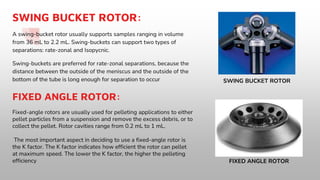
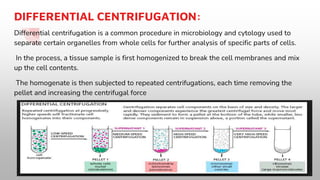
The document is a presentation on centrifugation, detailing its definition, history, principles, instrumentation, types, and applications. It explains how centrifugation uses centrifugal force to separate heterogeneous mixtures and outlines various centrifuge types and their uses in biological research. The conclusion emphasizes the significance of centrifugation in life sciences and its ability to separate particles based on size, density, and other properties.