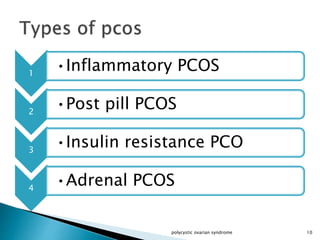
This presentation summarizes polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is a complex hormonal disorder common in women of reproductive age, characterized by enlarged ovaries with small cysts, irregular periods, and excess androgen. The presentation covers the definition, epidemiology, types, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnostic evaluation, management, and complications of PCOS. Key points include that PCOS can be inflammatory, post-pill, insulin resistance or adrenal-related, and treatment involves lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery depending on symptoms.