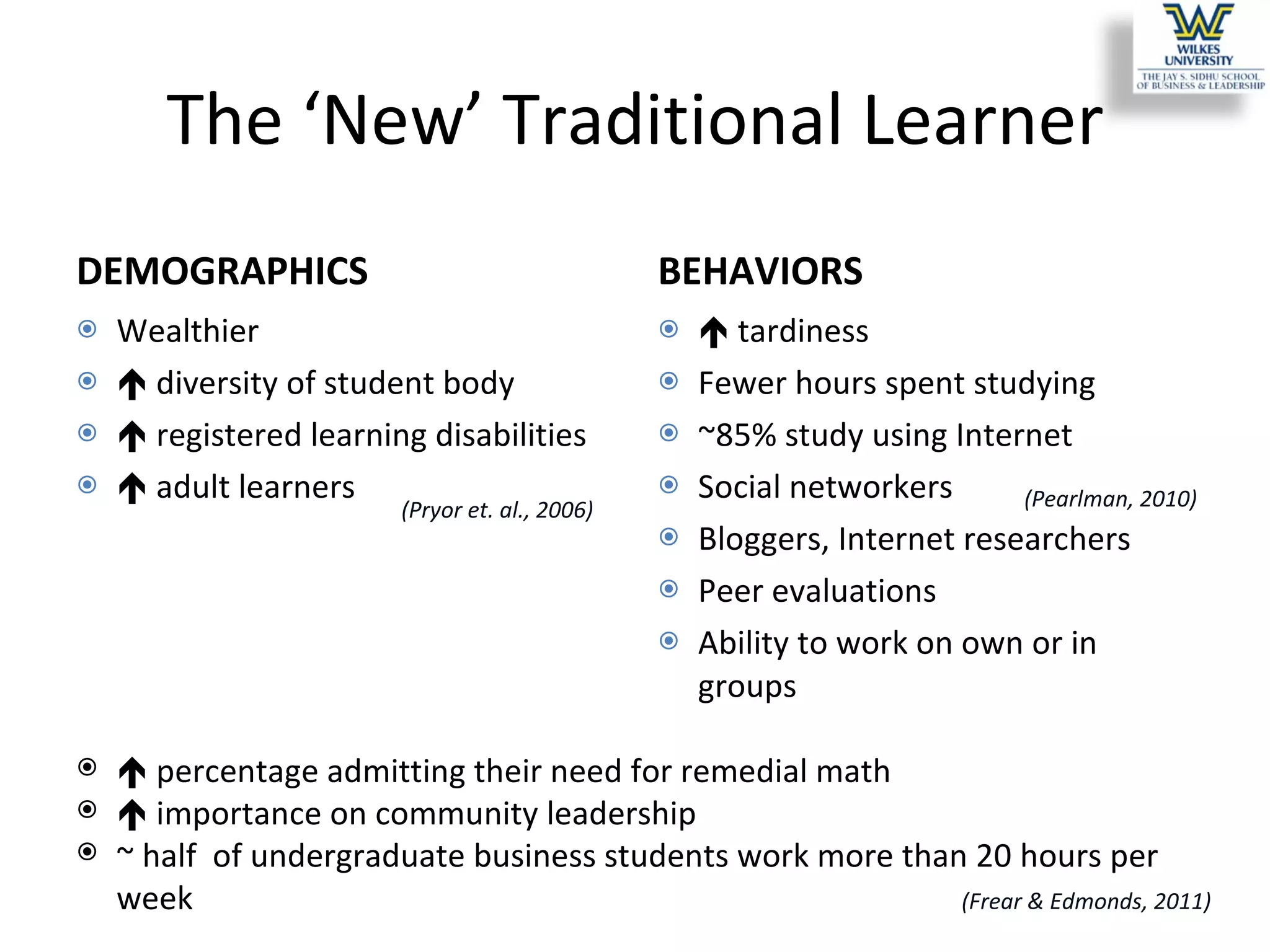
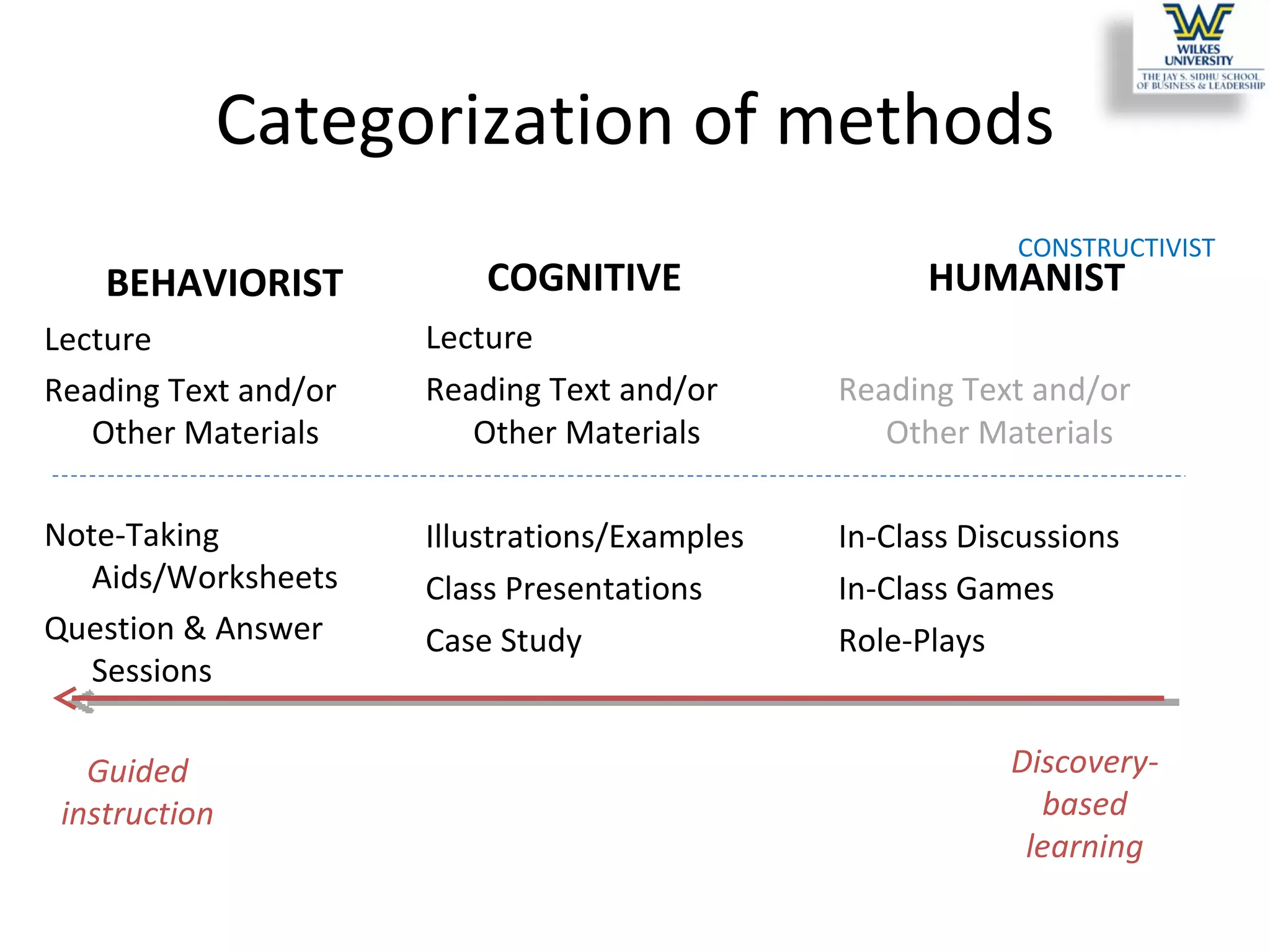
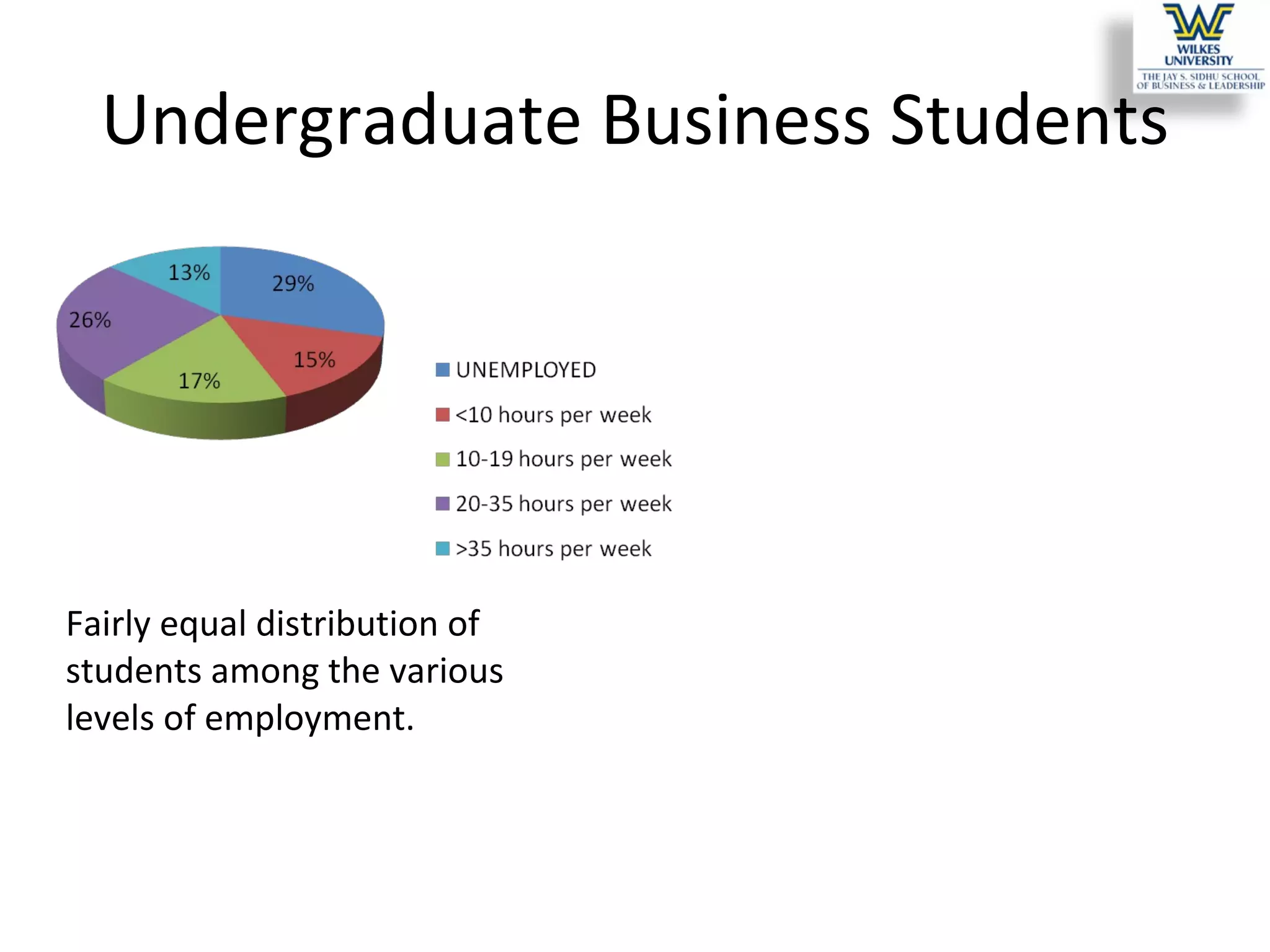
