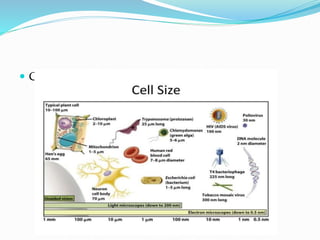
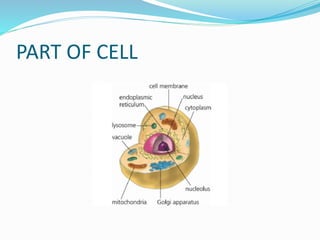
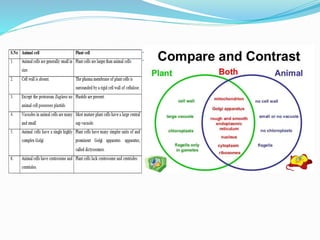
This document discusses cells and their discovery. It provides definitions of cells and notes that cells are the basic unit of structure and function for all living things. It describes how Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 using a microscope. The size of organisms is determined by the number of cells they contain. The document outlines key parts of cells like the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, chromosomes, and various cell organelles. It concludes with a comparison of plant and animal cells.