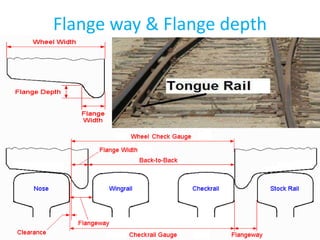
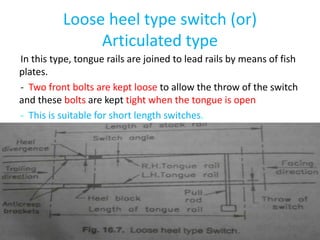
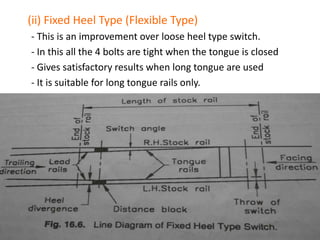
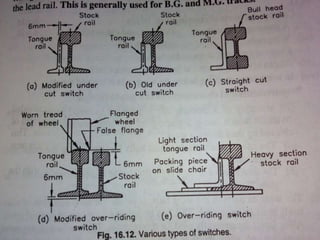
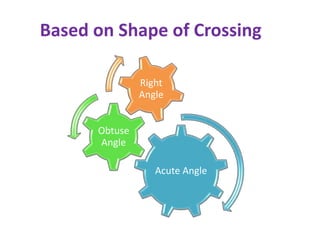
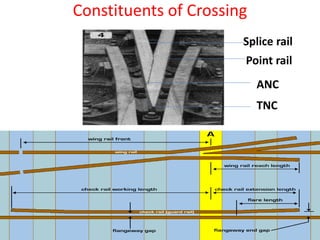
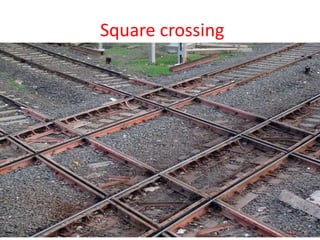
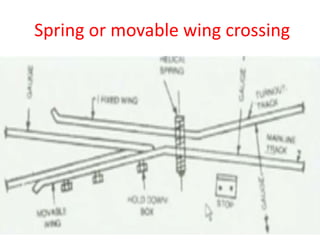
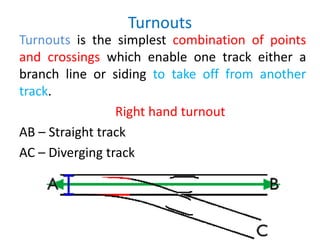
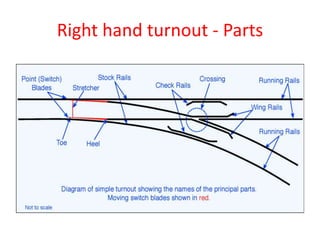
Points and crossings facilitate the diversion of trains between tracks through mechanical installations like turnouts, which are combinations of specific components including switches, stock rails, and vee crossings. Different types of turnouts include right and left hand turnouts, with variations such as loose heel and fixed heel types depending on the length and construction of the tongue rails. Crossings are categorized by angles (acute, obtuse, right) and consist of various configurations determined by their constituent parts.



![• A Pair of switches
A switch, turnout or [set of] points is a mechanical
installation enabling railway trains to be guided
from one track to another.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointsandcrossings-170328111038/85/Points-and-crossings-6-320.jpg)