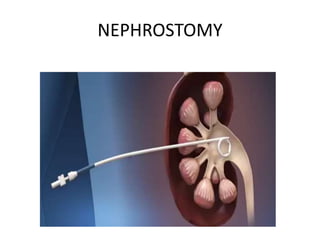
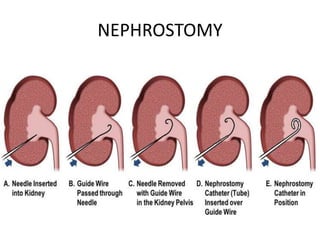
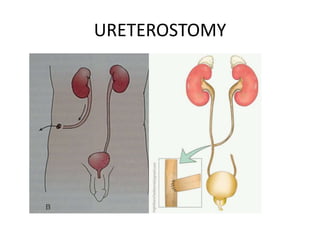
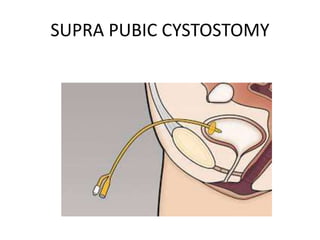
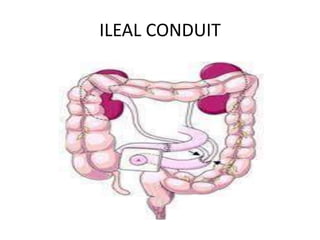
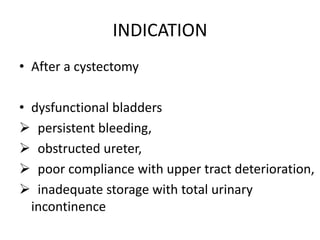
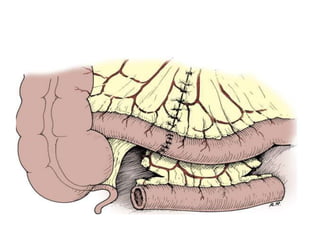
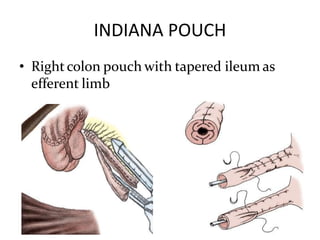
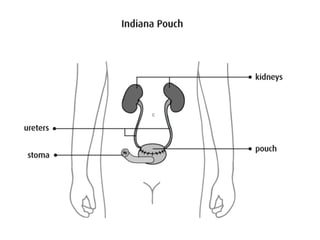
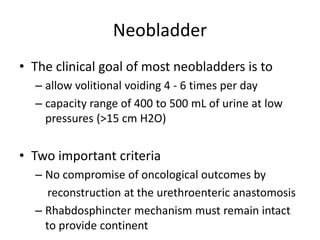
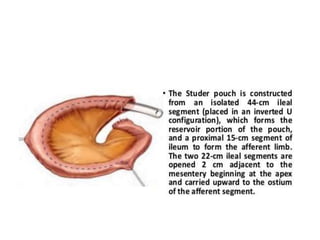
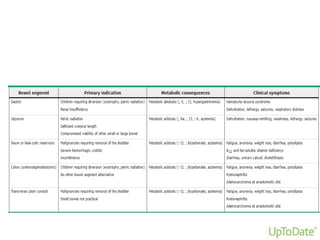
Urinary diversion involves redirecting the urinary pathway from the bladder due to conditions like muscle invasive bladder cancer. There are various types including continent, incontinent, internal, and external diversions. The ileal conduit is the most common non-continent diversion and involves using a segment of ileum as a urinary conduit connected to an abdominal stoma. Continent diversions like the Indiana pouch create an internal pouch that allows intermittent self-catheterization. Complications of urinary diversion can include metabolic abnormalities, infections, stone formation, and nutritional deficiencies depending on the bowel segment used.