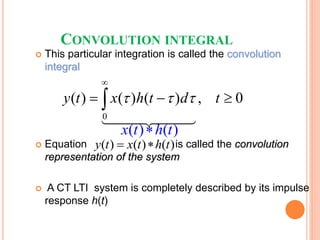
1) Convolution represents a discrete-time (DT) or continuous-time (CT) linear time-invariant (LTI) system as the summation or integral of the input signal multiplied by the impulse response.
2) The impulse response completely characterizes an LTI system.
3) Convolution exploits the properties of time-invariance and linearity of LTI systems to represent the output of the system in terms of a convolution between the input and impulse response.


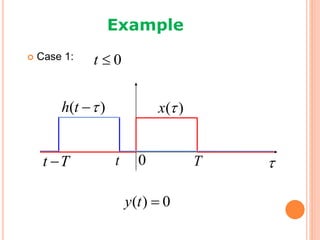
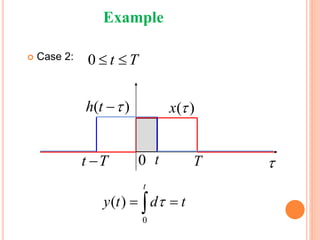
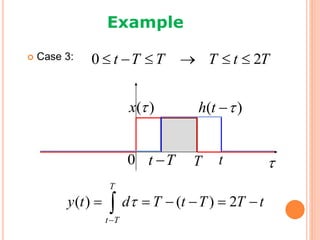
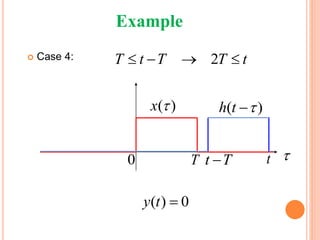
![ Consider the DT system:
If the input signal is and the system has no
energy at , the output
is called the impulse response of the system
[ ]y n[ ]x n
[ ]h n[ ]n
[ ] [ ]x n n
[ ] [ ]y n h n
System
System
0n
DT Unit-Impulse Response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-3-320.jpg)
![ Consider the DT system described by
Its impulse response can be found to be
[ ] [ 1] [ ]y n ay n bx n
( ) , 0,1,2,
[ ]
0, 1, 2, 3,
n
a b n
h n
n
EXAMPLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-4-320.jpg)
![ Let x[n] be an arbitrary input signal to a DT LTI system
Suppose that for
This signal can be represented as
0
[ ] [0] [ ] [1] [ 1] [2] [ 2]
[ ] [ ], 0,1,2,
i
x n x n x n x n
x i n i n
1, 2,n [ ] 0x n
PRESENTING SYSTEM IN TERM OF
SHIFTED AND SCALED IMPULS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-5-320.jpg)
![0
[ ] [ ] [ ], 0
i
y n x i h n i n
EXPLOTING TIME -
INVERIANCE AND LINEARITY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-6-320.jpg)
![ This particular summation is called the convolution sum
Equation is called the convolution
representation of the system.
A DT LTI system is completely described by its impulse
response h[n].
0
[ ] [ ] [ ]
i
y n x i h n i
[ ] [ ]x n h n
[ ] [ ] [ ]y n x n h n
CONVOLUTION SUM
(LINEAR CONVOLUTION)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-7-320.jpg)
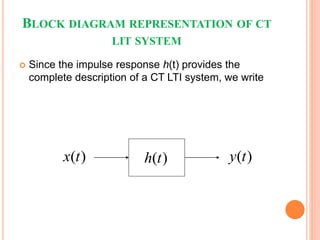
![ Since the impulse response h[n] provides the
complete description of a DT LTI system, we write
[ ]y n[ ]x n [ ]h n
BLOCK DIAGRAM
REPRESENTATION OF DT LTI
SYSTEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-8-320.jpg)
![ Suppose that we have two signals x[n] and v[n] that
are not zero for negative times .
Then, their convolution is expressed by the two-
sided series
[ ] [ ] [ ]
i
y n x i v n i
THE CONVOLUTION SUM FOR
NONCAUSAL SIGNALS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-9-320.jpg)
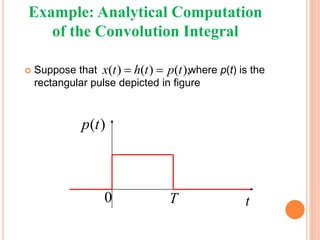
![ Suppose that both x[n] and v[n] are equal to the
rectangular pulse p[n] (causal signal) represent
below
EXAMPLE: CONVOLUTION OF TWO
RECTANGULAR PULSES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-10-320.jpg)
![ The signal is equal to the pulse p[i] folded about
the vertical axis
[ ]v i
THE FOLDED PULS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-11-320.jpg)
![SHIFTING V[N- I] OVER X[I]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-12-320.jpg)
![PLOT OF X[N]*V[N]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-13-320.jpg)
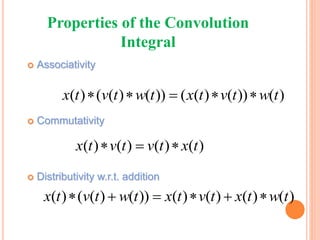
![ Associatively
Commutatively
Distributive w.r.t. addition
[ ] ( [ ] [ ]) ( [ ] [ ]) [ ]x n v n w n x n v n w n
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]x n v n v n x n
[ ] ( [ ] [ ]) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]x n v n w n x n v n x n w n
PROPERTIES OF CONVOLUTION SUM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss-190418114729/85/convolution-14-320.jpg)