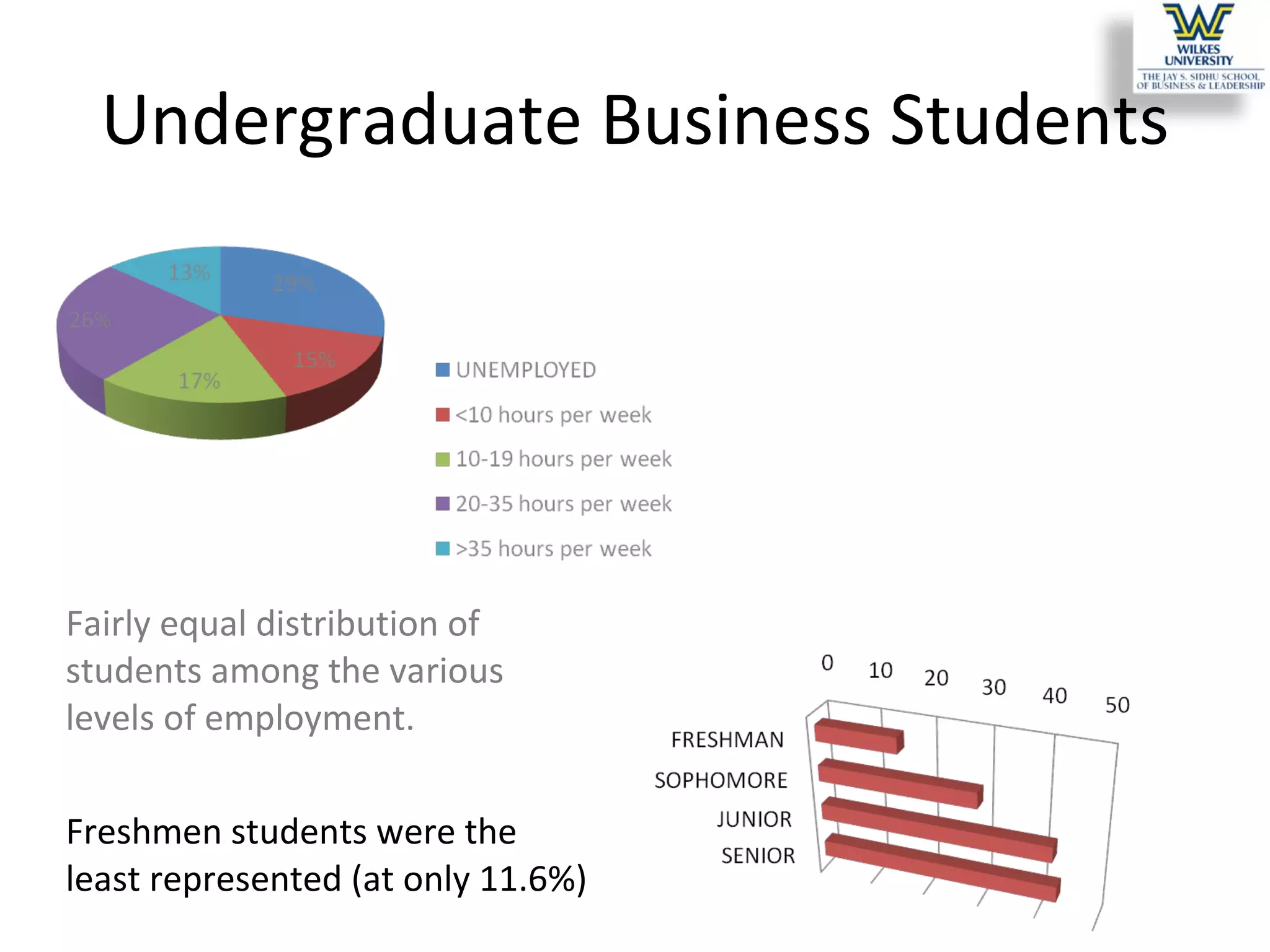
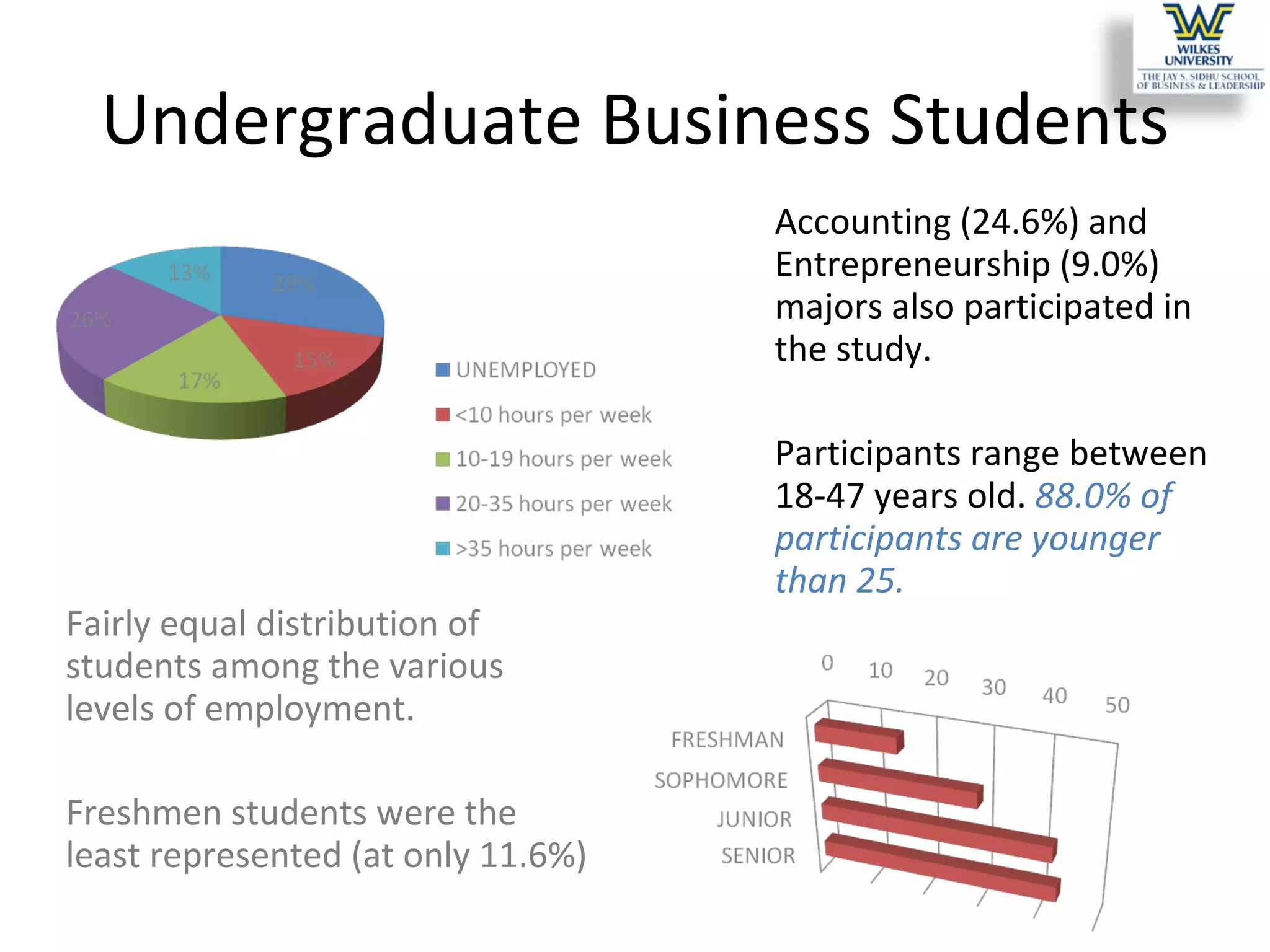
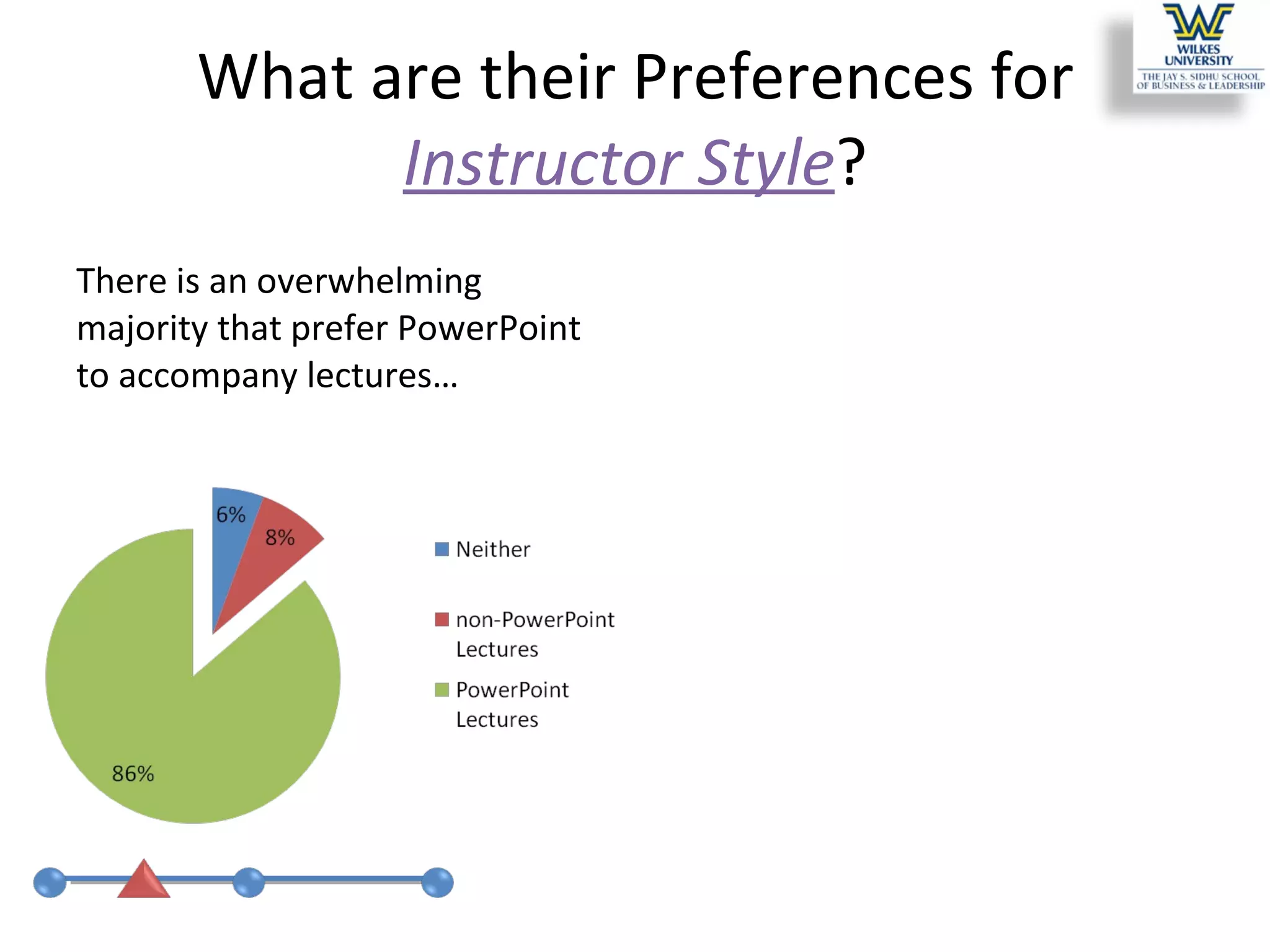
