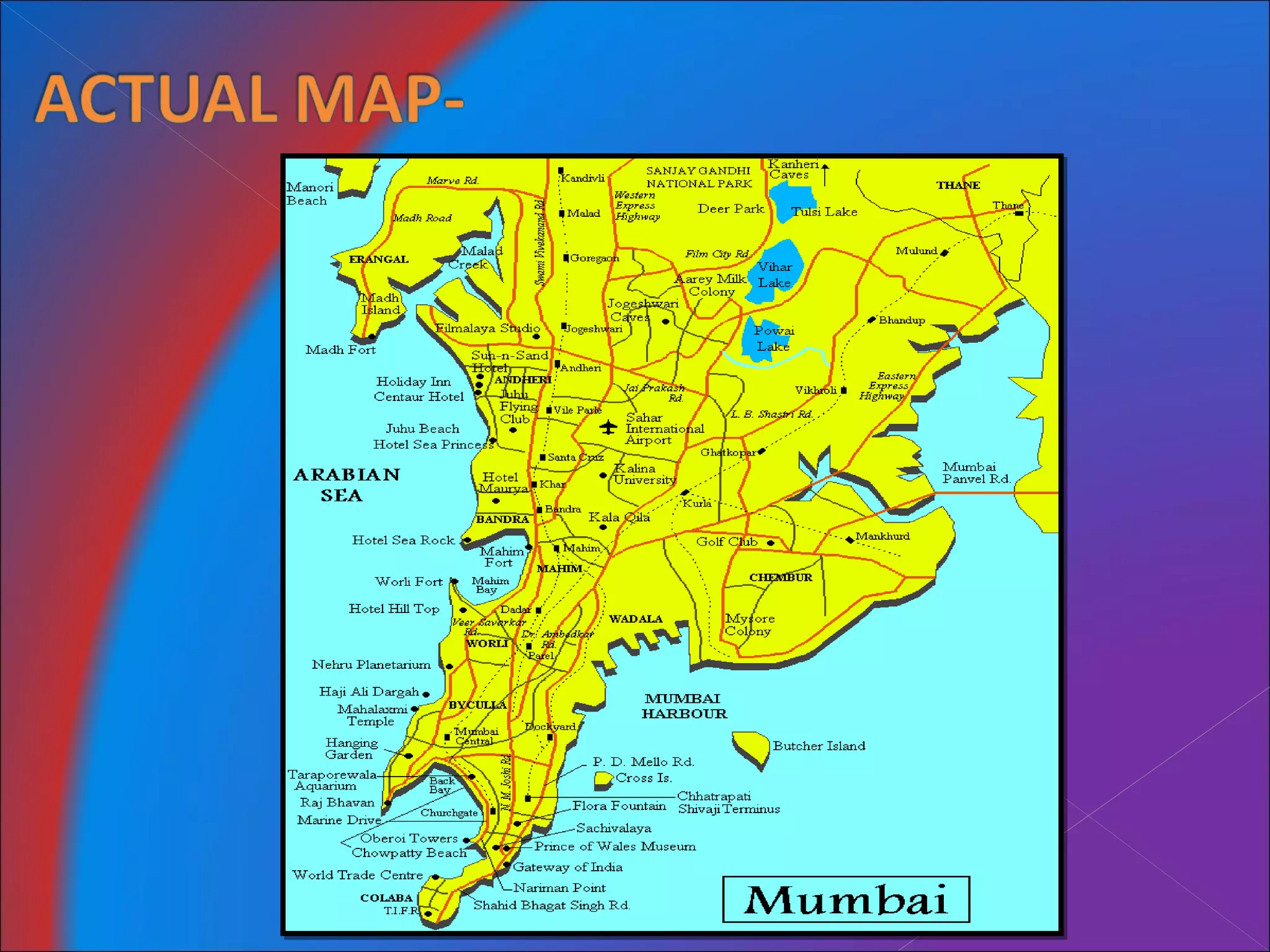
The document discusses Mumbai Suburban Railways, which carries over 6.6 million passengers daily and has one of the highest passenger densities of any urban rail system. It notes strengths like being a large employer but also weaknesses like delays, overcrowding, and lack of infrastructure upgrades. It analyzes demand and capacity constraints and surveys problems reported by passengers and employees. Suggestions are made to increase frequency and capacity of trains to better meet passenger needs.