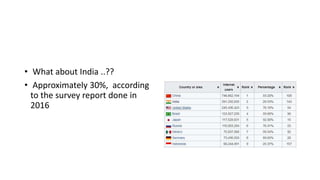
Project Loon aims to provide internet access to rural and remote areas using high-altitude balloons placed in the stratosphere. Each balloon can provide connectivity to a 40km area using a mesh network. The balloons move with wind currents and use algorithms to navigate to desired locations. Engineering challenges include operating in the stratosphere with low pressure, cold temperatures, and radiation. Project Loon seeks to deliver affordable, universal internet access worldwide.