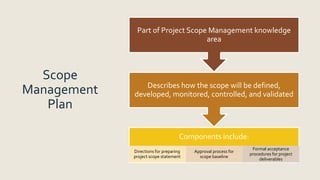
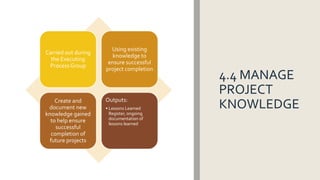
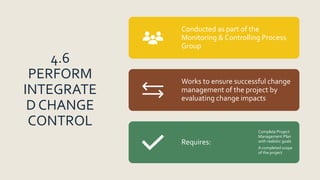
The document outlines the integration management knowledge area in project management, detailing its seven essential processes: developing project charter, developing project management plan, directing and managing project work, managing project knowledge, monitoring and controlling project work, performing integrated change control, and closing the project or phase. Each process is associated with specific project management process groups and serves to create cohesive projects while justifying the project manager's authority and the roles of sponsors and stakeholders. Comprehensive plans related to scope, requirements, changes, and communication are also emphasized as vital components of effective project management.