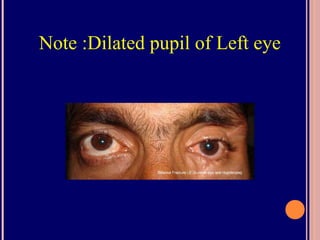
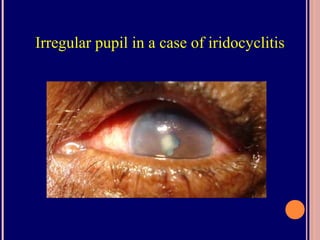
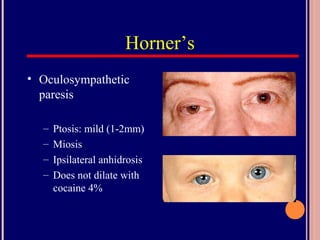
The pupil is a circular opening in the iris that controls the amount of light entering the eye. It constricts (miosis) and dilates (mydriasis) under autonomic nervous system influence. The iris contains two muscle groups - the sphincter pupillae and dilator pupillae - that regulate pupil size. Abnormal pupils may be unequal in size (anisocoria), irregularly shaped, or have abnormal reactions to light or accommodation. Various diseases and drugs can cause pupil abnormalities.