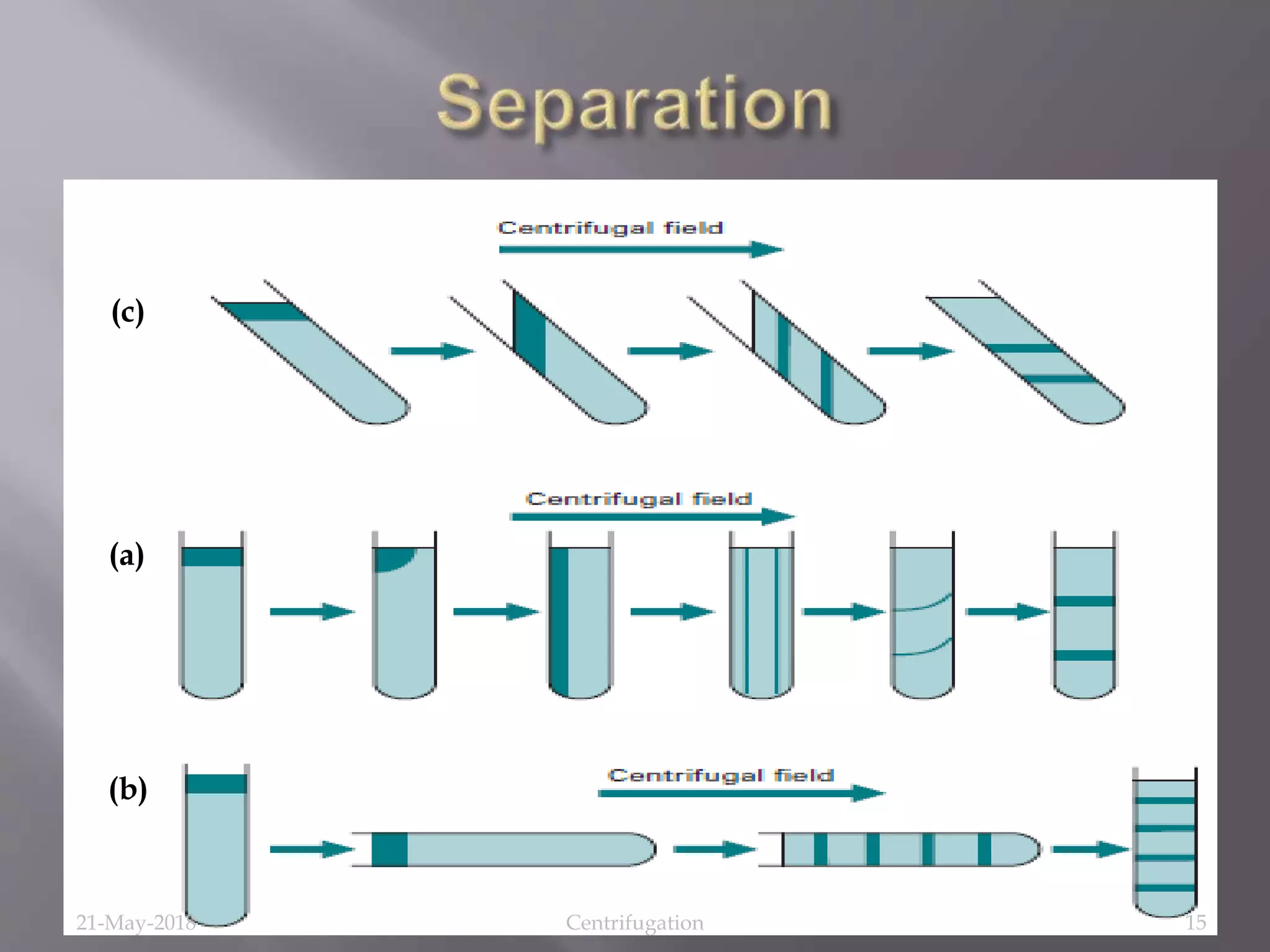
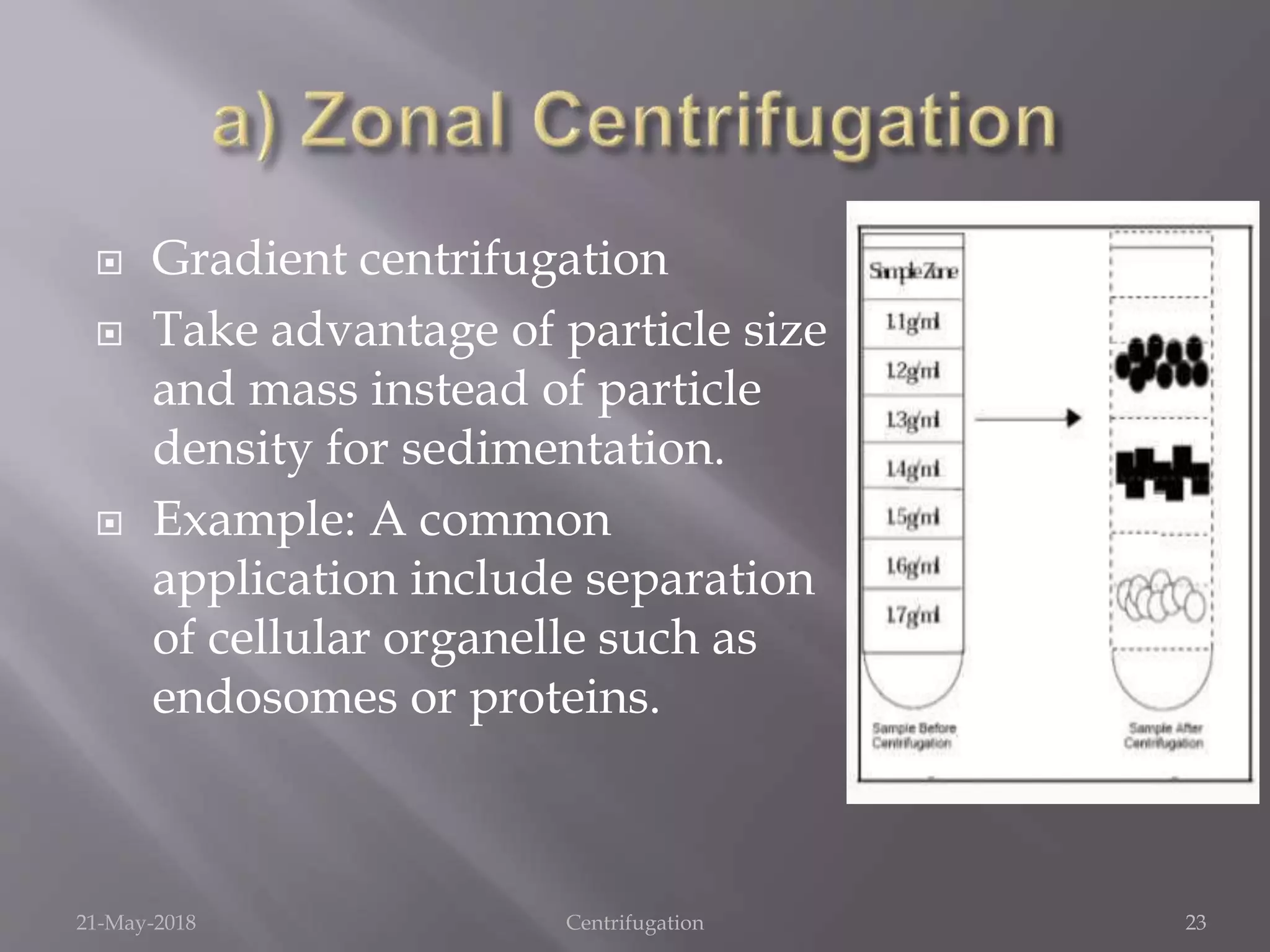
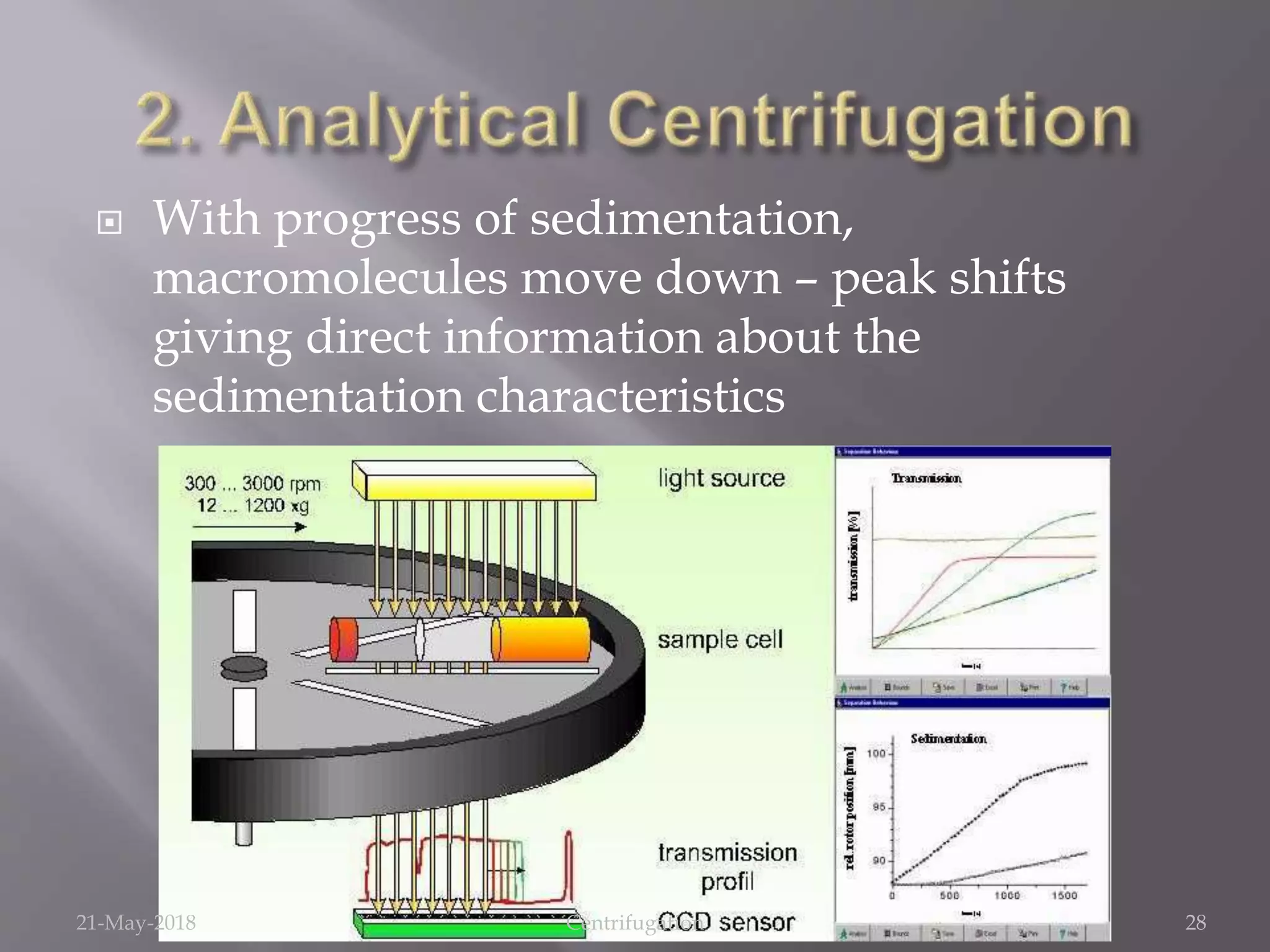
Centrifugation is a technique that uses centrifugal force to separate substances of different densities, crucial for isolating cells, macromolecules, and subcellular fractions. It involves various types of centrifuges, including low-speed, high-speed, and ultracentrifuges, each suited for specific applications and requiring careful operational conditions. This method is widely utilized in laboratories for tasks like isolating cellular components from biological samples and separating nucleic acids and proteins.