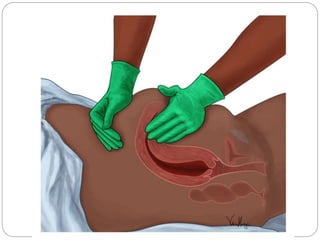
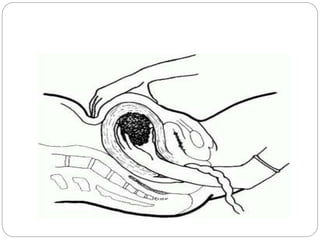
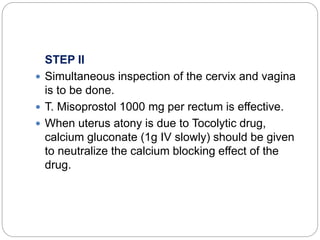
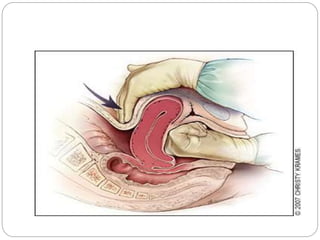
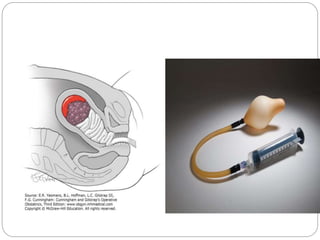
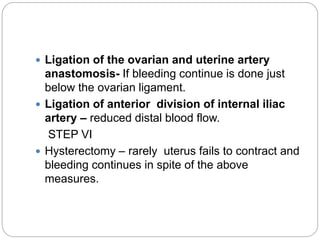
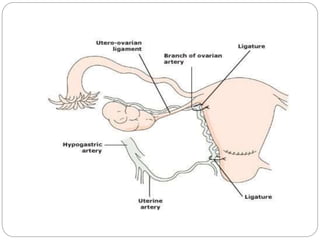
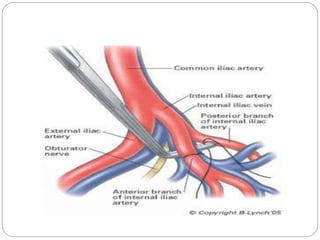
This document discusses postpartum haemorrhage (PPH), defined as blood loss exceeding 500 ml following childbirth. It notes that PPH has various causes including an atonic uterus, trauma during delivery, retained placental tissues, and coagulation disorders. The primary types are those occurring within 24 hours of delivery. Management involves controlling blood loss, administering oxytocics, and may require interventions like uterine packing or hysterectomy in severe cases. Prevention strategies include active management of the third stage of labour and being prepared to treat PPH as a potential complication of childbirth.