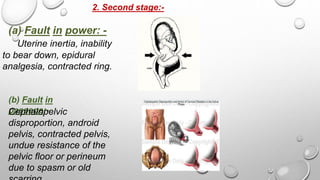
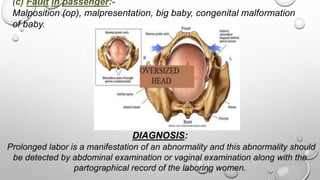
This presentation discusses prolonged labor, which occurs when labor lasts over 20 hours for first-time mothers or 14 hours for women who have given birth before. Prolonged labor can happen in the latent or active phases of the first stage, or the second stage. Causes include problems with uterine contractions, the birth canal, or the baby. Prolonged labor can endanger the baby through hypoxia or infection and endanger the mother through hemorrhage, trauma, or infection. Management involves identifying the cause, monitoring for effects, and treating any issues through techniques like amniotomy, oxytocin infusion, pain relief, or cesarean delivery if needed to deliver the baby safely.