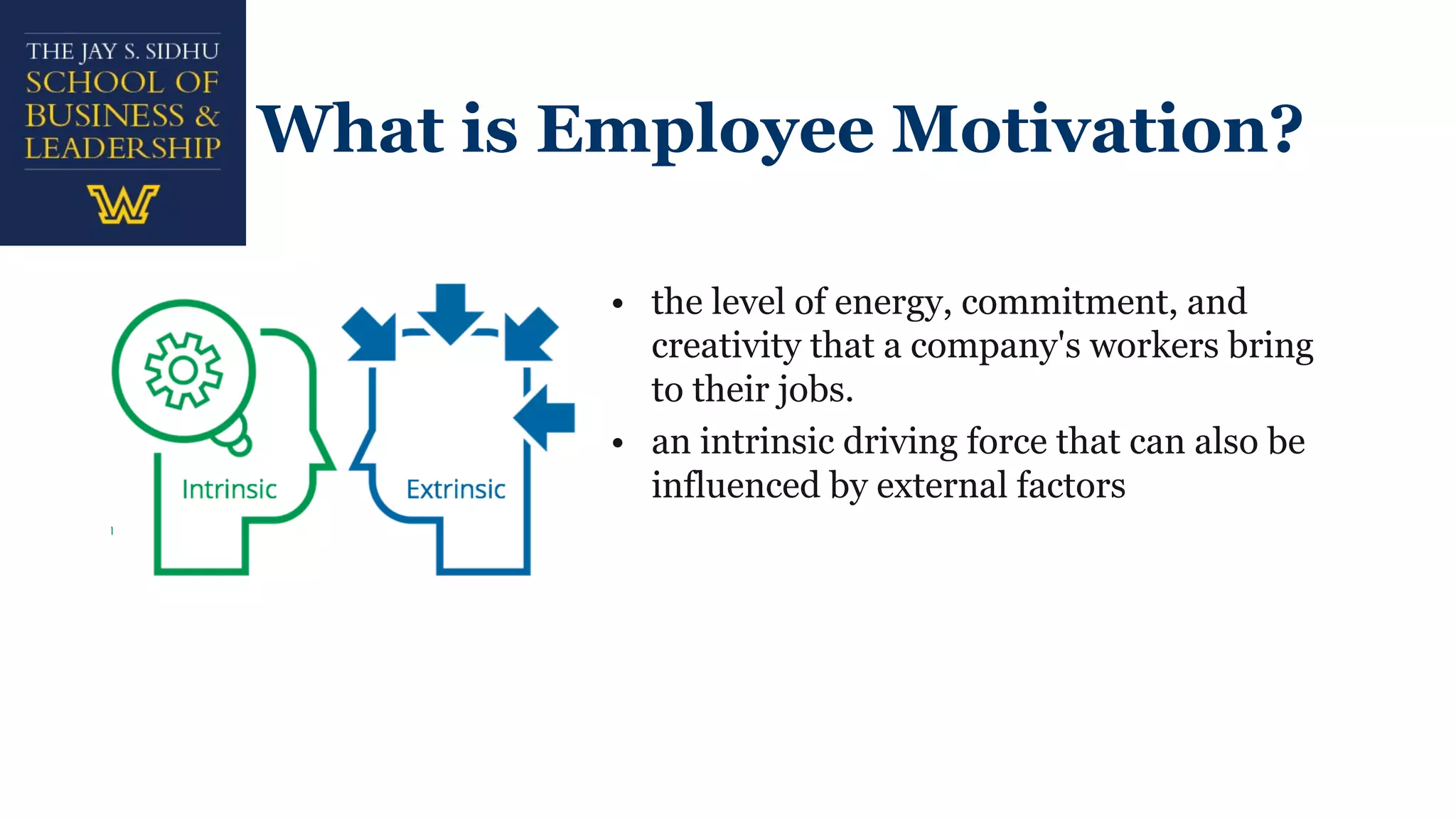
