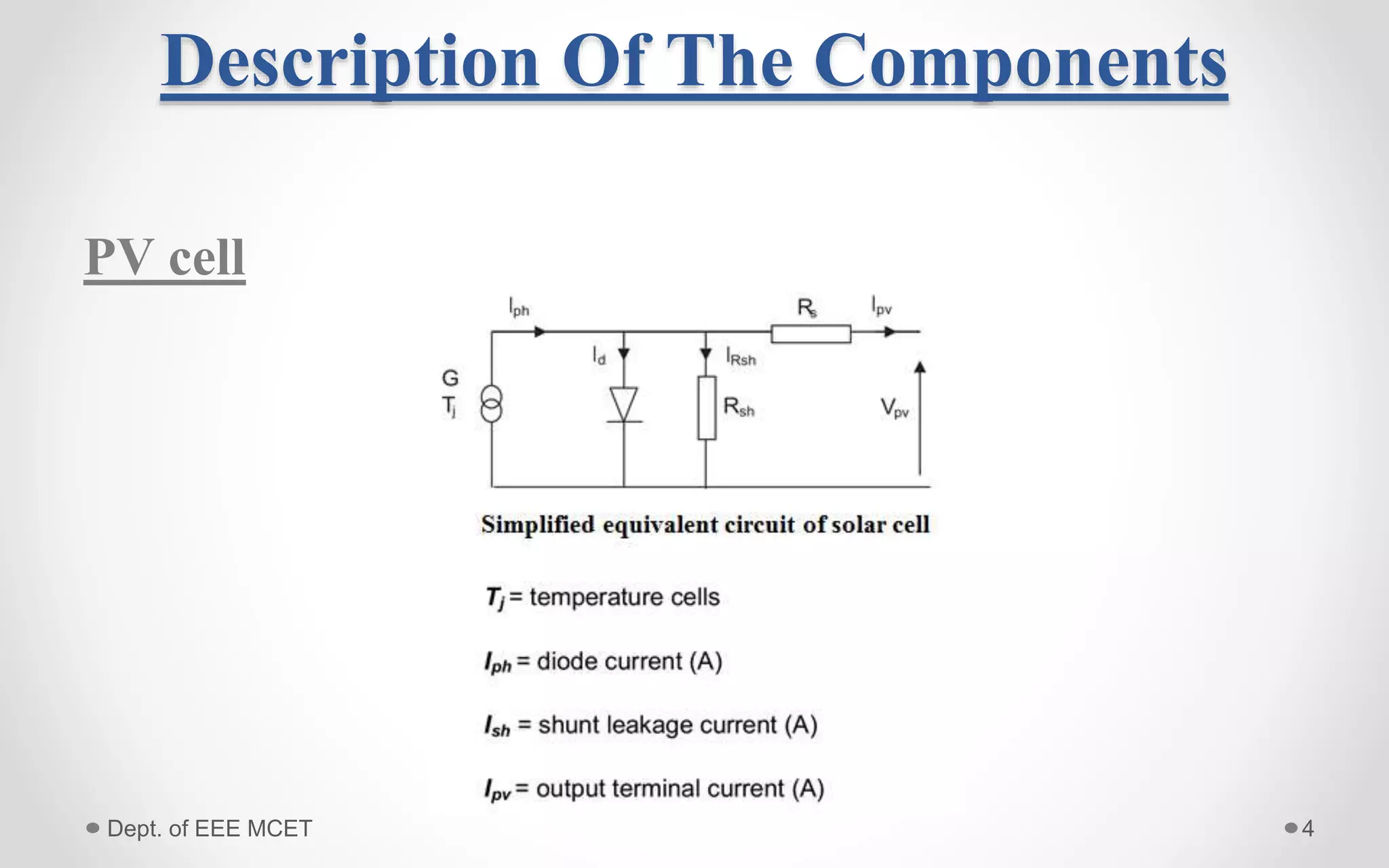
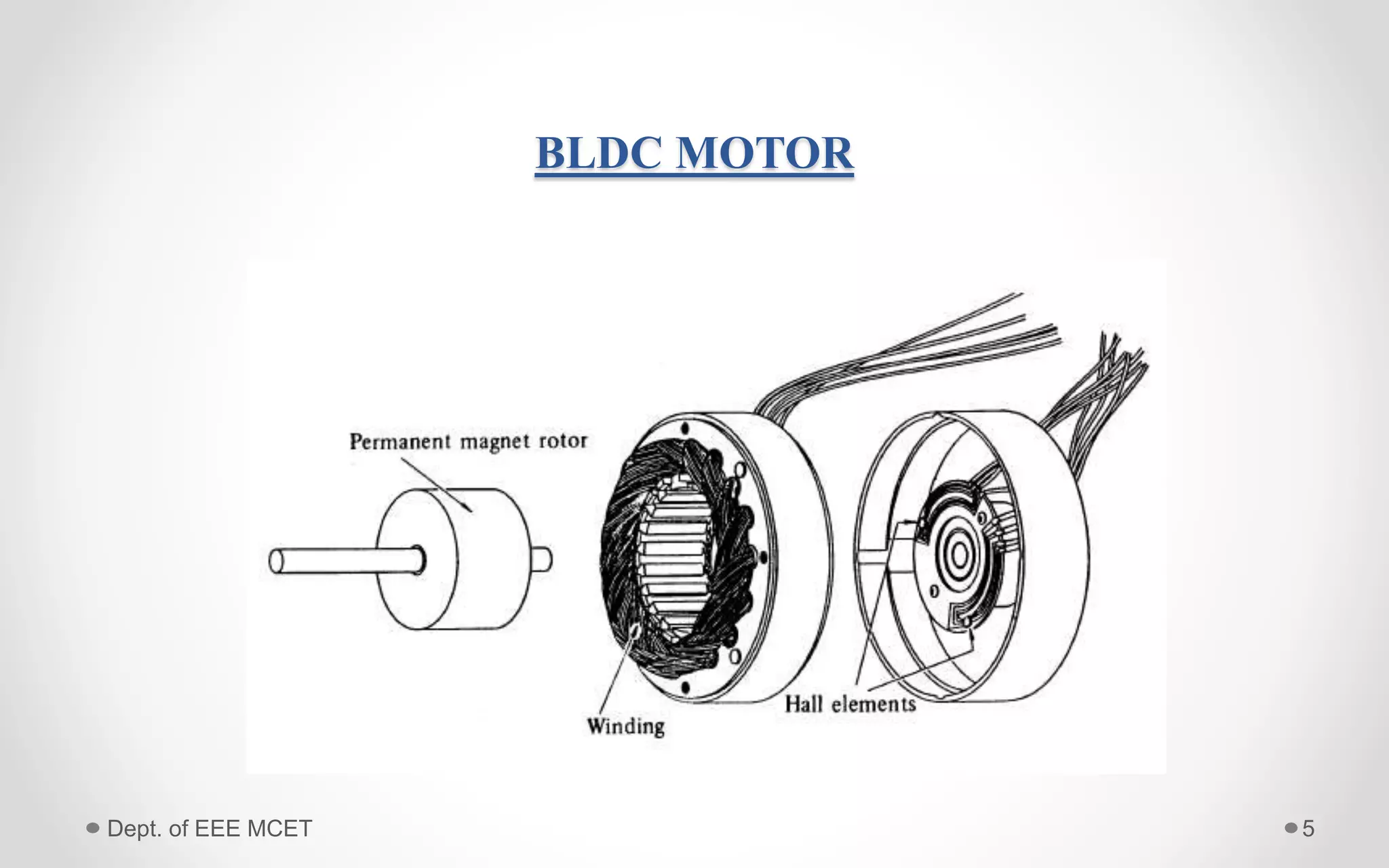
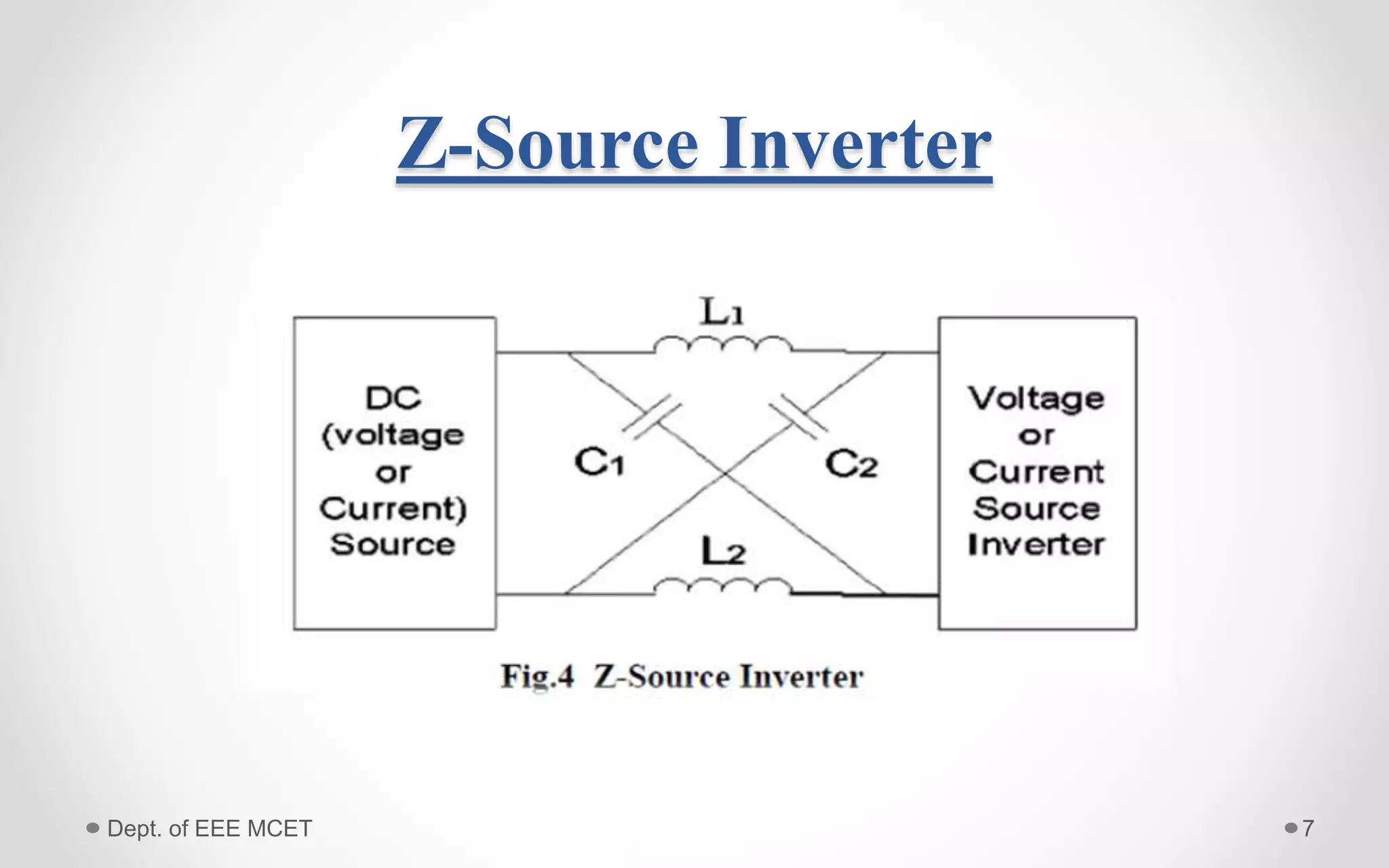