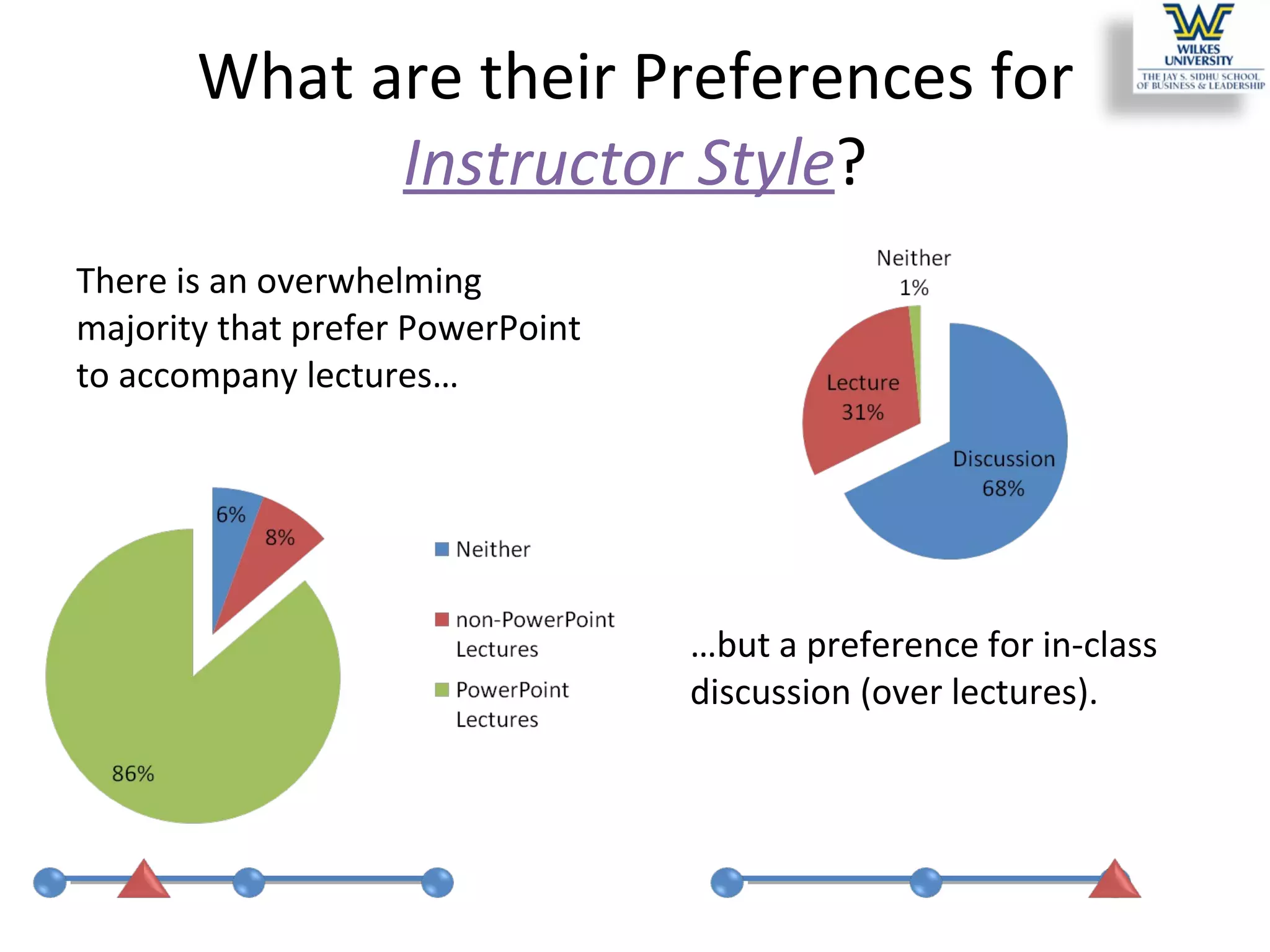
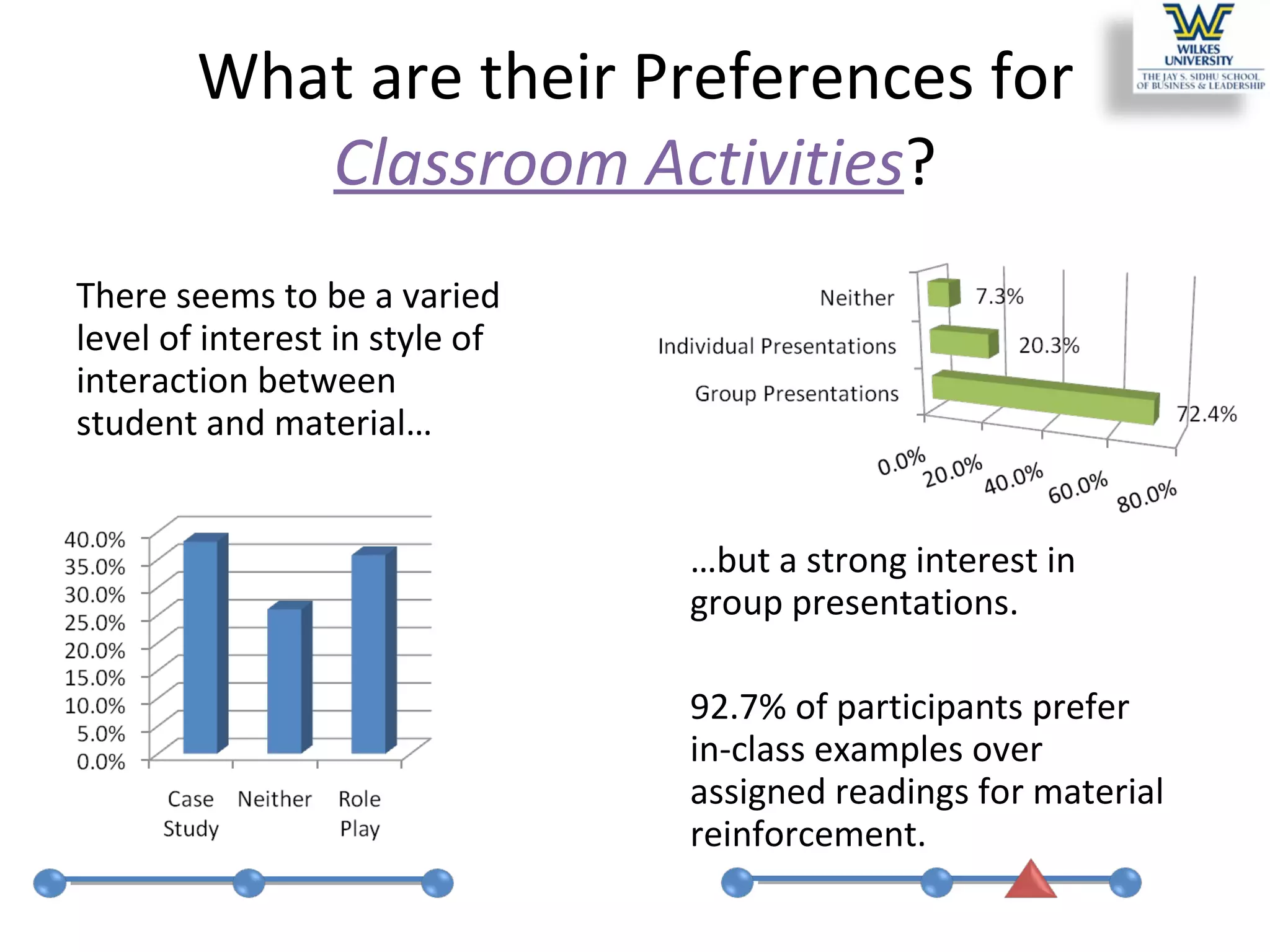
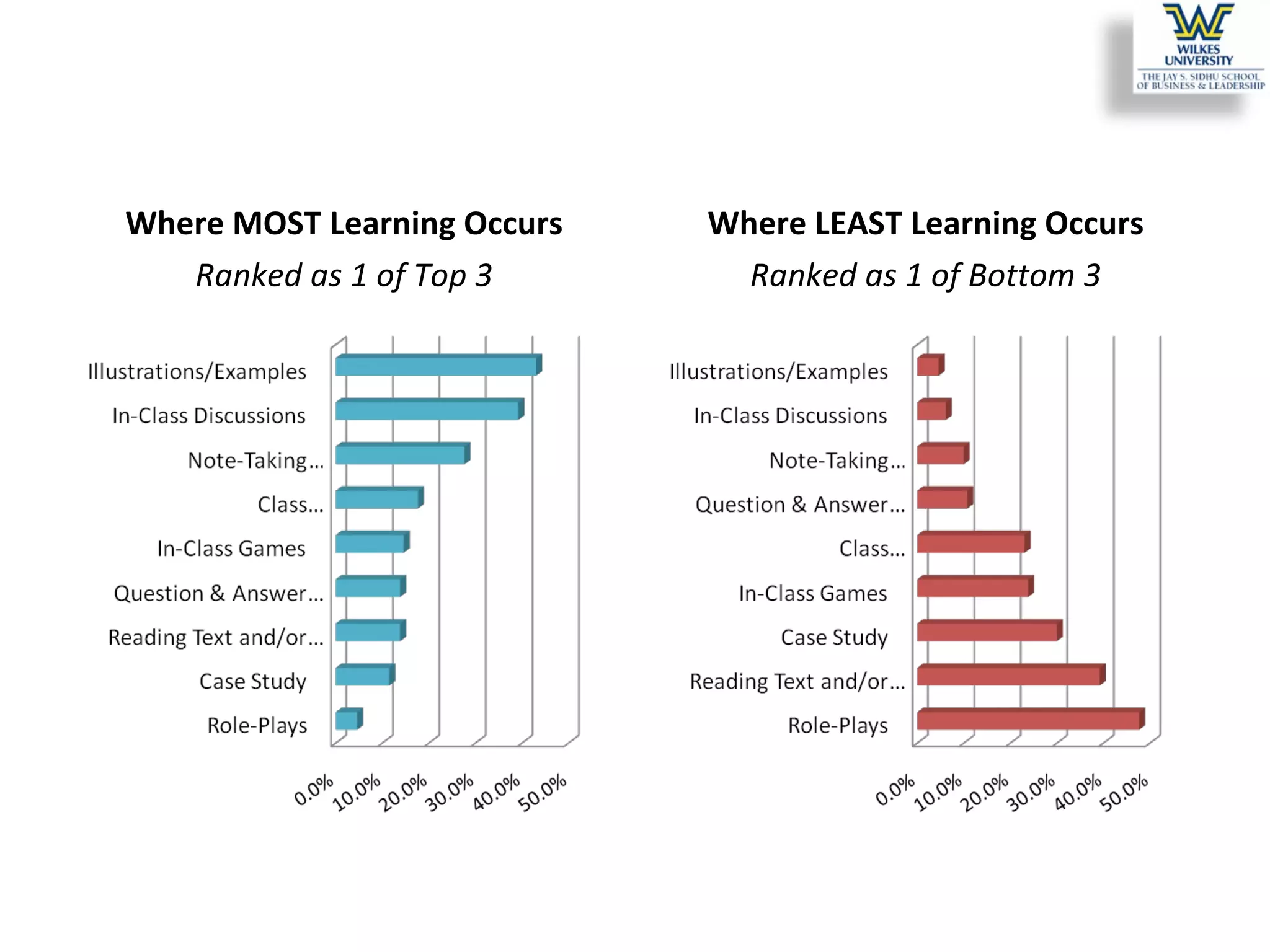
