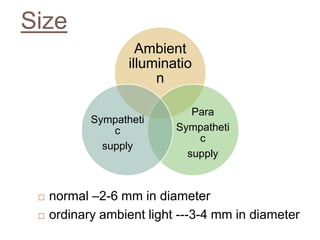
The pupil is a circular opening located in the center of the iris that controls the amount of light entering the eye to ensure optimal vision. Key characteristics of a normal pupil include being equal in size and round between both eyes. Abnormal pupils can be too small (miosis) or too large (mydriasis) and may be caused by medical conditions, drugs, or neurological disorders. Doctors examine the pupil's size, shape, equality, reaction to light, and accommodation to evaluate for any abnormalities.





























![HORNER’S SYNDROME [J. F.
Horner]
Sympathetic dysfunction
Ptosi
s
Miosis Anhidrosis
Apparent
enophthalmo
s
Loss of the
ciliospinal reflex
Ocular
hypotony
Increased
amplitude
of
accommoda
tion
vasodilatio
n in
affected
distributio
n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pupil-170314112531/85/Pupil-32-320.jpg)