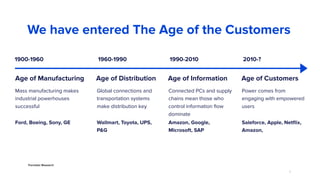
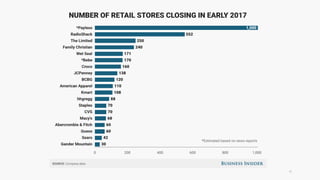
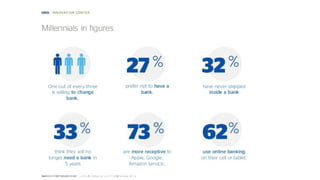
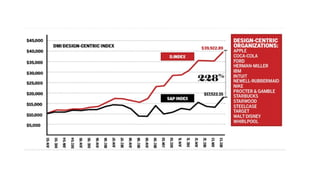
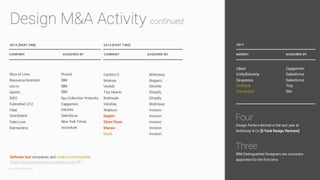
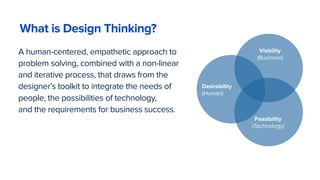
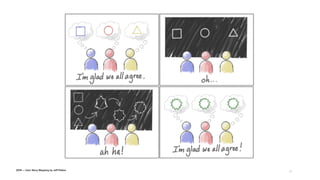
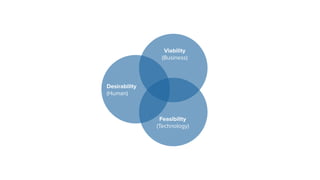
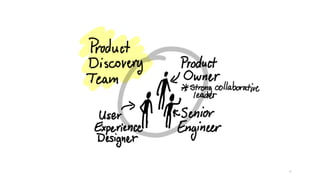
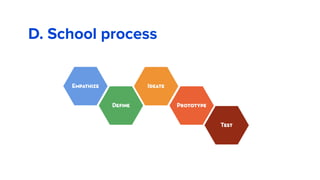
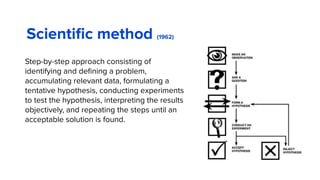
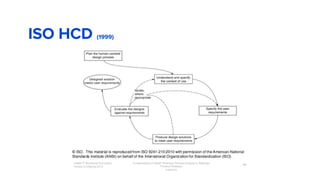
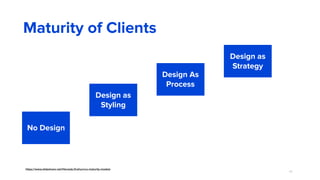
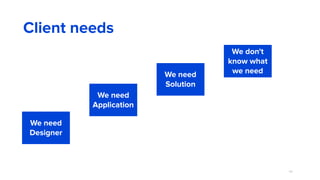
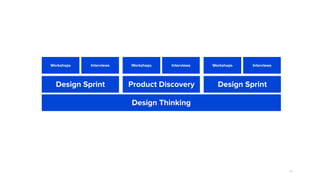
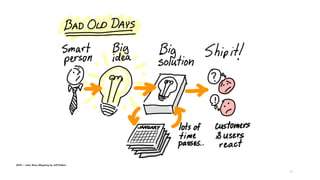
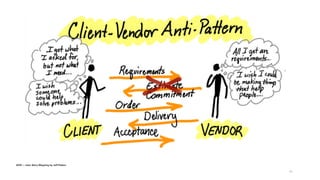
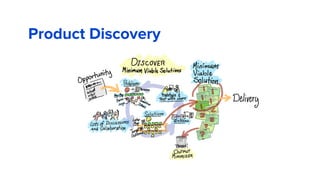
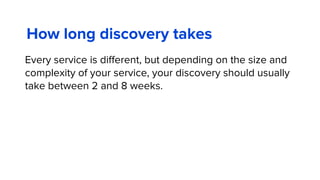
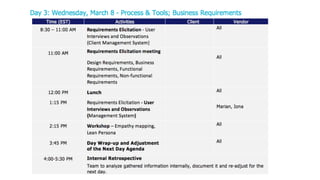
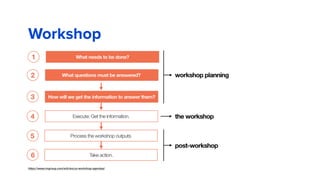
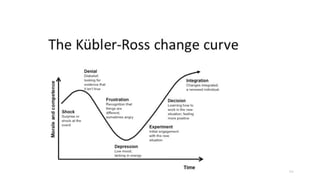
The document discusses the evolution of customer-centric business models and the growing importance of user experience (UX) in differentiating brands in a digital age. It highlights the shift from traditional product and pricing strategies to a more empathetic, design thinking approach that prioritizes understanding customer needs and feelings. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of collaboration and continuous prototyping in developing effective products and solutions.