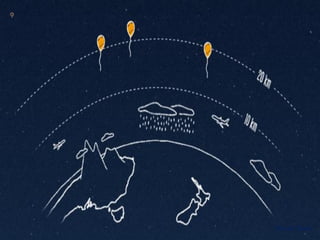
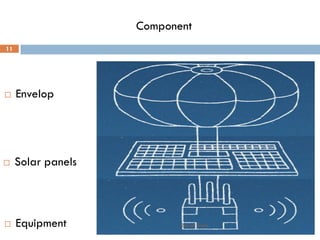
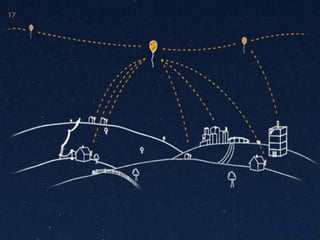
Project Loon is a network of balloons traveling in the stratosphere designed to connect people in rural areas. An experimental pilot launched 30 balloons over New Zealand in 2013 to test the technology. The balloons float 20 miles above the Earth, using software to ride wind currents to positions that form a communications network. Each balloon provides internet coverage to an area of about 40 square kilometers using solar power and bouncing signals between balloons. The goal is to increase internet access for remote areas around the world.