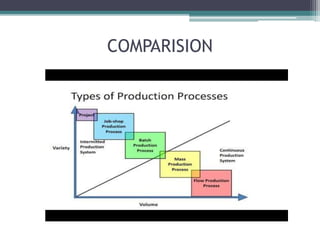
Automation is the use of technology to control and operate production processes. It is used to increase productivity, address labor shortages and high labor costs, improve quality, and reduce manufacturing time. Common machines used in automation include numerically controlled machines, robotics, and automated quality inspection systems. Automation can be applied in continuous processes like chemical plants, mass production like automobiles, batch production like books, and job shop production like prototypes. While automation focuses on reducing unit production time, CAD/CAM additionally aims to reduce design time. The benefits of automation include increased productivity, reduced time, less floor space needed, and less human fatigue, but the costs can be high initially and development costs unpredictable.