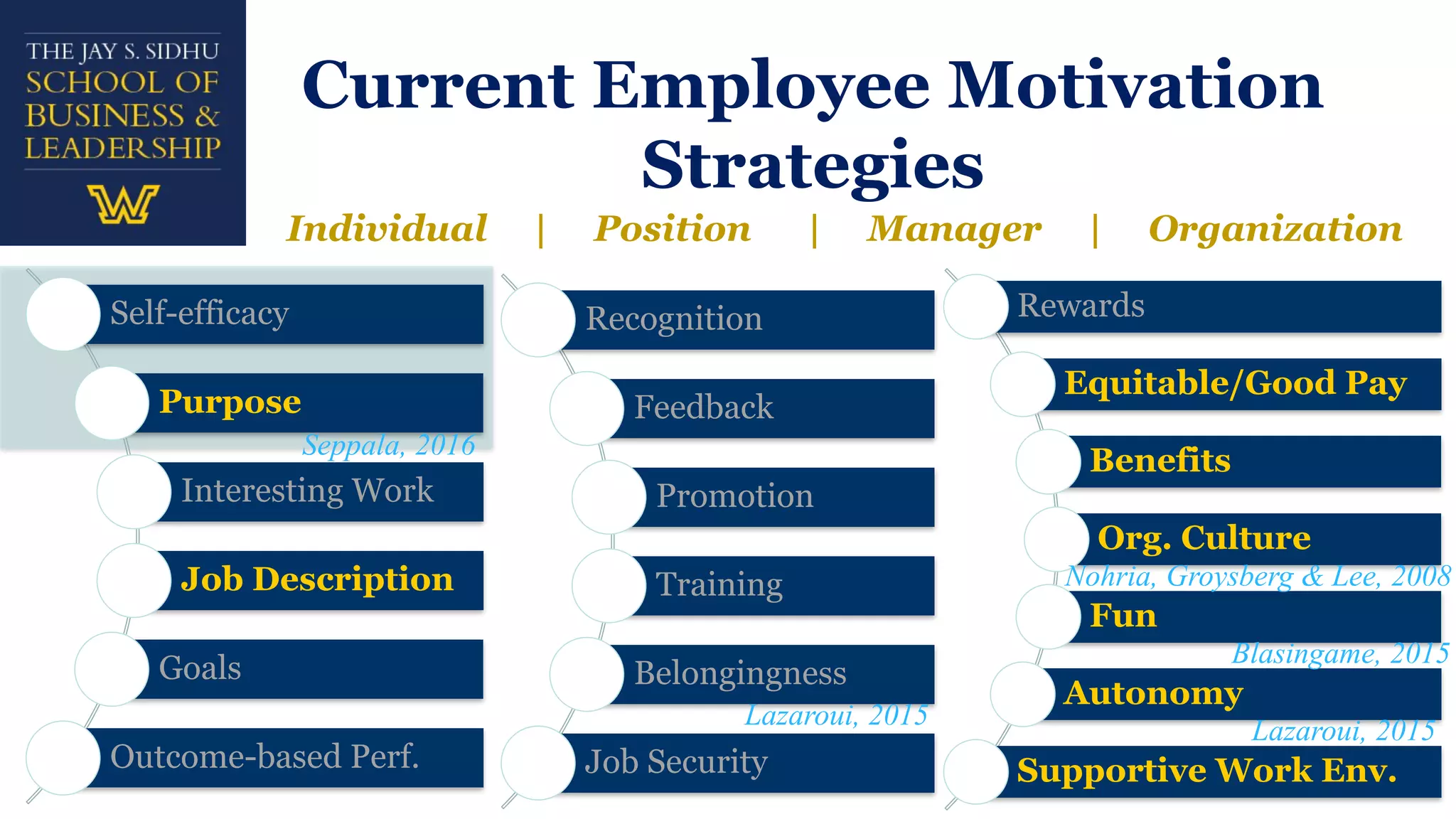
