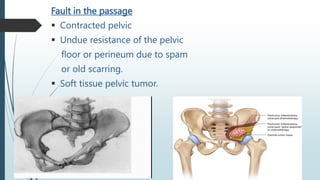
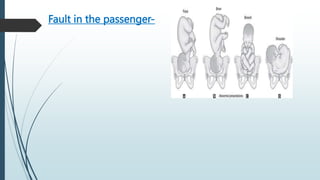
1) Prolonged labor is defined as labor lasting over 20 hours for first time mothers and over 14 hours for mothers who have previously given birth. It can be caused by issues like malpresentation, cephalopelvic disproportion, or problems with uterine contractions.
2) Signs of prolonged labor include exhaustion, dehydration, high pulse rate, and potential fetal distress. It increases risks for both mother and baby.
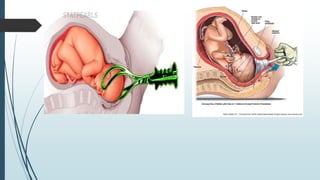
3) Management of prolonged labor involves identifying the cause, giving the mother fluids and pain relief, monitoring progress and fetal wellbeing, and potentially assisting delivery or performing a C-section if vaginal delivery is not possible or safe.