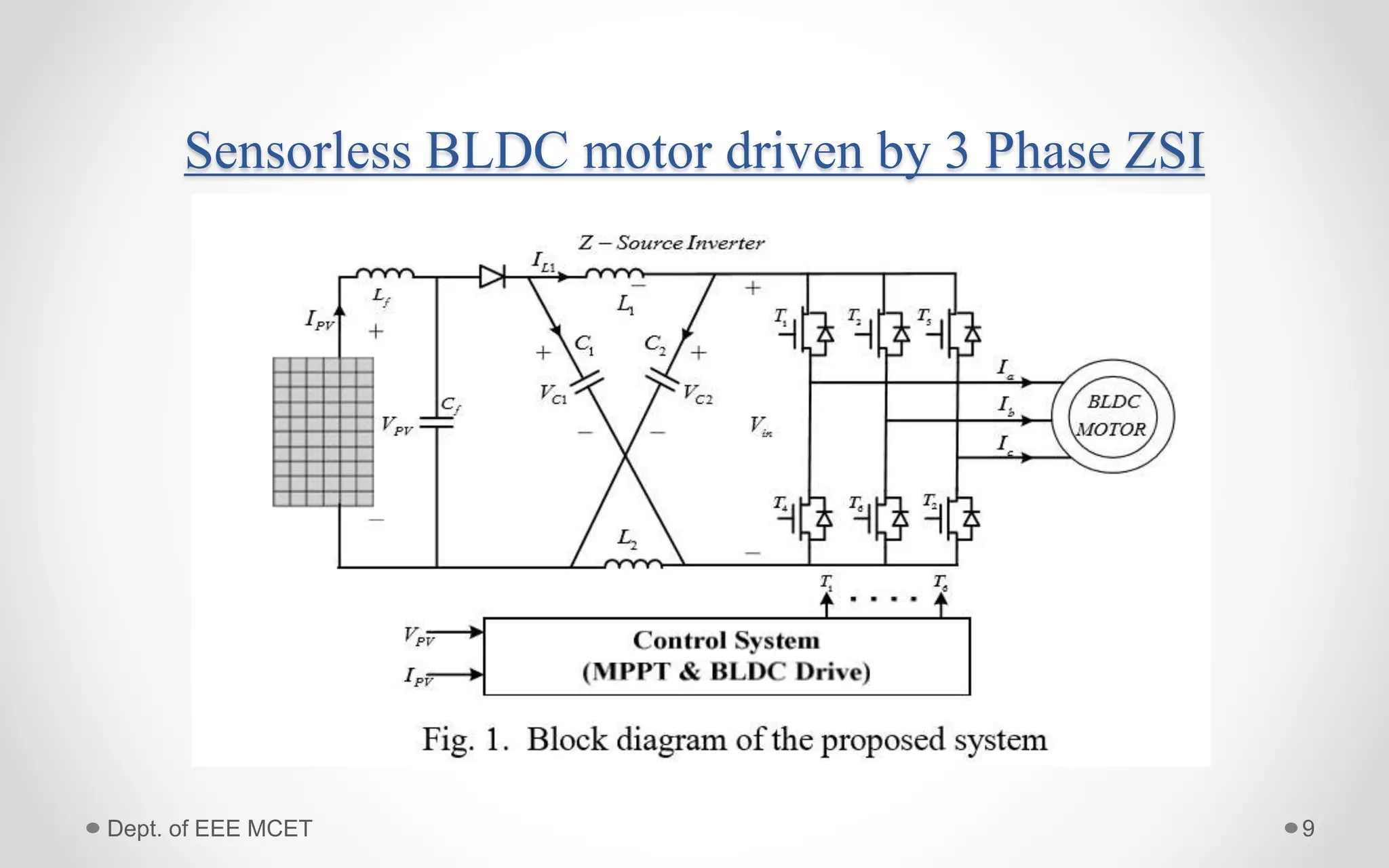
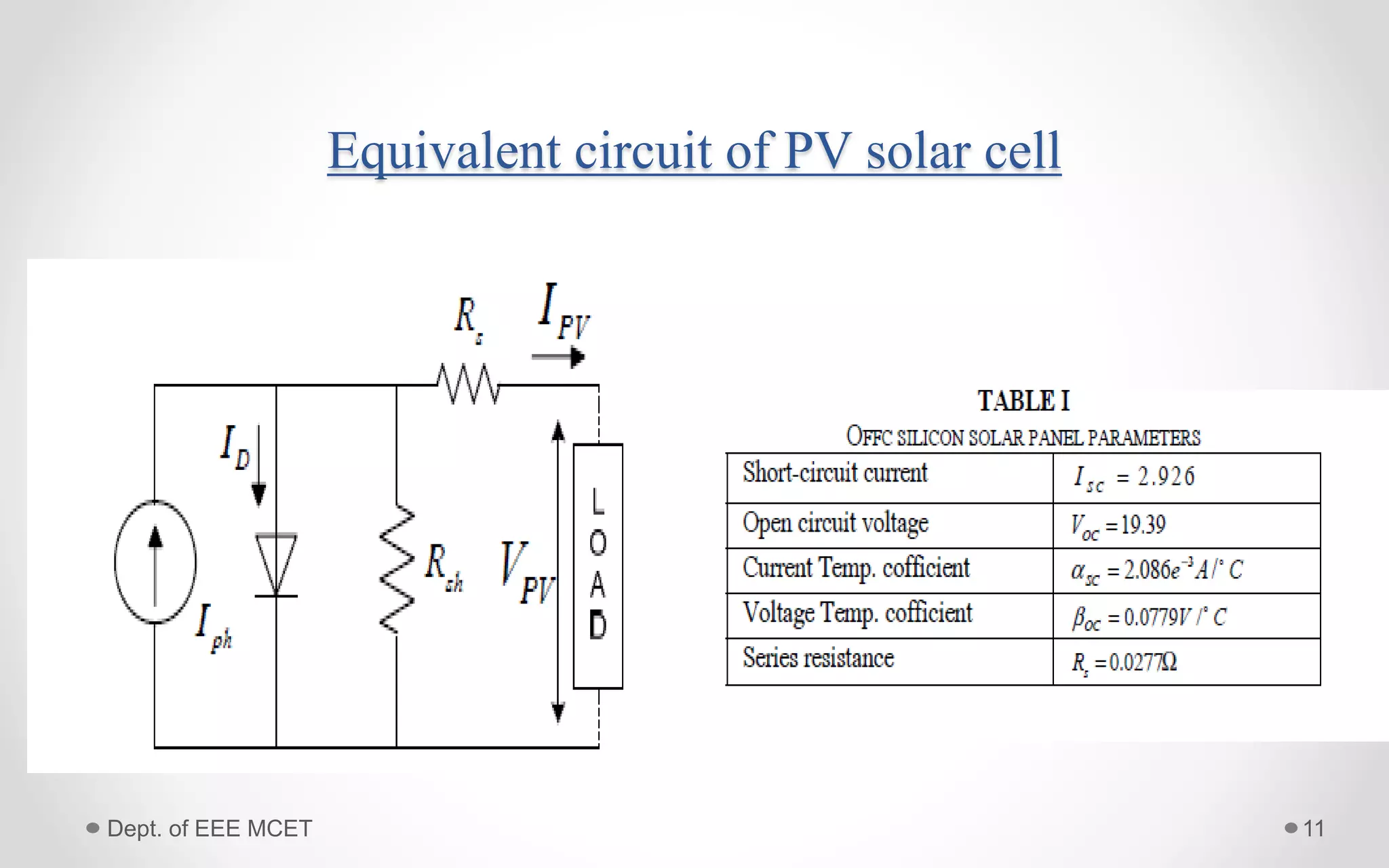
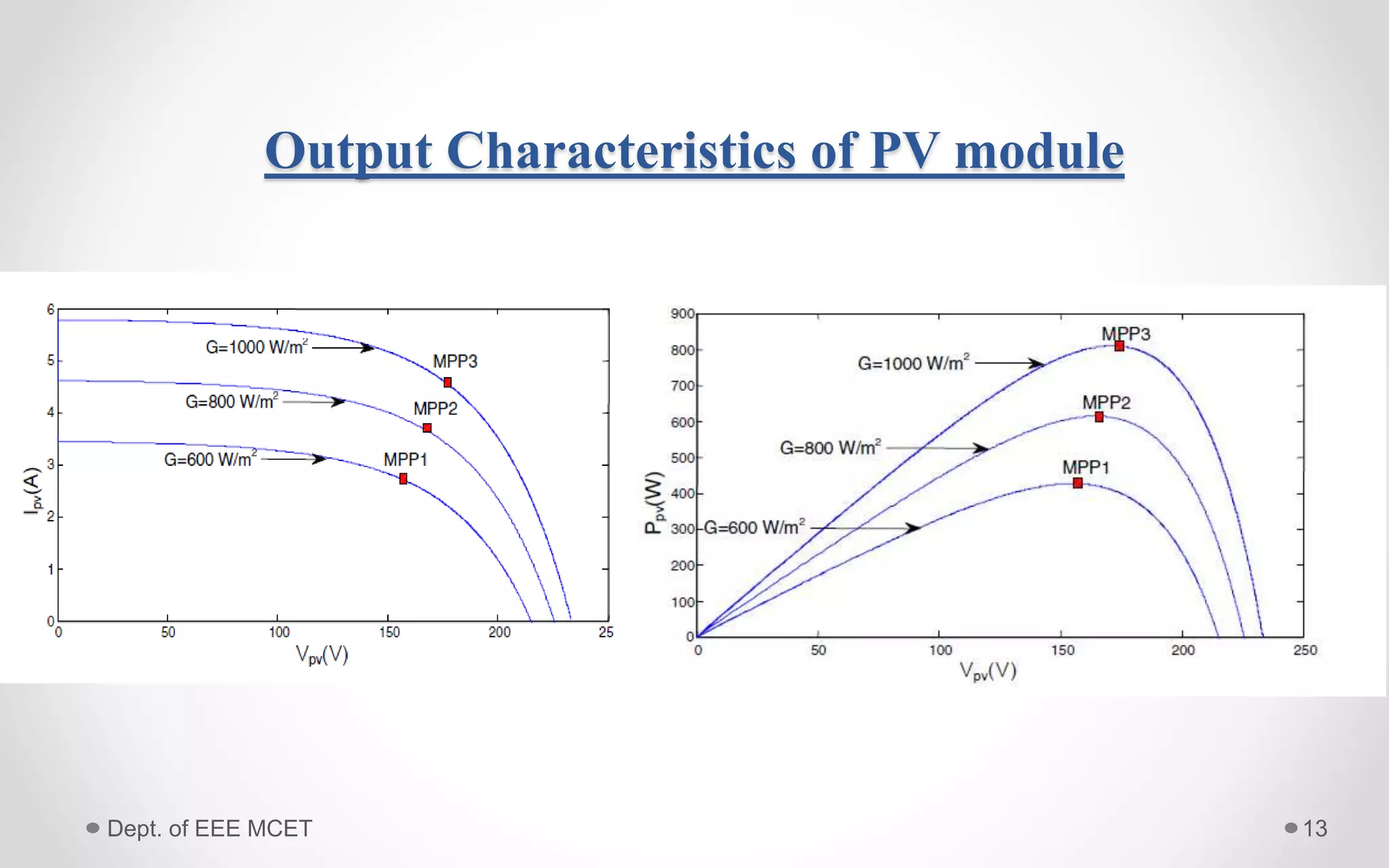