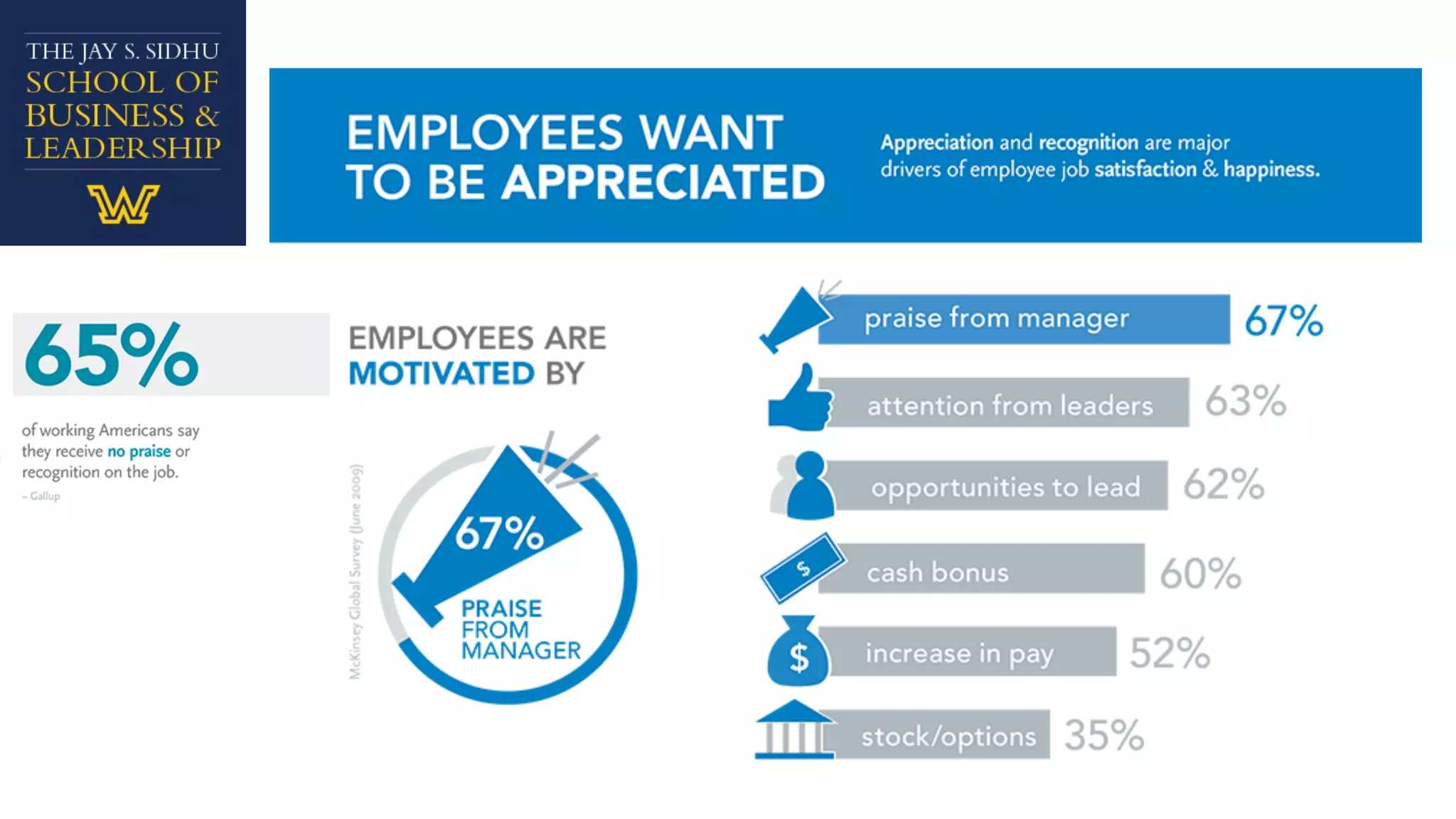
