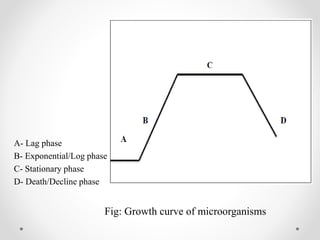
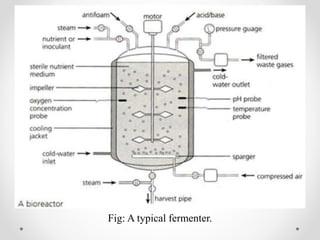
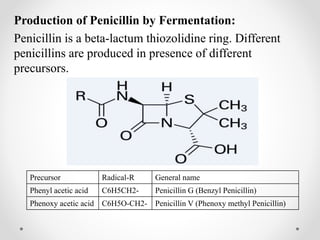
Fermentation is the process involving the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones using microorganisms, commonly applied in biotechnology for mass production of useful materials. Various microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and actinomycetes are utilized, and different culturing methods like batch, continuous, and fed-batch cultures are employed depending on the desired outcomes. Key industrial products from fermentation include antibiotics, solvents, vitamins, and organic acids, with specific processes like penicillin production illustrating the complexities of cultivating and harvesting beneficial compounds.