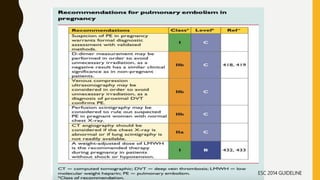
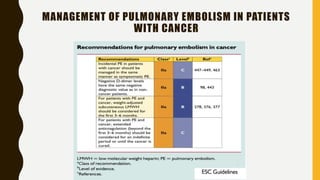
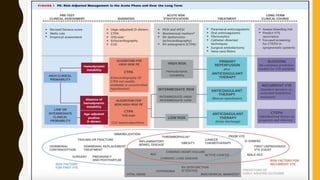
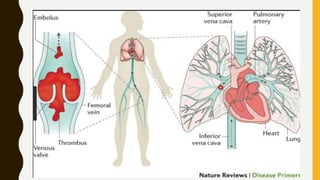
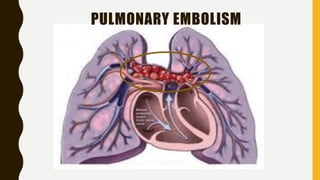
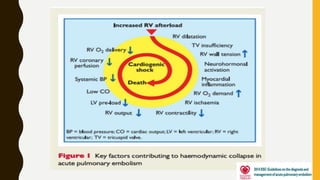
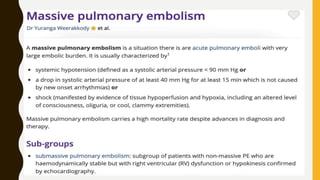
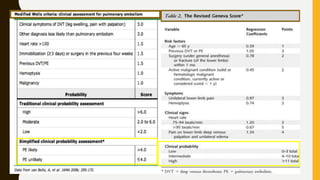
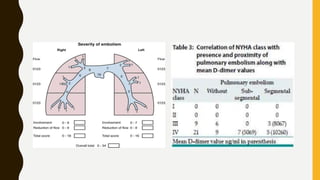
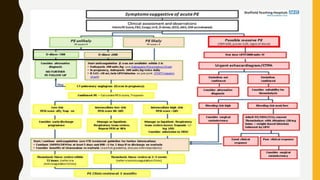
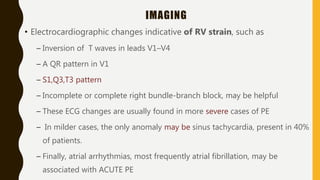
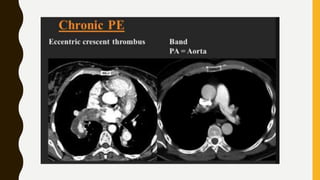
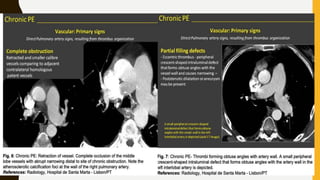
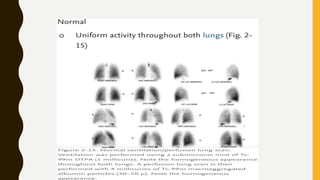
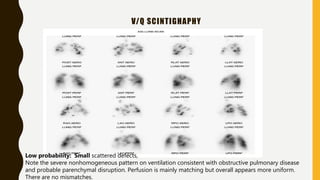
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common clinical disorder associated with high morbidity and mortality. PE occurs when deep vein thrombi detach and embolize to the pulmonary circulation, obstructing blood flow and impairing gas exchange. Clinical presentation of PE is variable but often includes dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia, and pleuritic chest pain. Diagnosis involves assessment of clinical probability, d-dimer testing, imaging studies like CT pulmonary angiography, ventilation-perfusion scanning, echocardiography and assessment of right ventricular function. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications including right heart failure and death.




















![LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
• In blood gas analysis:
– Hypoxaemia is considered a typical finding in acute PE, but up to 40% of the
the patients have normal arterial oxygen saturation and 20% a normal
alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient.[normal PaO2 (ABG: 75-100mmHg vs VBG
35-40mmhg)]
– Hypocapnia is also often present [normal PCO2 (ABG: 38-42mmHg vs VBG
41-51mmhg)]
– Respiratory alkalosis (normal PH :7.38-7.42 ; HCO3 : 22-28mEq/L)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolism-190629085041/85/Pulmonary-embolism-31-320.jpg)





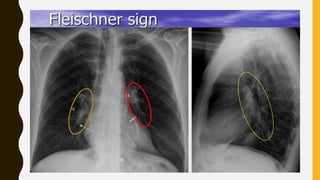
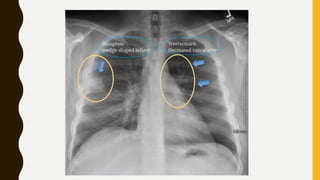
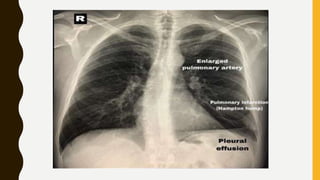
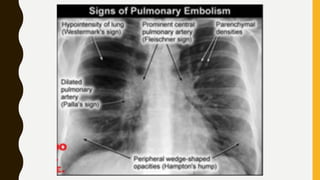




