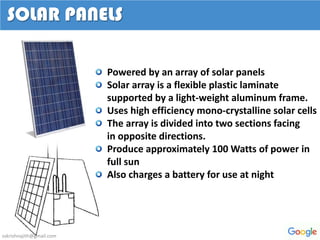
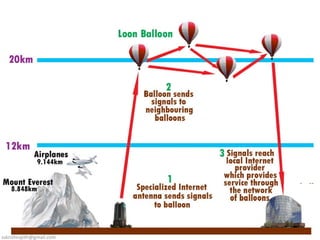
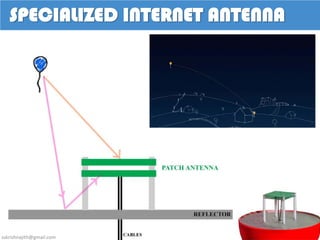
Project Loon is a Google project that aims to provide internet access to rural and remote areas using high-altitude balloons placed in the stratosphere. The balloons operate between 18-25 km in altitude, where wind speeds are relatively low and stable. Each balloon connects to hundreds of users via wireless connections and moves between wind layers to direct its course around the globe. The balloons use solar panels and batteries to power communications equipment and systems to control altitude. If successful, Project Loon could help provide affordable internet access to the two-thirds of the world not currently connected.






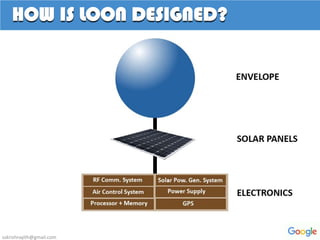
![Inflatable part of the balloon
Made from sheets of polyethylene
plastic[0.076 mm thick]
It strongly keeps from stretching
& popping at even high altitude
Measure 15m wide by 12m tall
when fully inflated
Inside envelope, there is another
chamber, called bladder
A parachute attached to the top of
the envelope
ENVELOPE
sskrishnajith@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectloon-150909175016-lva1-app6891/85/Project-loon-12-320.jpg)