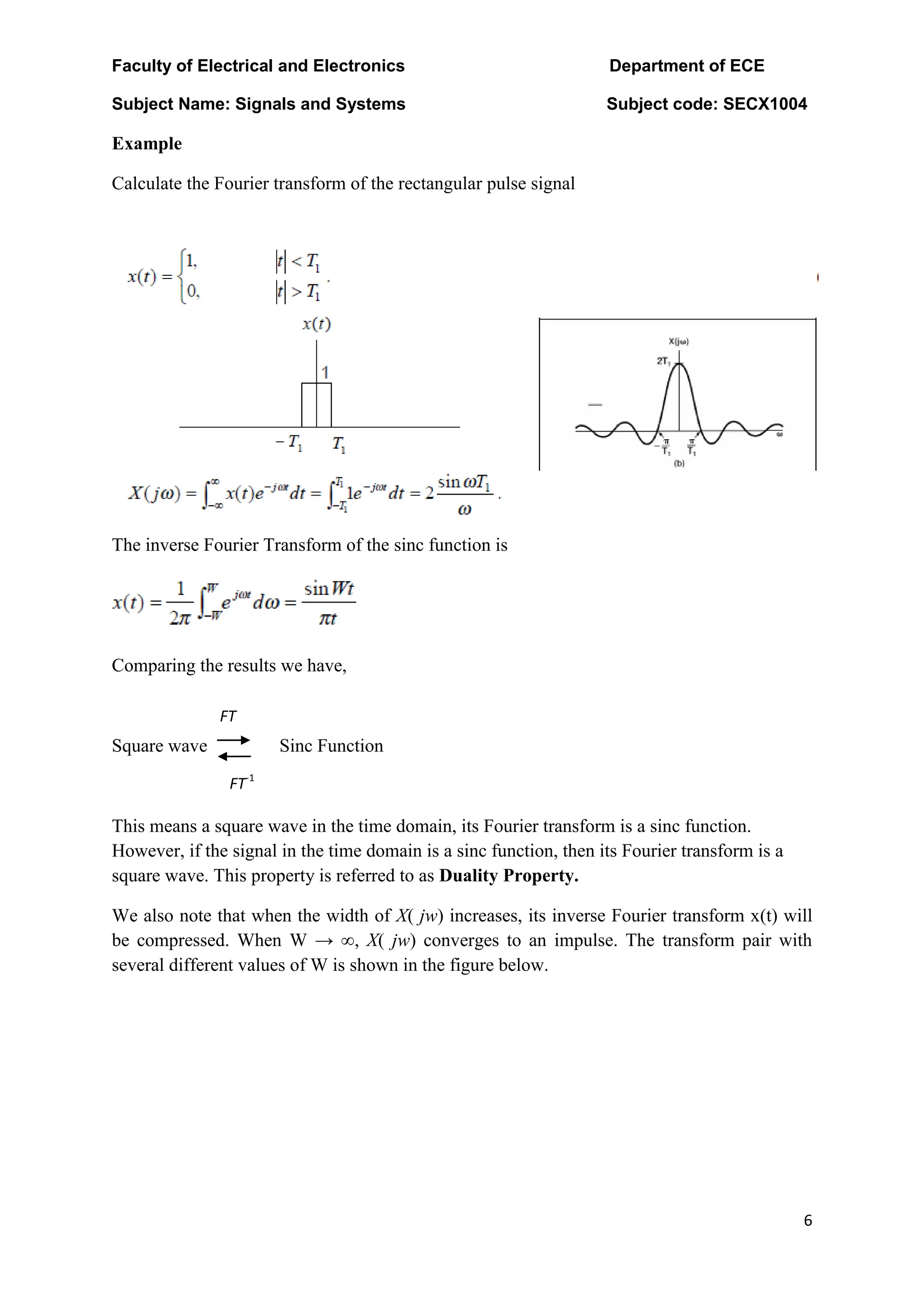
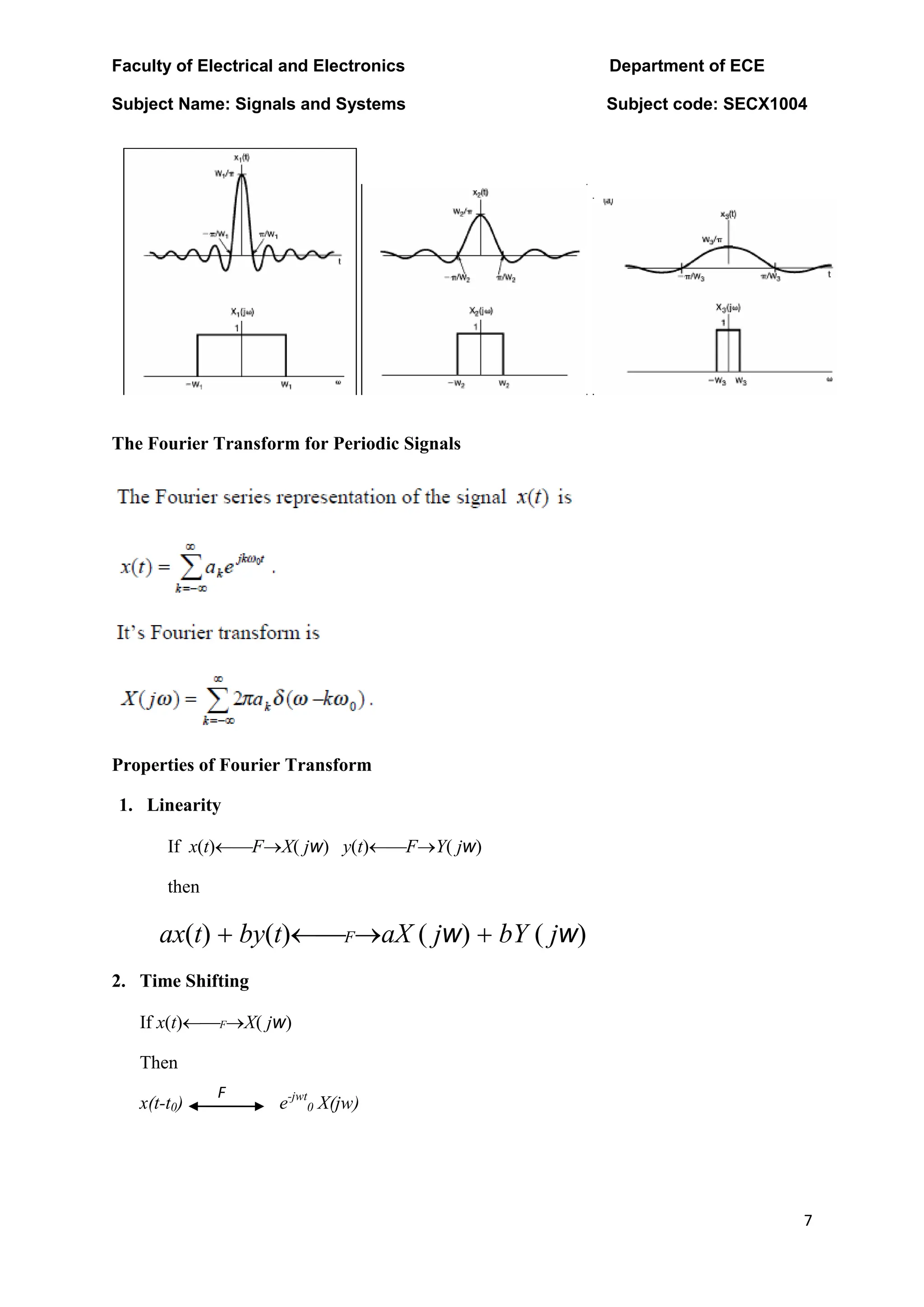
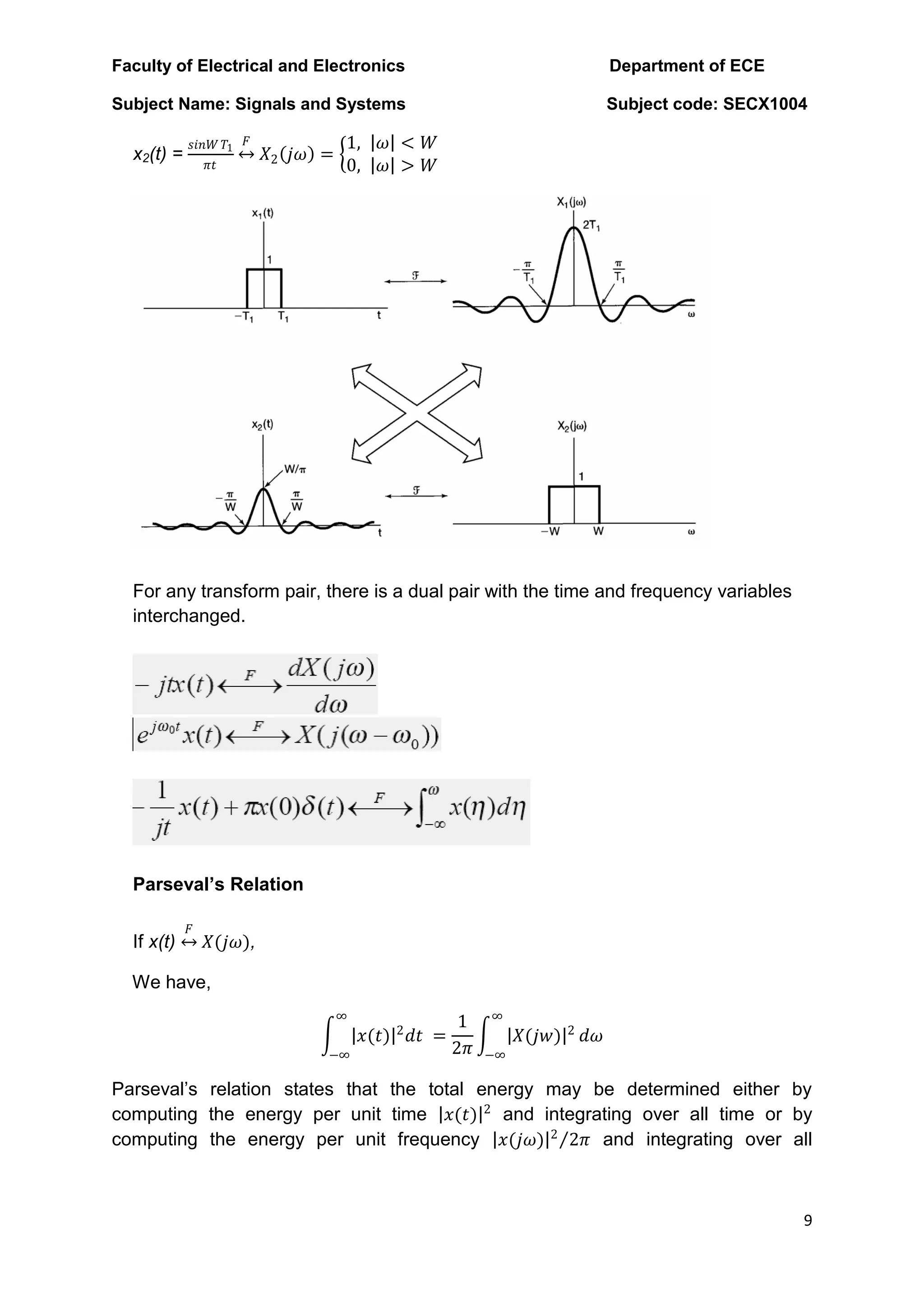
The document discusses