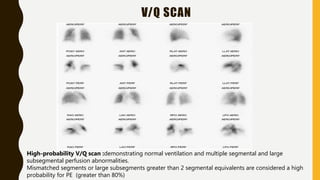

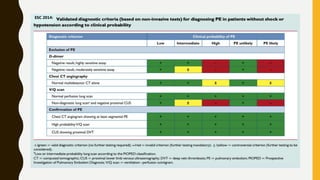
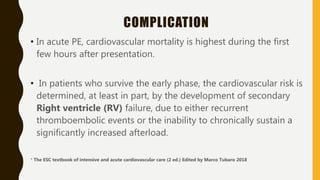

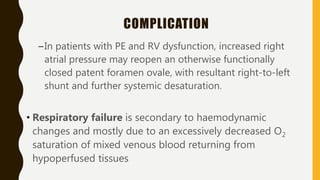




![TREATMENT
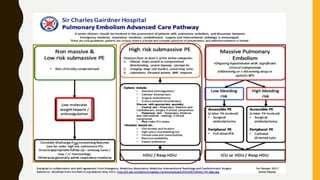
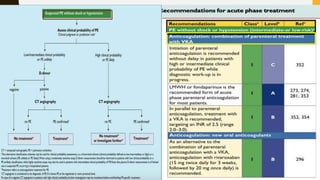
• Anticoagulation
– In patients with acute PE, anticoagulation is recommended, with the
objective of preventing both early death and recurrent symptomatic
or fatal VTE.
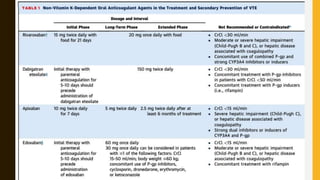
– The standard duration of anticoagulation, at least 3 months :Within
this period, acute-phase Rx consists of administering parenteral
anticoagulation
• Unfractionated heparin (UFH) : 75U/kg iv bolus then infusion of
18U/kg/hr
• Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) 1mg/kg s/c , or fondaparinux]
• Over the first 5–10 days
• Target INR (2.0 -3.0)
• STG guideline 2017
• ACCP guidelines 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolism-190629085041/85/Pulmonary-embolism-74-320.jpg)










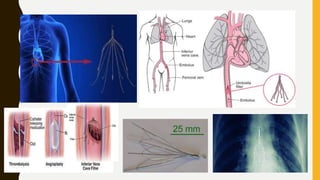
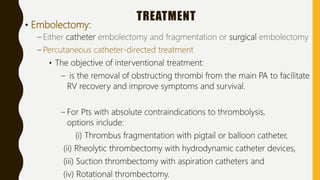
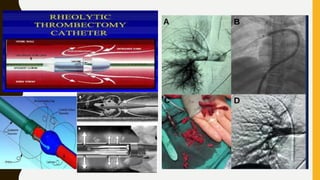
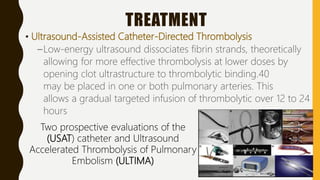

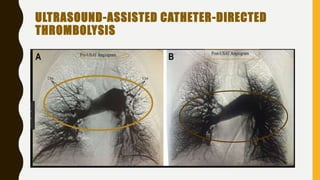
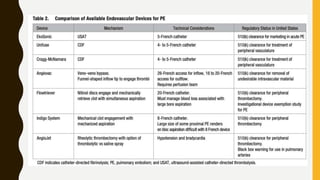
![MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING
• The first step is to discontinue both the thrombolytic and anticoagulation
infusions.
• The next step is to institute supportive therapy, which may include the
application of pressure to bleeding sites, volume repletion with blood
products and fluids, and emergency surgery.
– Protamine sulfate is an antidote to heparin overdose.
• The dose required for heparin reversal is 1mg of protamine for every 100U of
heparin, for a max. 50 mg [Considering heparin’s t1/2 (60 to 90 minutes) when
calculating the protamine dose]
– Aminocaproic acid: 4 g to 5 g should be injected into a 250-ml bag of
diluent and administered over one hour.
– Cryoprecipitate may be indicated in pts (treatment should be reserved for
life-threatening situations)
– IV tranexamic acid has also been used in patients with post-tPA bleeding.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolism-190629085041/85/Pulmonary-embolism-99-320.jpg)