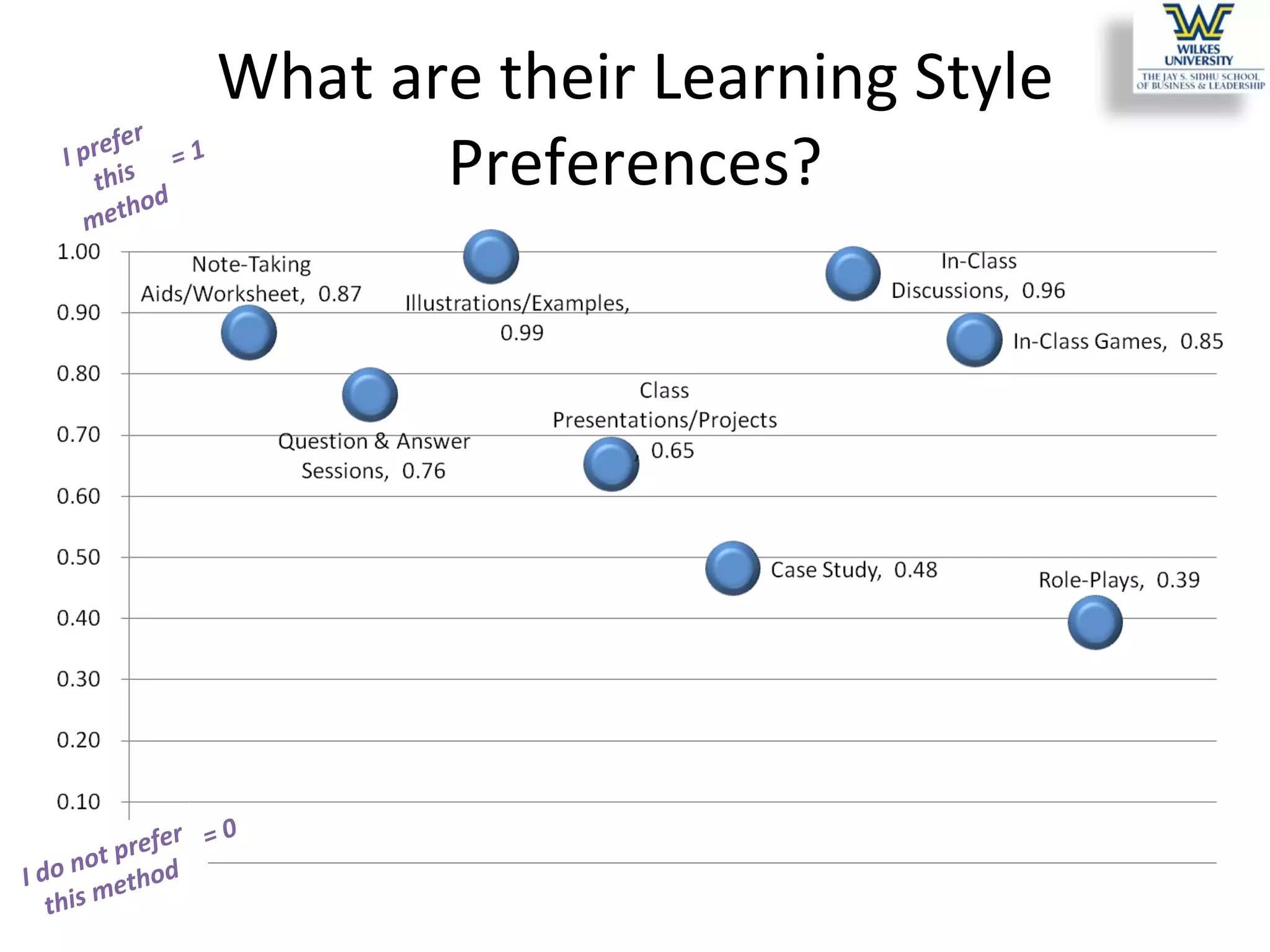
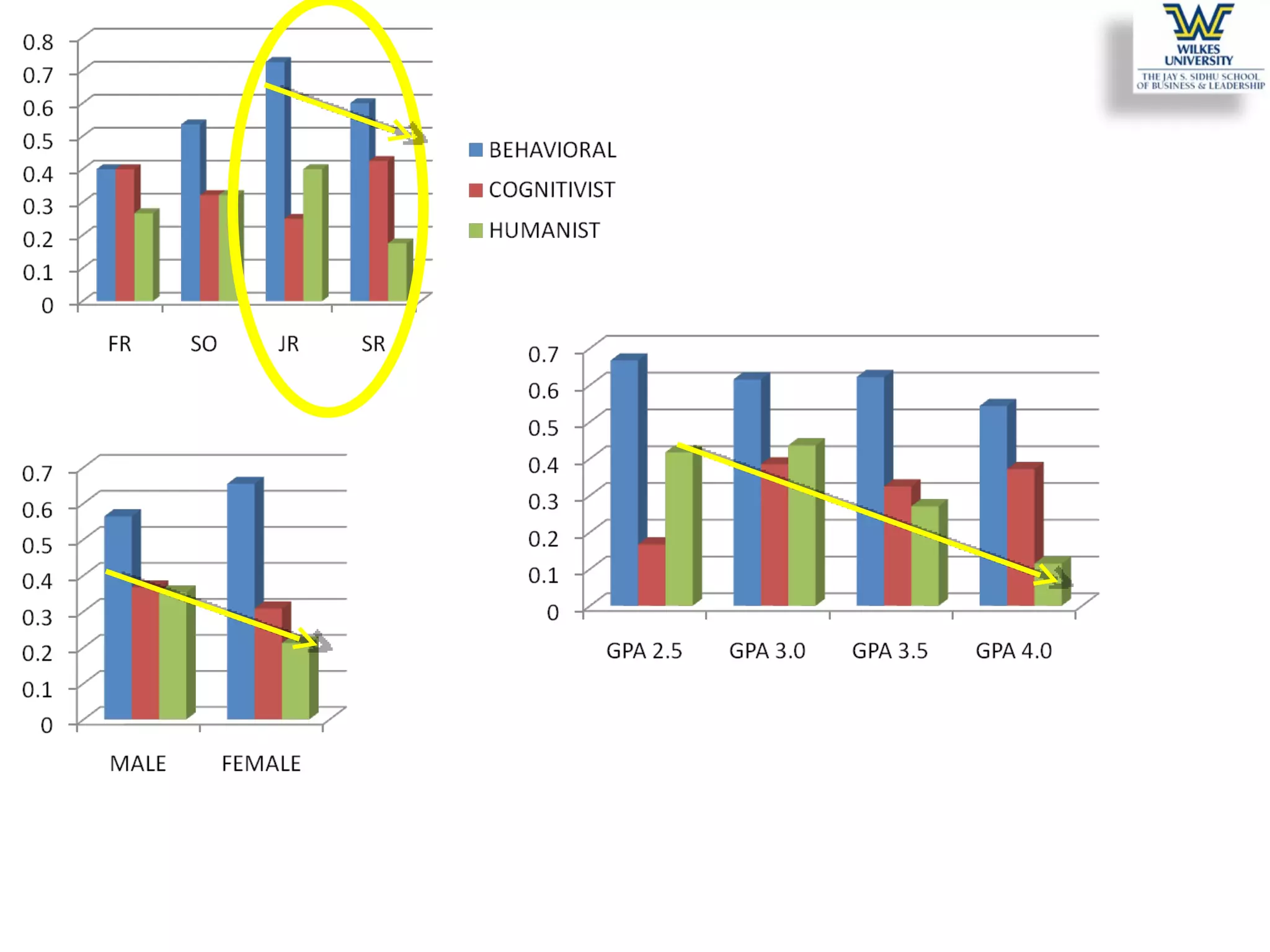
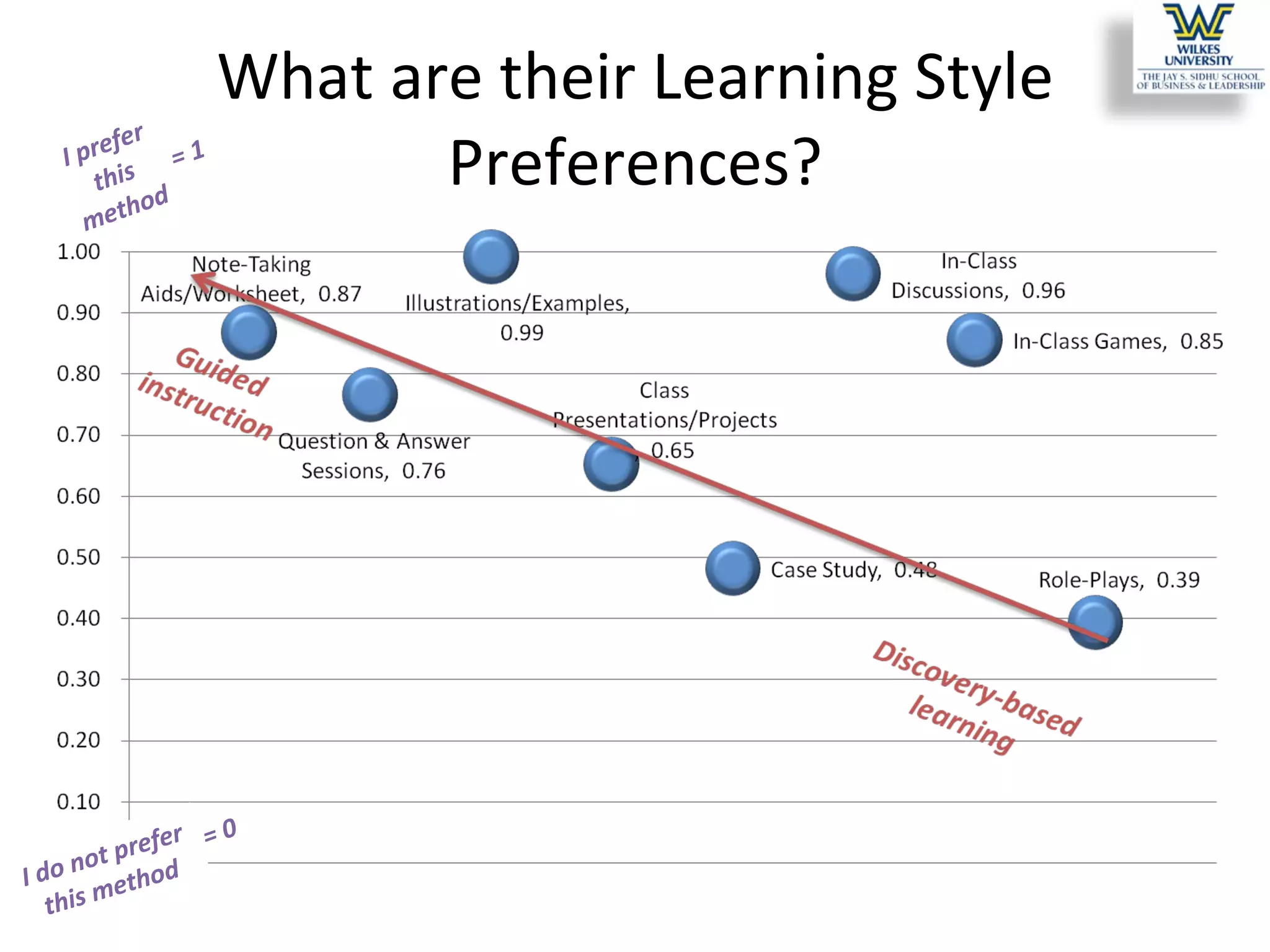
