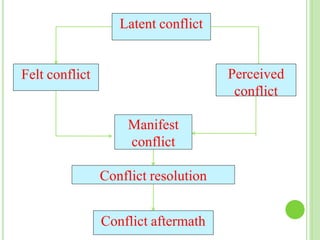
The document defines conflict and describes its causes and types. It discusses the conflict process, effects of conflict, and signs of conflict between individuals. It then outlines different outcomes of conflict and strategies for managing, handling, and resolving conflicts between parties. These include avoiding conflict, compromising, confronting issues, collaborating to find win-win solutions, and problem solving to generate gains for all parties.