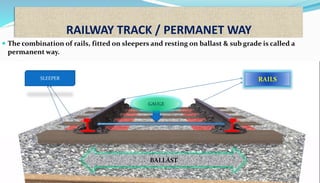
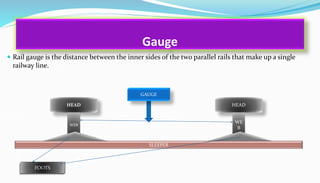
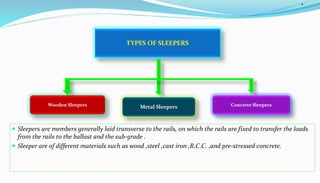
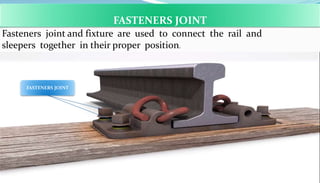
This document provides an overview of railway engineering. It defines railway engineering as dealing with the design, construction, and maintenance of railway tracks. It then discusses the history of railways in India and introduces some key terms like railway track components, gauge, rails, sleepers, ballast, and fasteners. The railway track combines rails, sleepers, ballast, and other components to form the permanent way for train movement. Different types of rails, sleepers, and gauges used in India are also outlined.