the Fourier transform and Laplace transform. Some key points:
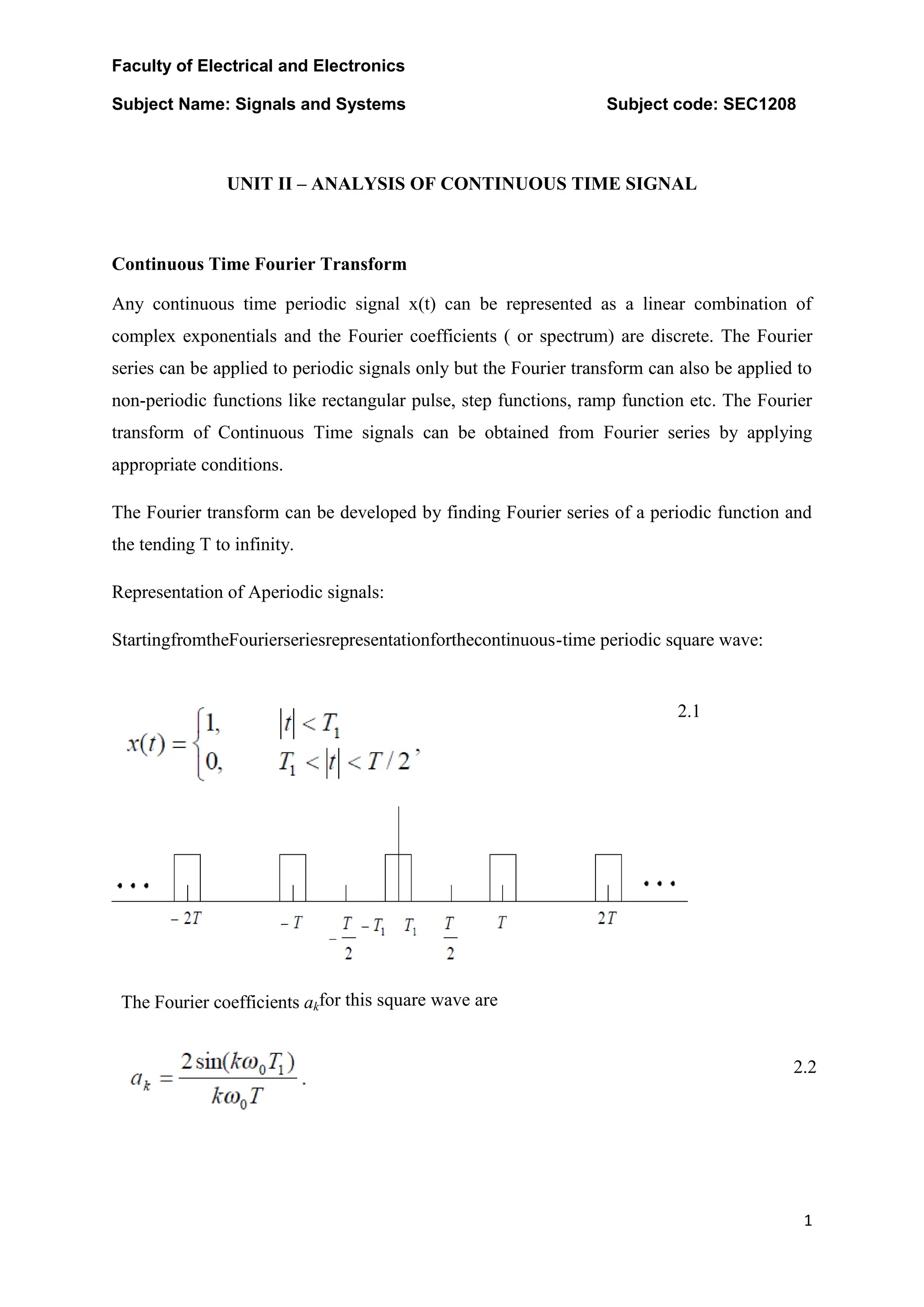
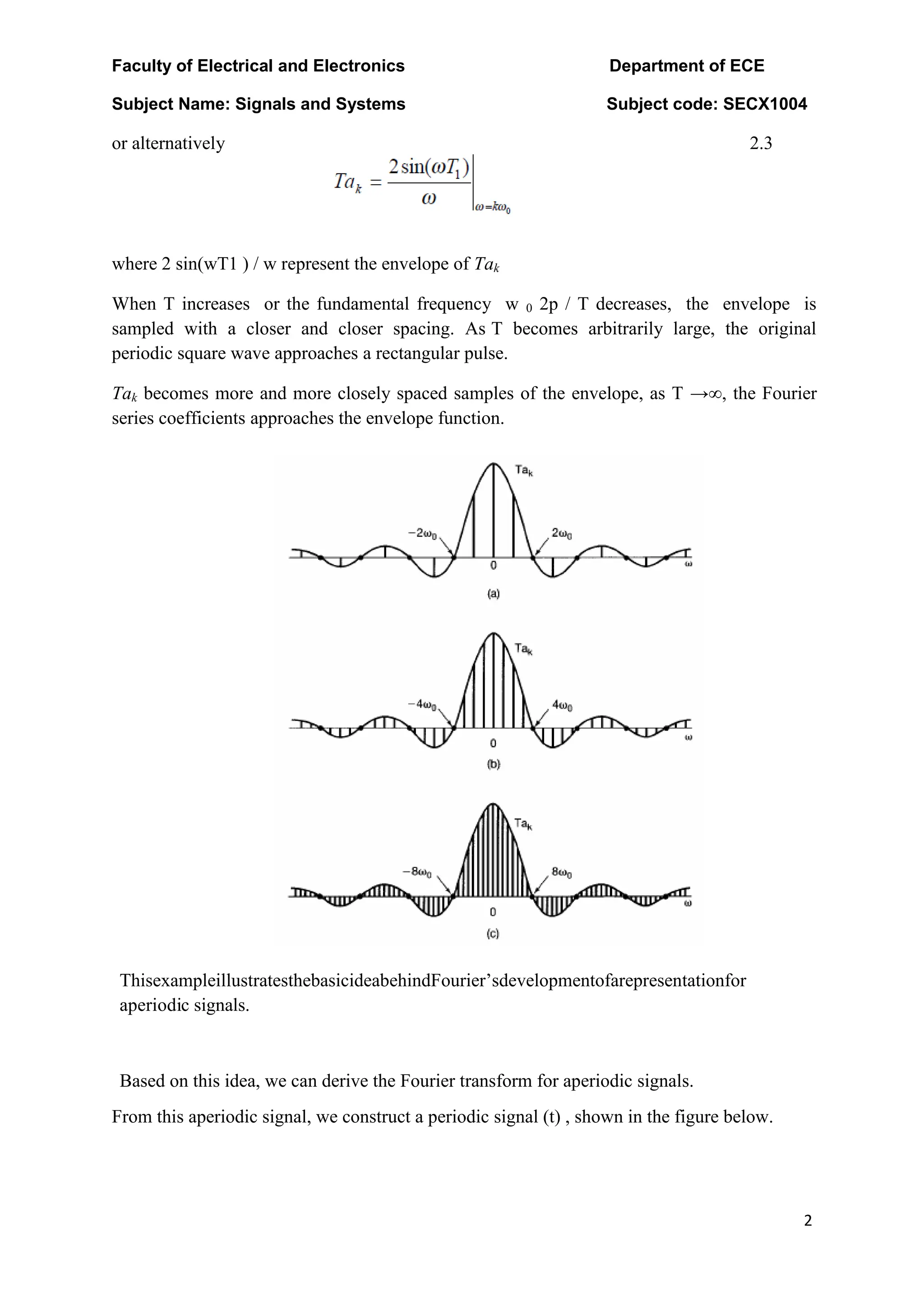
