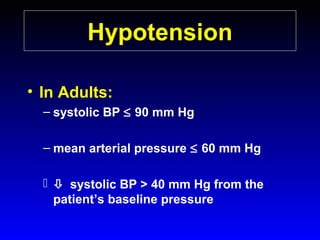
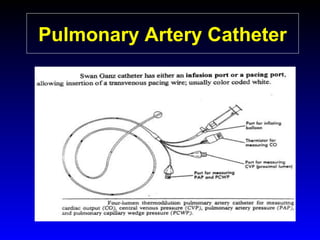
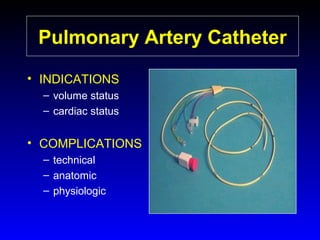
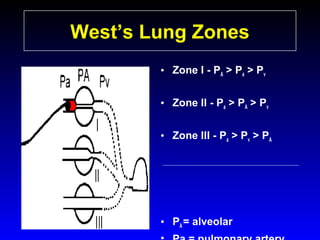
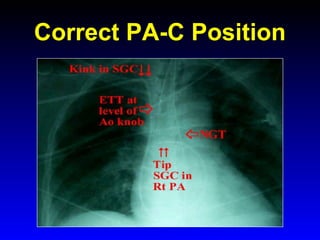
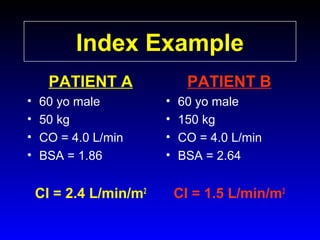
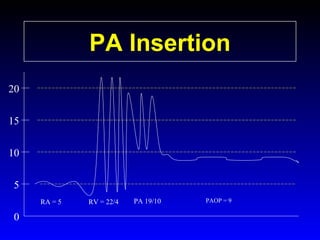
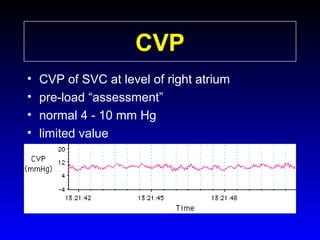
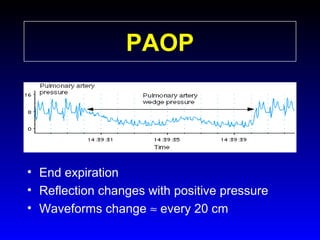
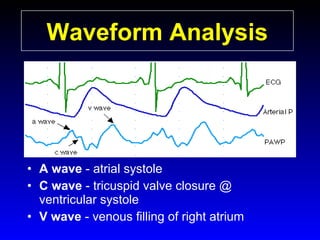
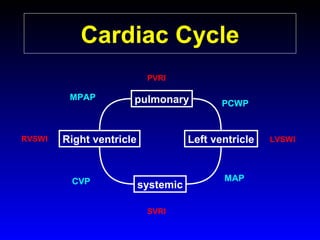
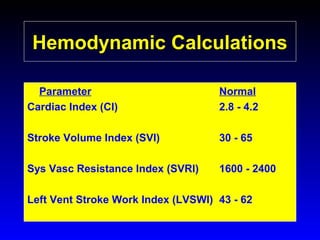
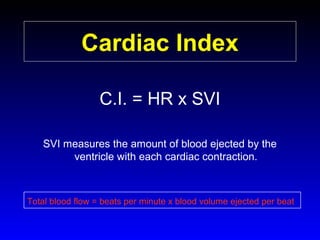
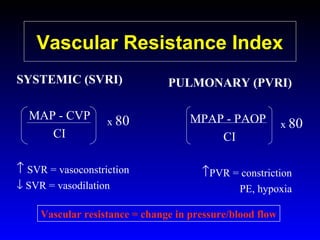
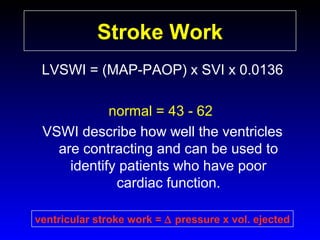
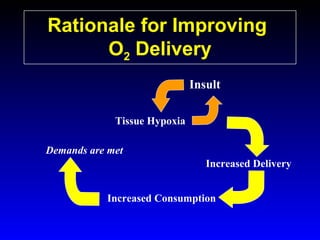
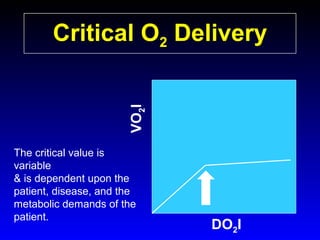
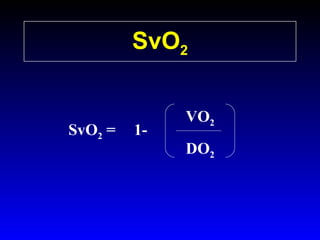
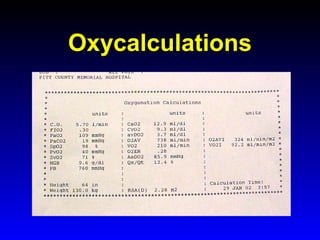
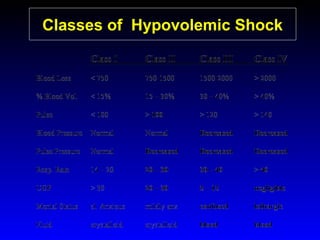
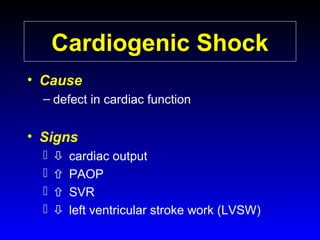
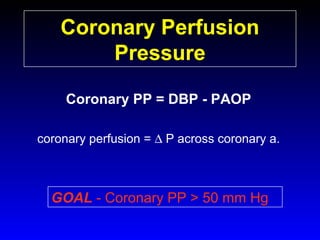
