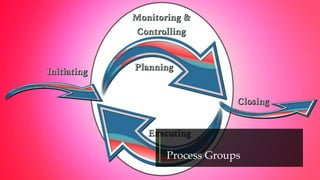
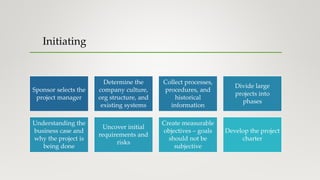
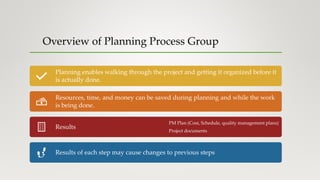
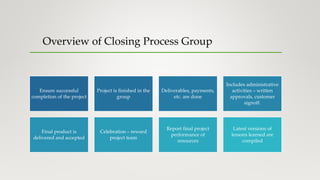
The document outlines the various project management processes and their corresponding process groups, including initiation, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. It details specific processes within each knowledge area, such as scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, communications, risk, procurement, and stakeholder management. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of planning and execution phases in delivering project objectives, ensuring stakeholder engagement, and successfully closing a project.