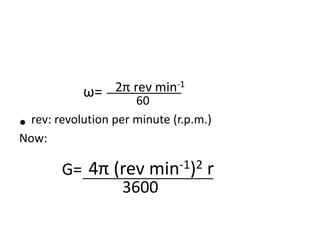
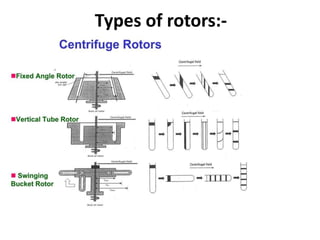
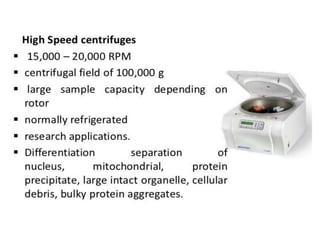
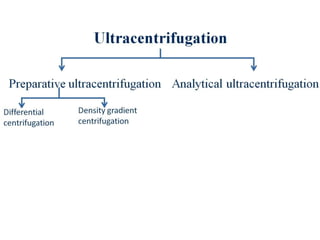
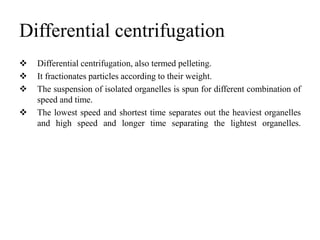
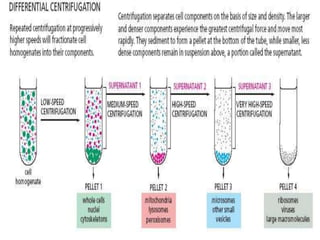
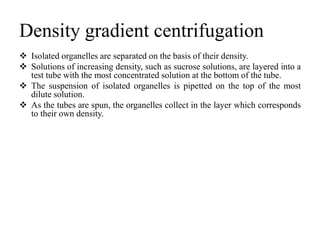
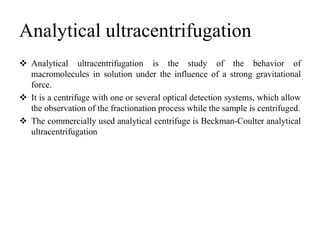
Centrifugation is a process that uses centrifugal force to separate particles in a solution based on their density. It can be used to sediment particles, isolate cellular components like organelles, and separate molecules and complexes. Different types of centrifuges include low-speed, high-speed, and ultracentrifuges, which separate particles through differential centrifugation or density gradient centrifugation. Analytical centrifugation allows observation of fractionation processes and is used to study macromolecules. Centrifugation has various applications including concentration, separation, isolation of organelles, and separation of blood components or cream from milk.