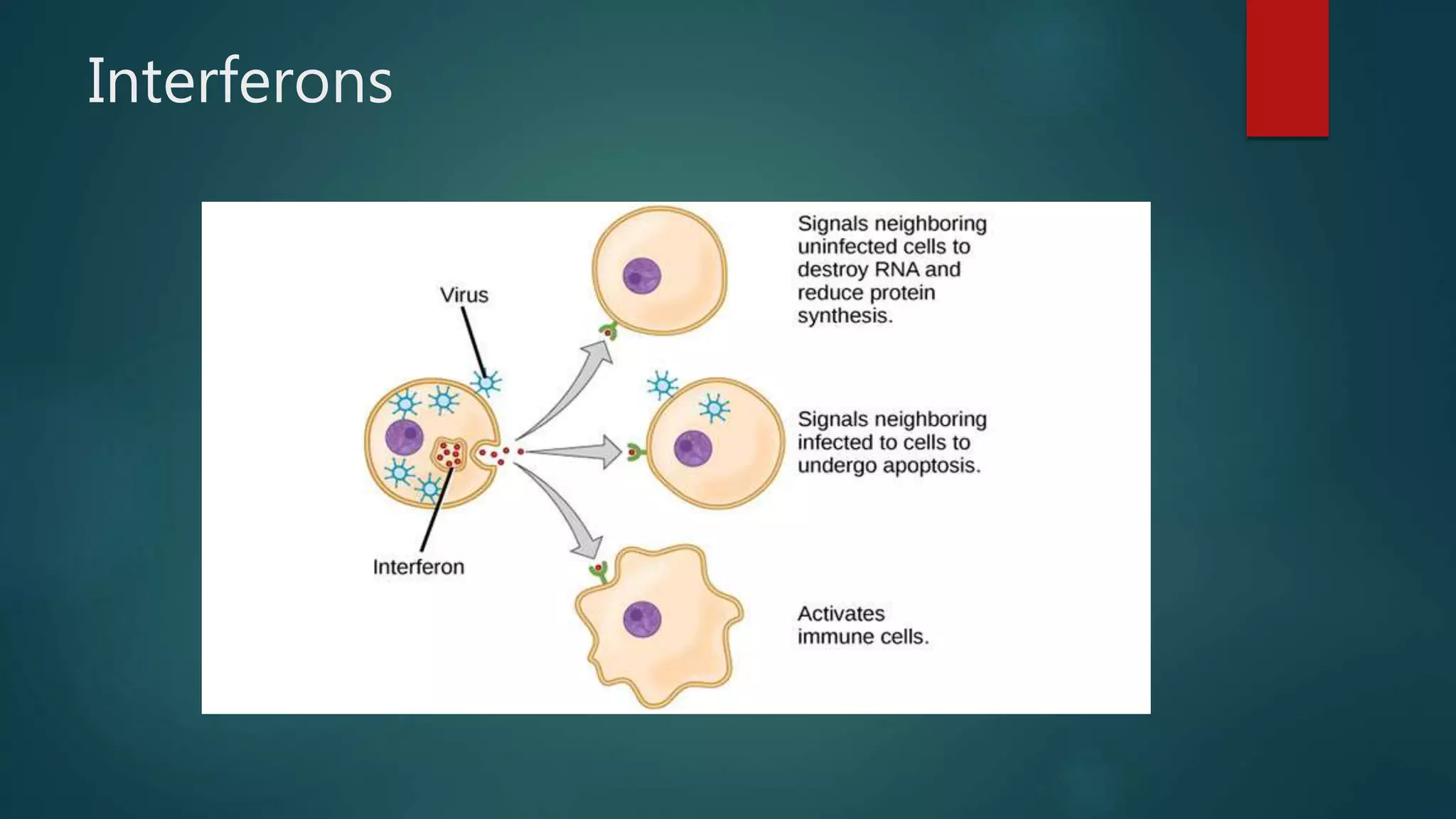
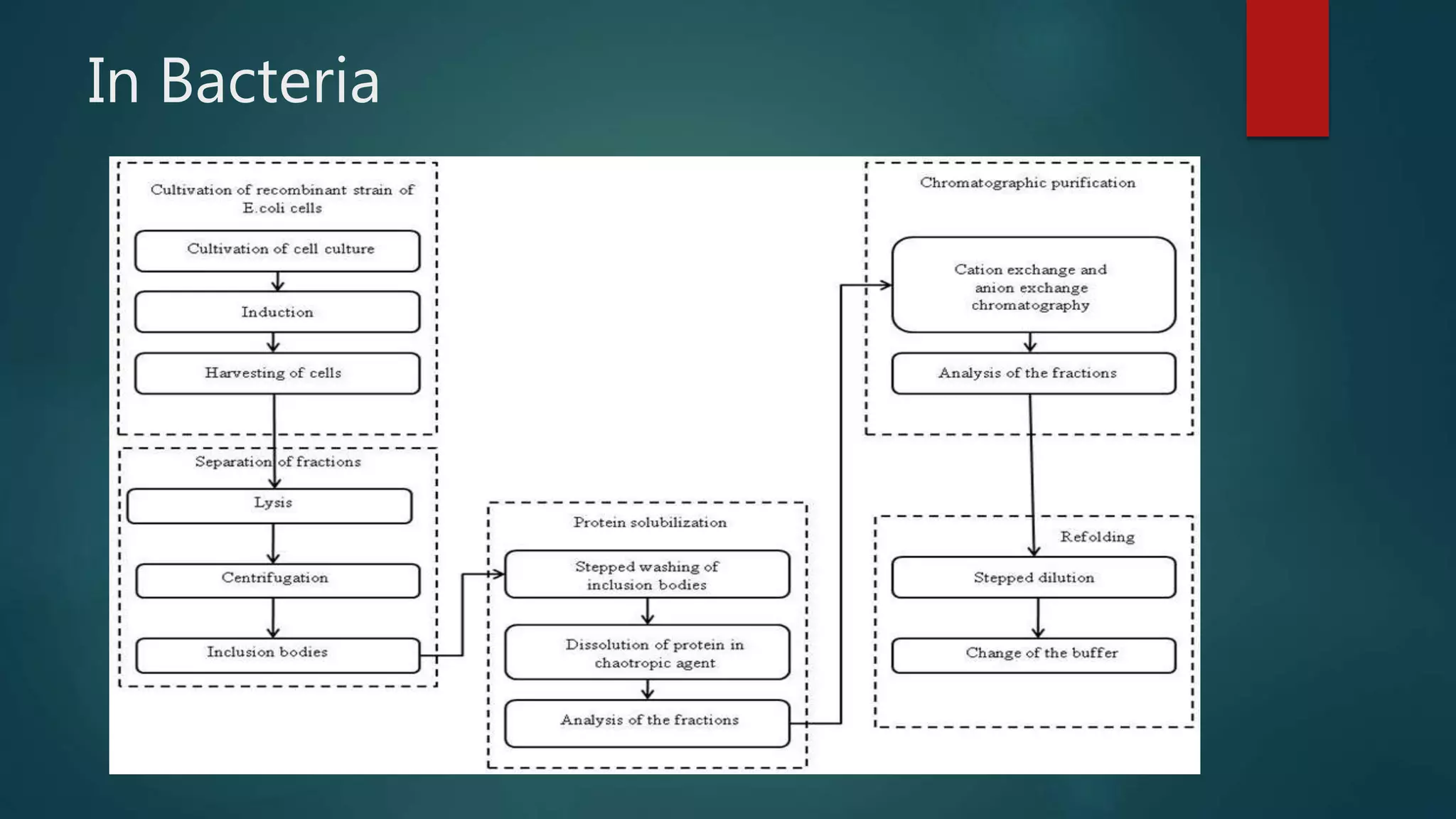
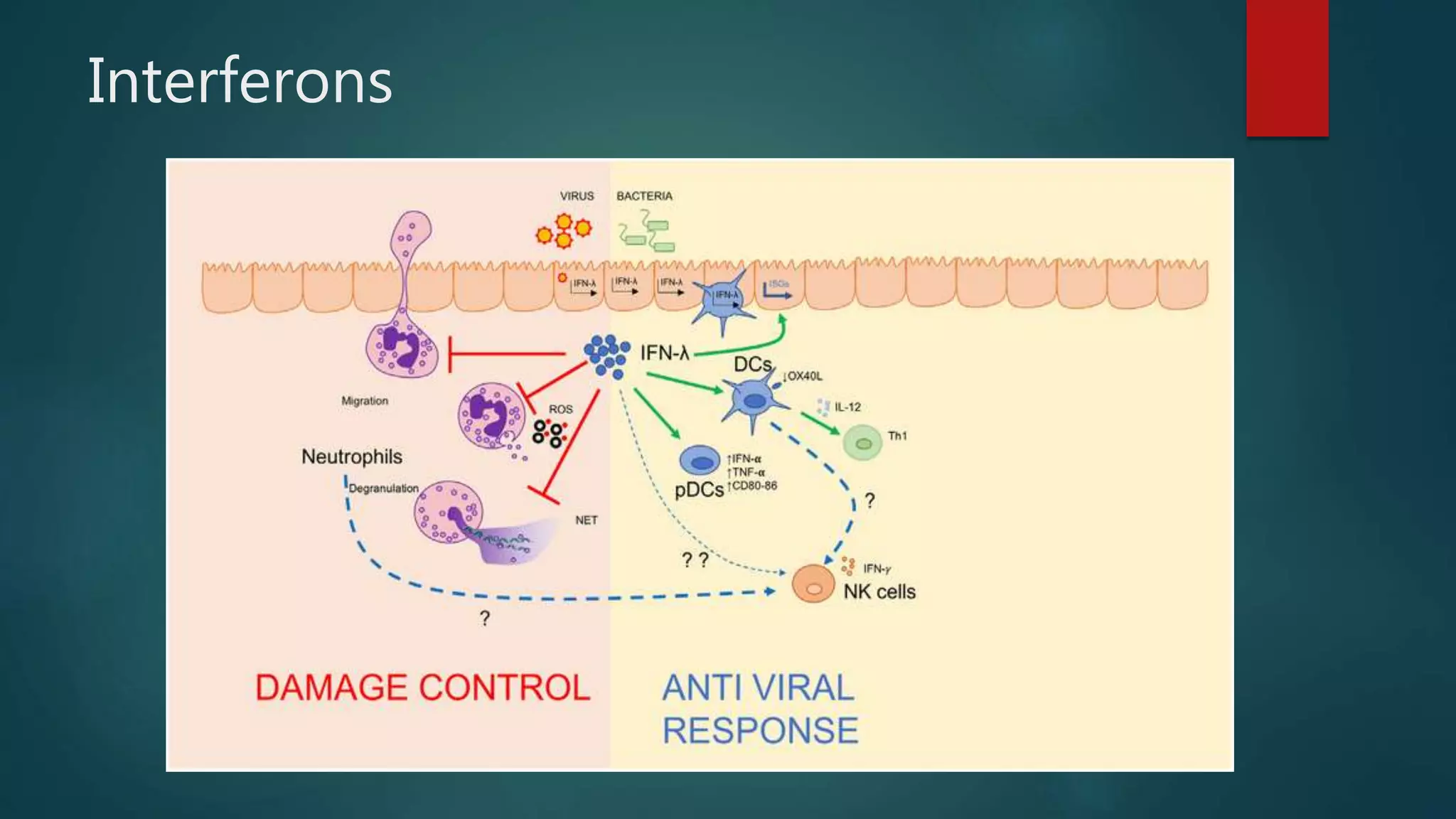
Interferons are proteins produced by living animal cells in response to viral infection, with their synthesis requiring the expression of specific cellular genes. The production is initiated by viral maturation and is influenced by interferon inducers like double-stranded RNA, affecting the signaling pathways in neighboring uninfected cells to trigger antiviral defenses. Interferons are categorized into type I (α and β) and type II (γ), each with distinct genes and regulatory mechanisms.