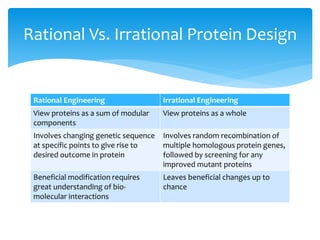
This document discusses protein engineering through directed evolution. It explains that directed evolution involves randomly recombining genes from protein libraries and screening mutant proteins for improved functions. This leaves beneficial changes up to chance but generates diversity. Rational design is also used to map important protein interactions to guide evolution. The document provides an example of using directed evolution to modify a cytochrome P450 enzyme to more efficiently convert alkanes to alcohols over multiple generations. However, it notes that expressing evolved proteins in vivo and requiring expensive cofactors limit the commercial potential of this approach.