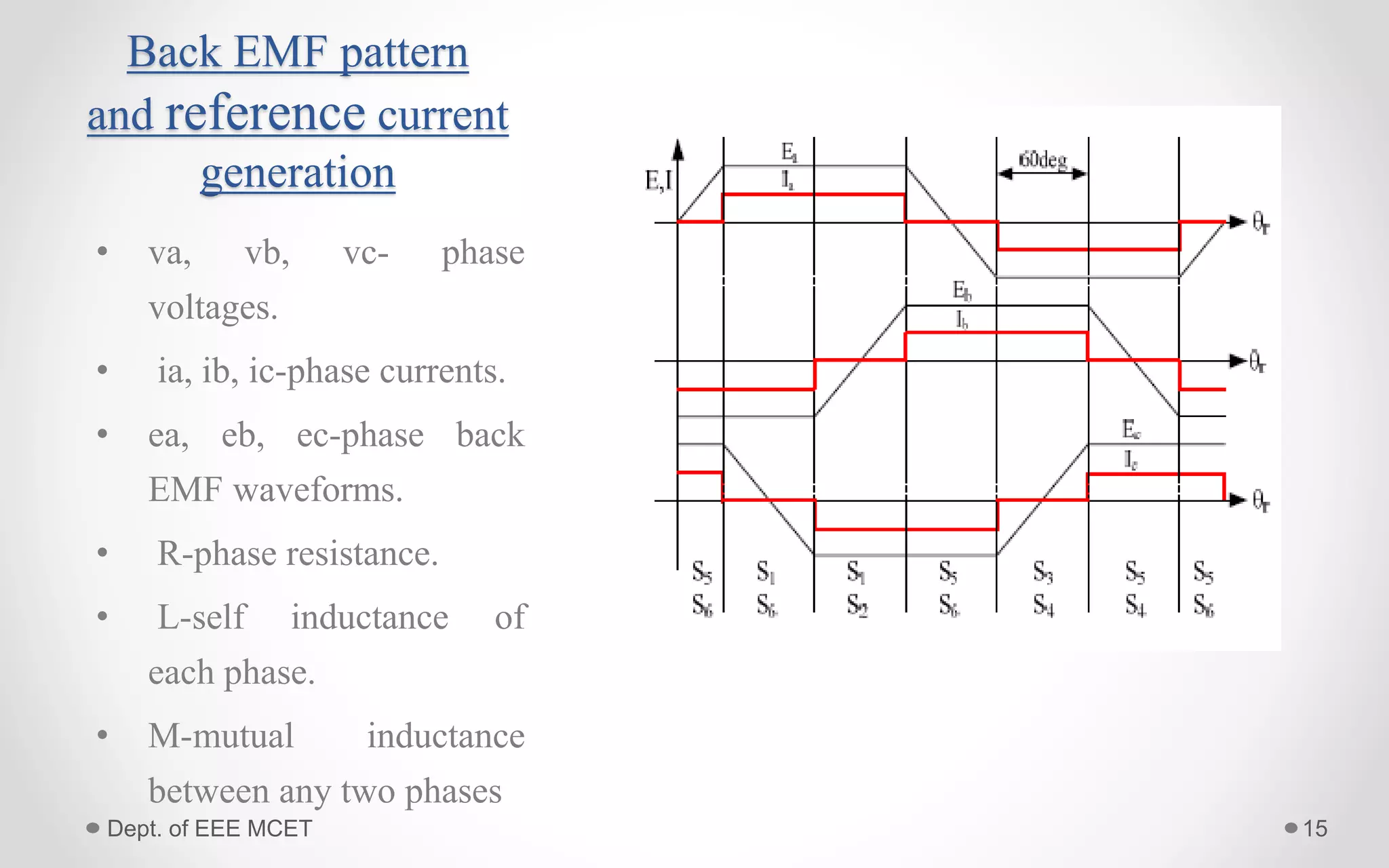
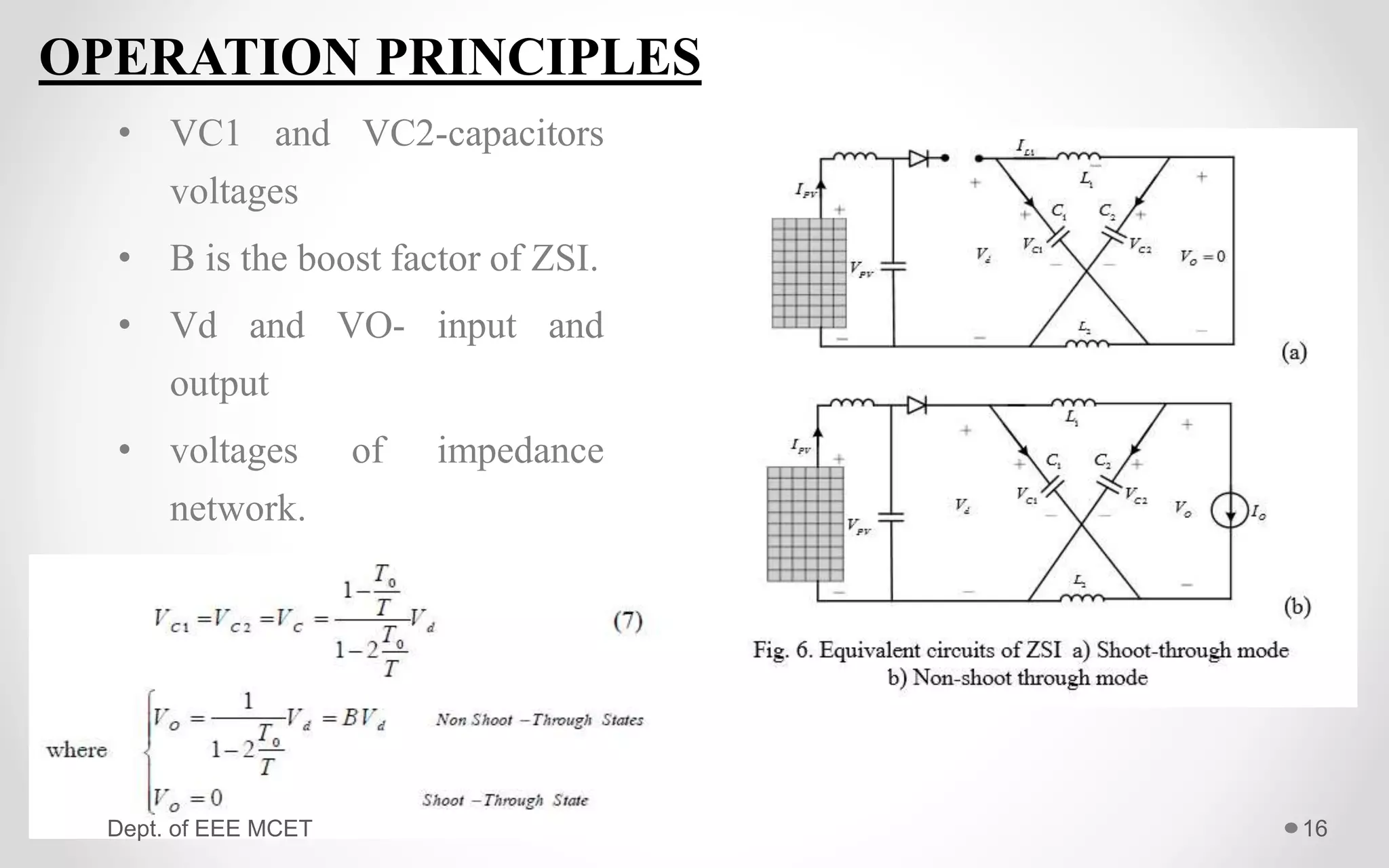
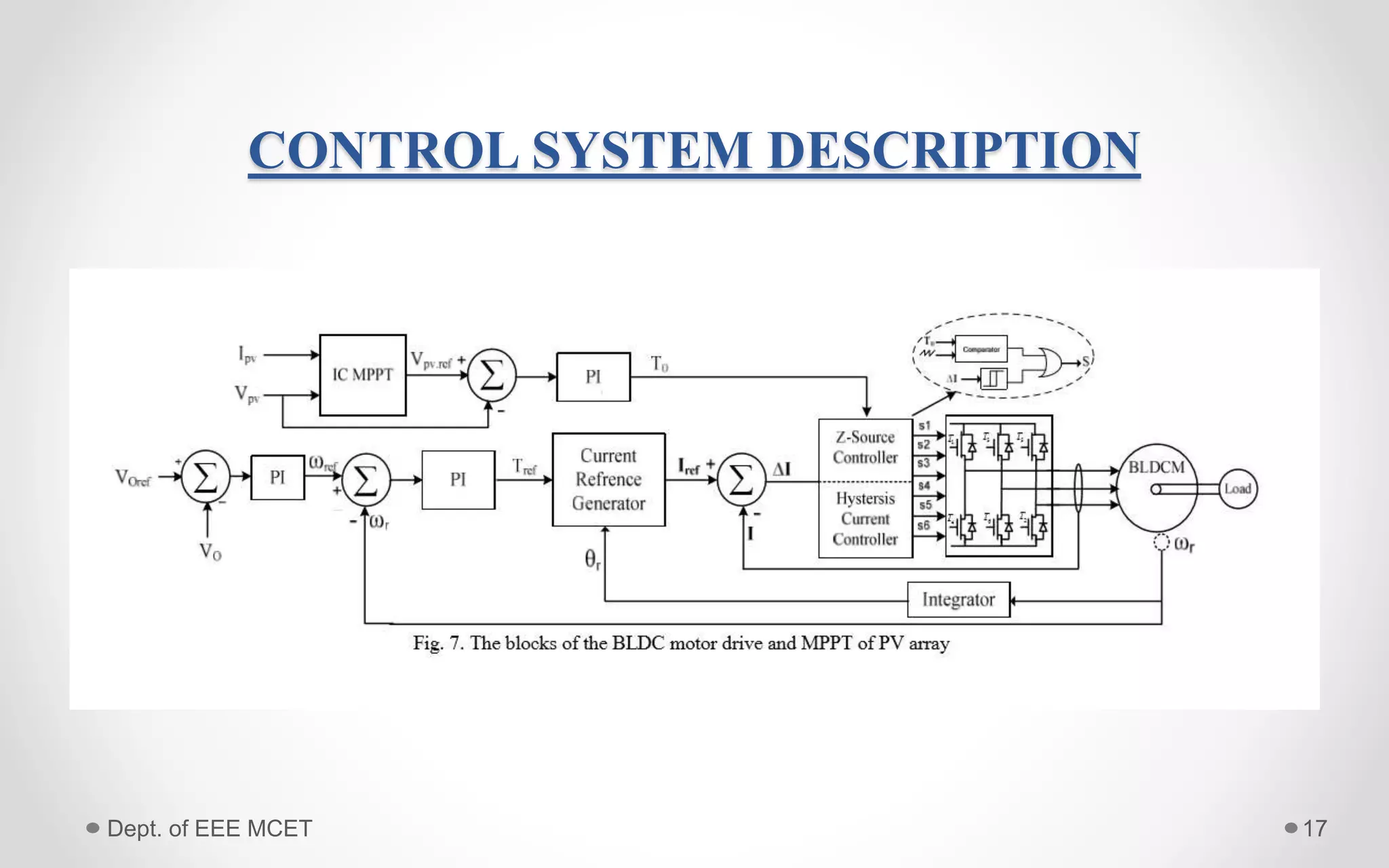
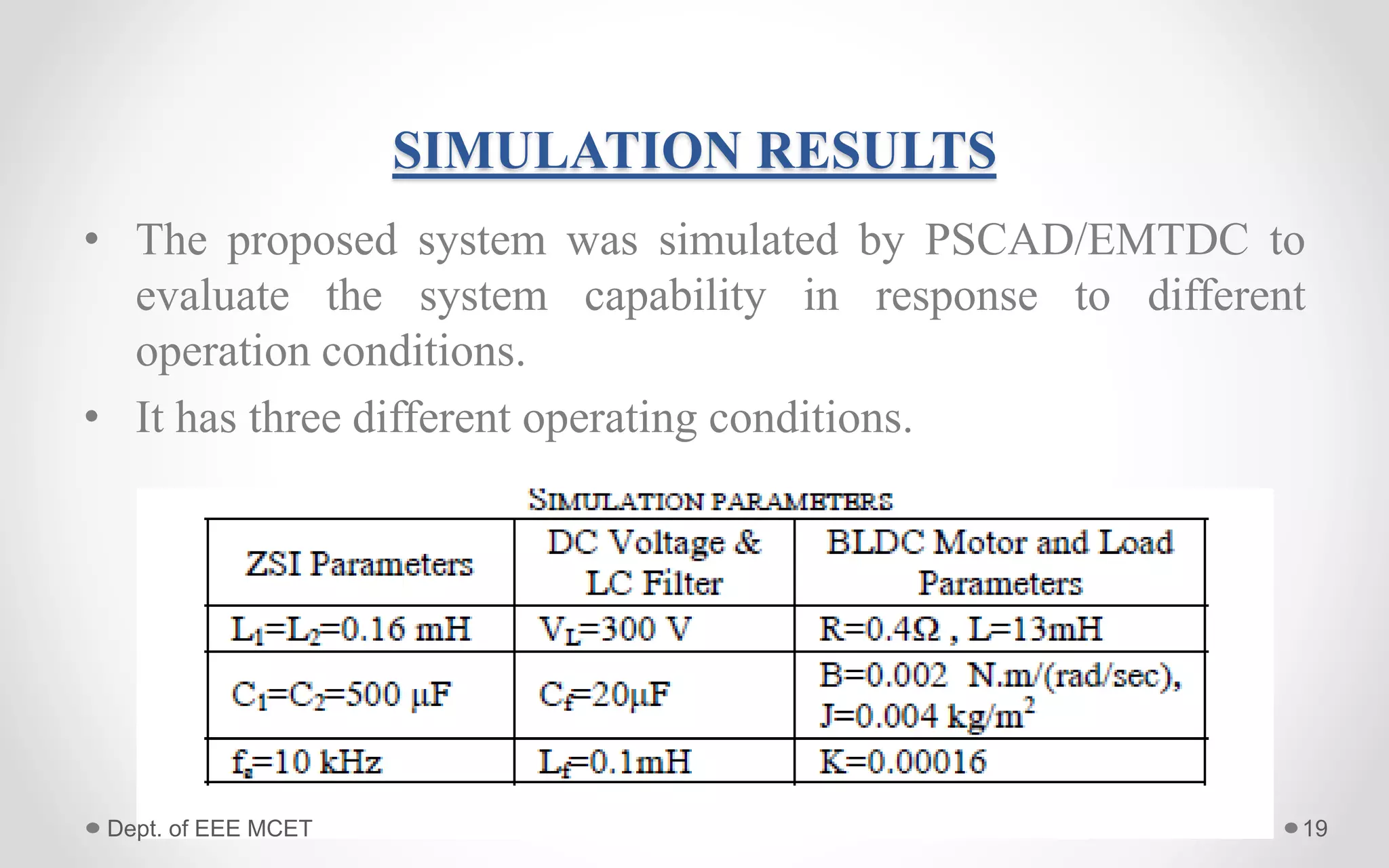
