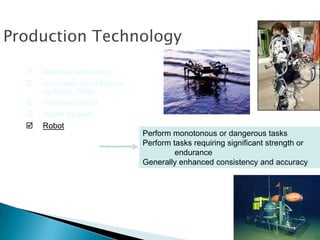
Capital intensity refers to the mix of equipment and human skills in a process, with greater capital intensity indicating a higher relative cost of equipment. Automation is a self-acting and self-regulating system or process. There are two main types of automation: fixed automation, which produces a single product in a set sequence of operations, and flexible automation, which can be changed to handle different products. Automation provides advantages like low variability, efficiency, and standardization but also has disadvantages such as high costs and decreased flexibility.