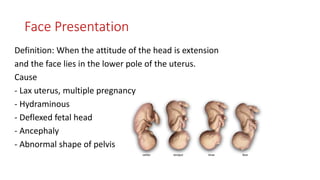
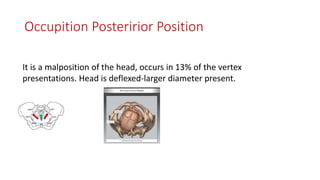
This document discusses various fetal malpresentations and malpositions that can occur during labor, including breech presentation, brow presentation, shoulder presentation, face presentation, and occiput posterior position. It defines each condition, describes potential causes, signs for diagnosis, and general management approaches during labor. Complications are also outlined for each abnormal presentation.