Embed presentation
Downloaded 224 times



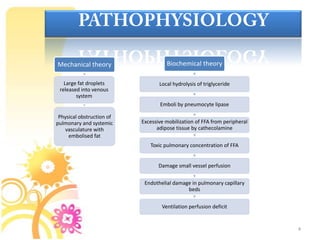
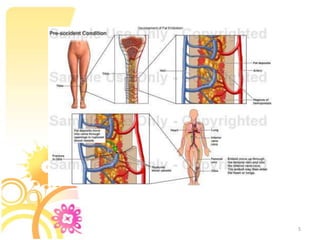


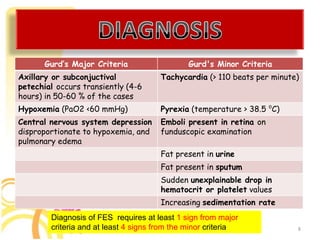



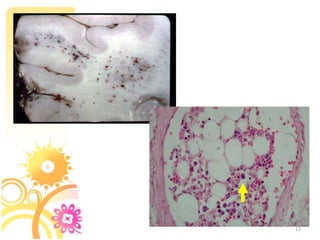


1. Fat embolism syndrome is a serious condition caused by fat emboli obstructing blood vessels, most commonly after long bone or pelvic fractures. It typically manifests 1-3 days after injury. 2. Patients present with a classic triad of hypoxemia, neurological abnormalities, and petechial rash. The most severe cases can involve respiratory distress, restlessness, and coma. 3. Diagnosis requires signs from both major criteria like hypoxemia and petechiae, as well as four minor criteria. Treatment focuses on supportive care like oxygenation, ventilation, hemodynamics, and early stabilization of fractures to prevent further emboli.