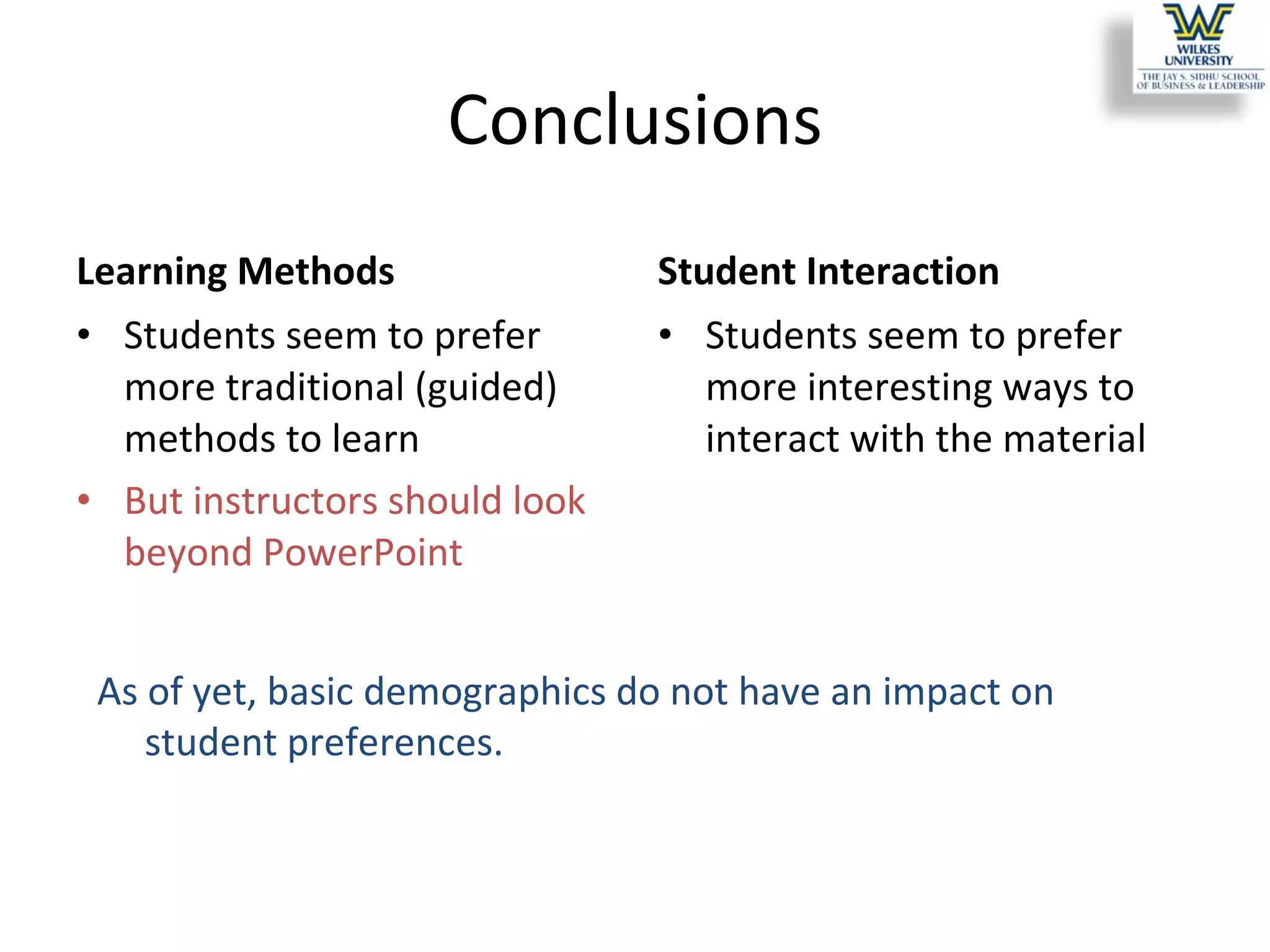
This study investigates the learning style preferences of undergraduate business majors, focusing on differences based on age, class standing, and gender. Findings indicate a strong preference for PowerPoint presentations alongside in-class discussions and examples over traditional lectures and readings. The research highlights the need for educators to adopt diverse and interactive methods to enhance student learning, as current demographics do not significantly influence preferences.