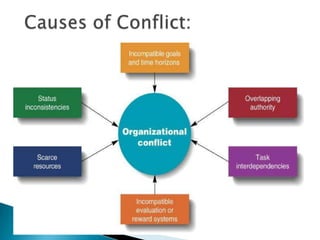
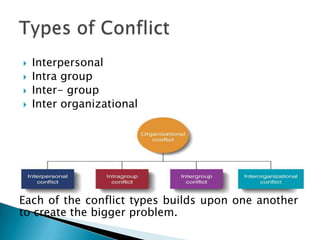
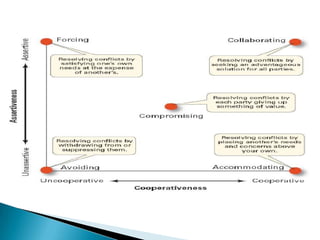
Conflict arises from differences in ideas, priorities, beliefs, and goals between two or more parties. It can be constructive by clarifying issues and building understanding, or destructive if it hinders productivity and causes tension. There are various types of conflict including interpersonal, intra-group, inter-group, and inter-organizational. Conflict management strategies include avoiding or accommodating conflict, competing for one's own position, compromising, and collaborating for mutually agreeable solutions. Diagnosing issues, planning a strategy, preparing through problem-solving and practice, and implementing and evaluating the resolution process can help manage conflicts effectively.