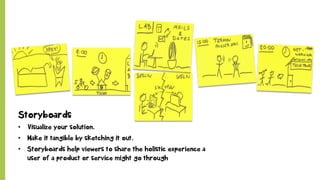
The document discusses the importance of prototyping in problem-solving, emphasizing that it is a collaborative process that encourages rapid iteration and communication within teams. It outlines various prototyping techniques, including role plays, storyboards, and low-fidelity mockups, which help in understanding user experiences and gathering feedback. The key takeaway is that prototyping should be rough and timeboxed to facilitate honest feedback and continuous improvement.