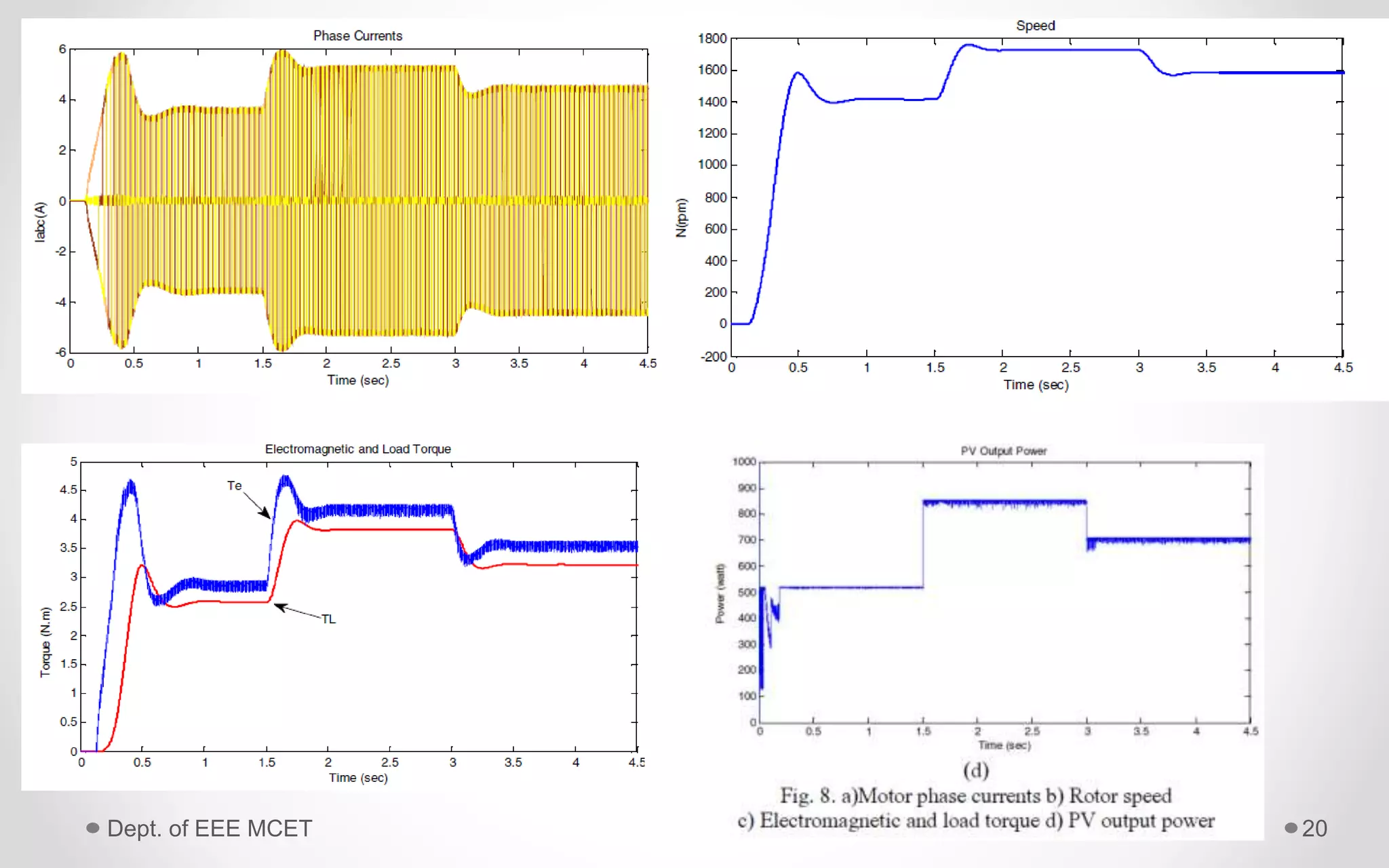
This document proposes a system using a photovoltaic array, maximum power point tracking, and a Z-source inverter to power a sensorless brushless DC motor. A PV array extracts solar energy and MPPT control maximizes the output power. A Z-source inverter can boost the PV voltage and supplies power to the BLDC motor. Simulation results show the system can successfully operate under different conditions and regulate motor speed while maximizing solar energy harvesting. The system has advantages of fewer power switches, smaller capacitors/inductors, and fast dynamic response compared to conventional PV systems.