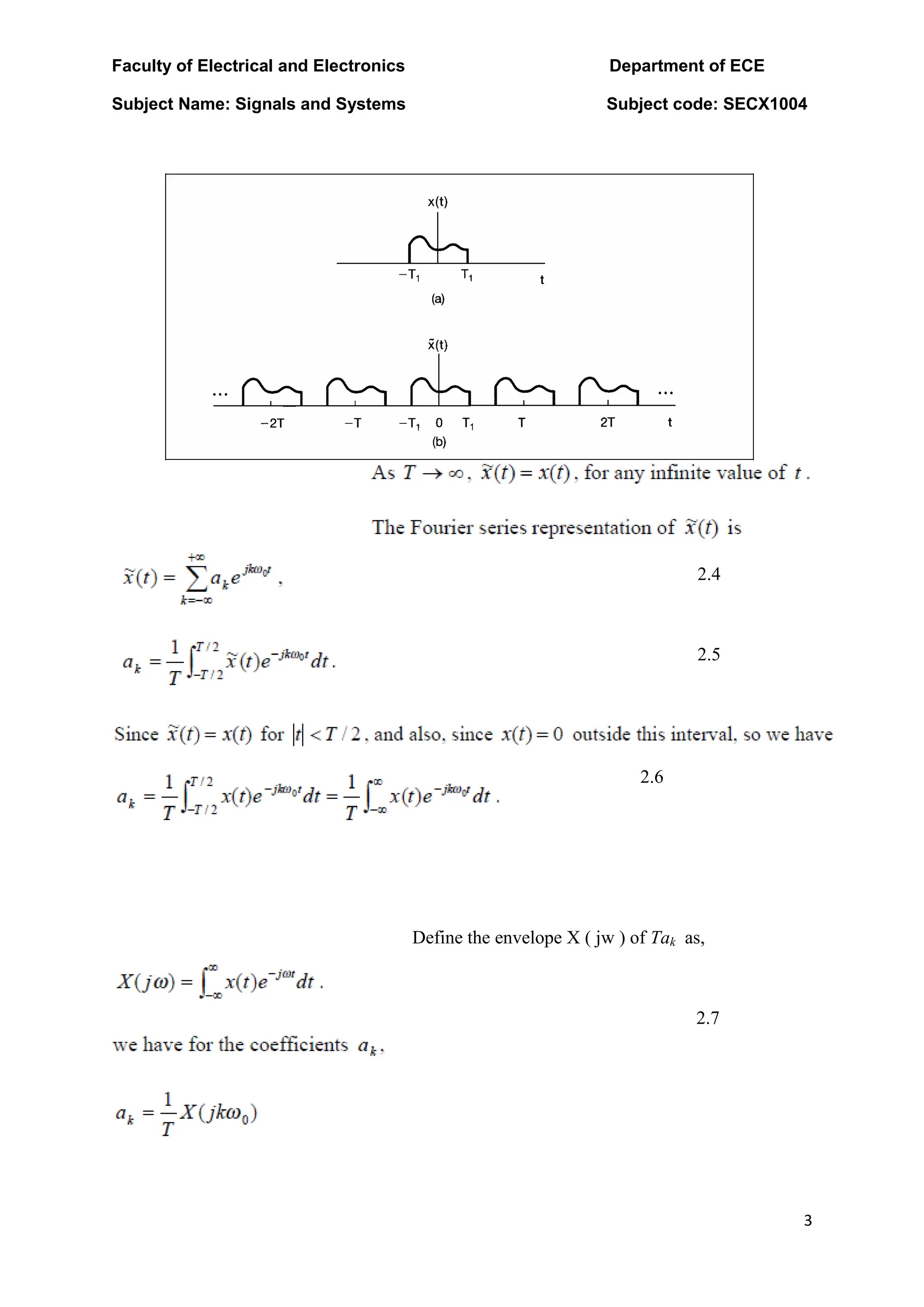
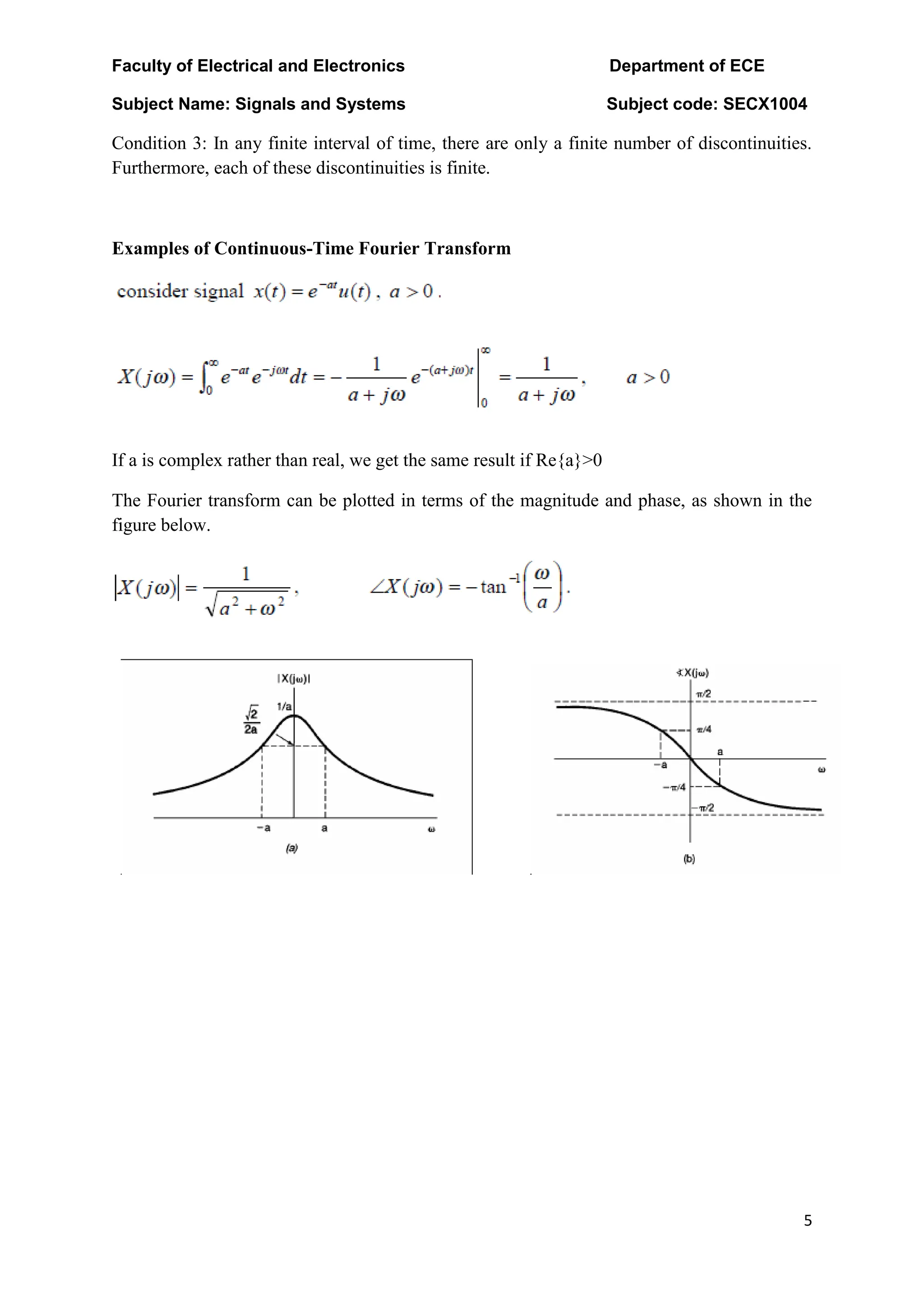
- The Fourier transform represents periodic and non-periodic signals as a sum of complex exponentials, allowing representation of aperiodic signals. It converges if the signal has finite energy.
- The Laplace transform generalizes the Fourier transform to a broader class of signals by using a complex variable 's' instead of just 'jw'. It can represent signals that are not absolutely integrable.
- The Fourier transform is a special case of the Laplace transform when s = jw, along the imaginary axis where σ = 0.
- Both transforms allow mapping between a signal and its frequency spectrum, with applications in analyzing signals and systems.