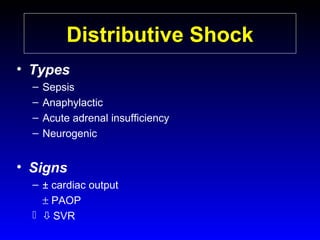
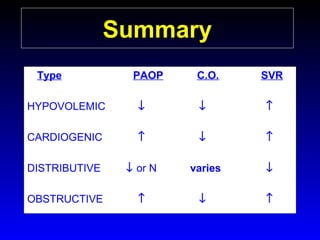
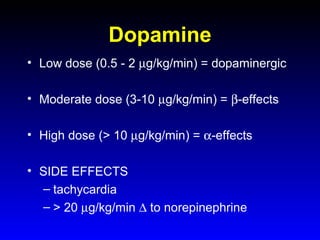
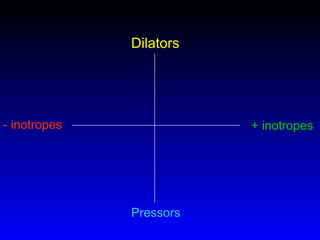
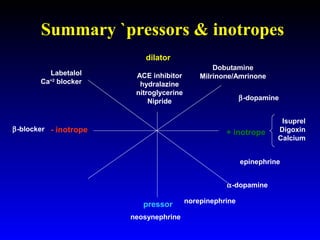
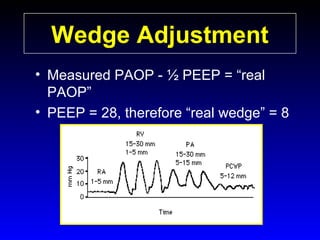
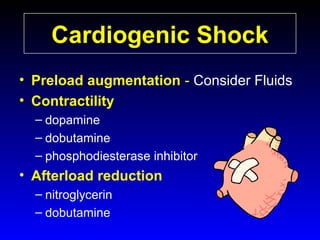
This document provides an overview of shock and hemodynamic monitoring using a pulmonary artery catheter. It defines shock as inadequate organ perfusion and outlines the main categories of shock: hypovolemic, cardiogenic, distributive, and obstructive. It discusses goals of fluid resuscitation in shock and reviews hemodynamic parameters measured by a pulmonary artery catheter such as cardiac output, vascular resistances, and oxygen transport variables. The document uses case studies to demonstrate how these parameters can be utilized to diagnose and guide treatment in different shock states.