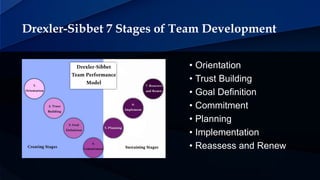
The Drexler-Sibbet Team Performance Model outlines the stages of team development, divided into 'creating' and 'sustaining' phases. The creating stages include orientation, trust building, goal definition, and commitment, while the sustaining stages focus on planning, implementation, and reassessment. Each stage addresses specific team dynamics, such as defining roles and building cohesion, essential for achieving team objectives.