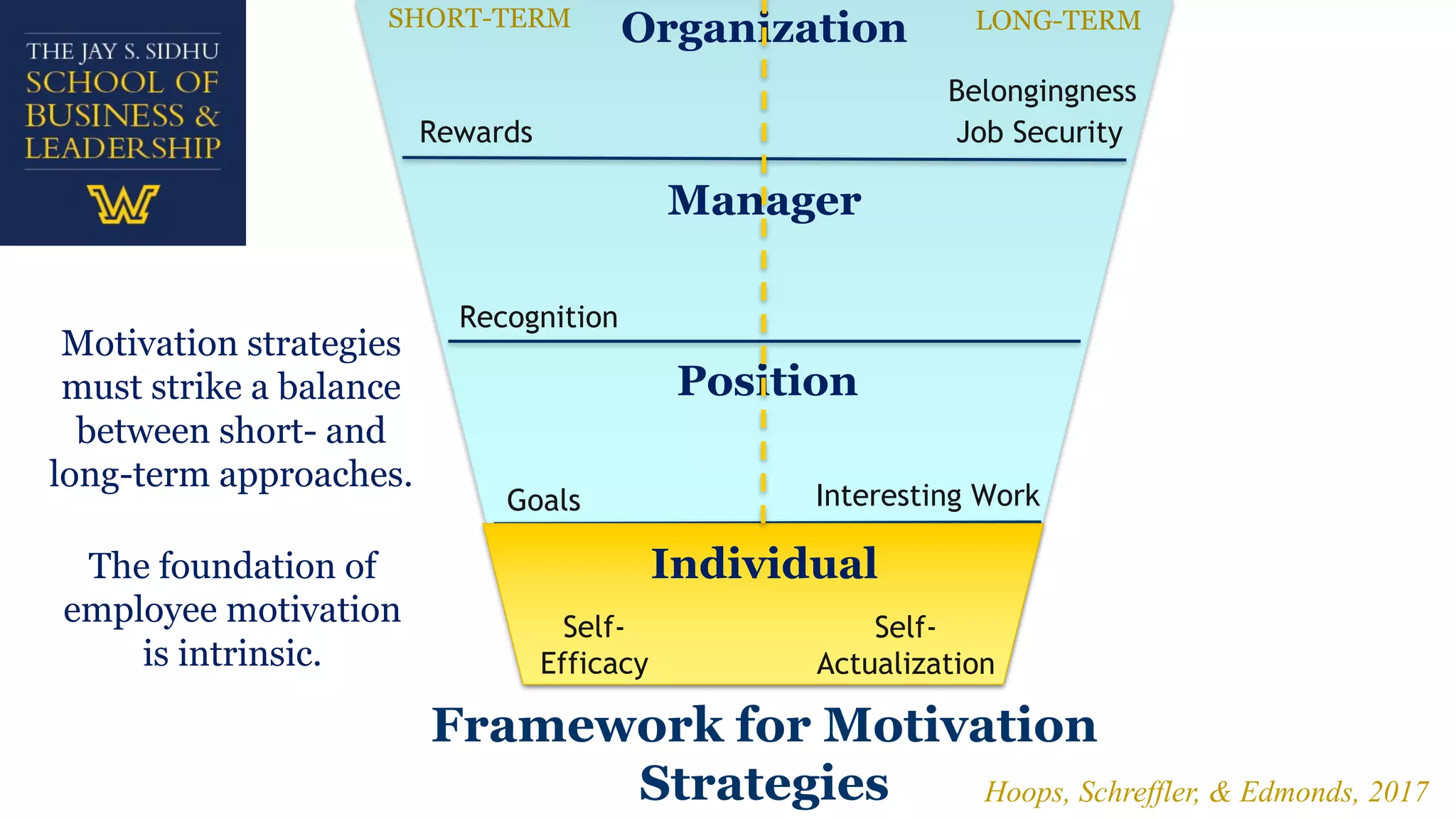
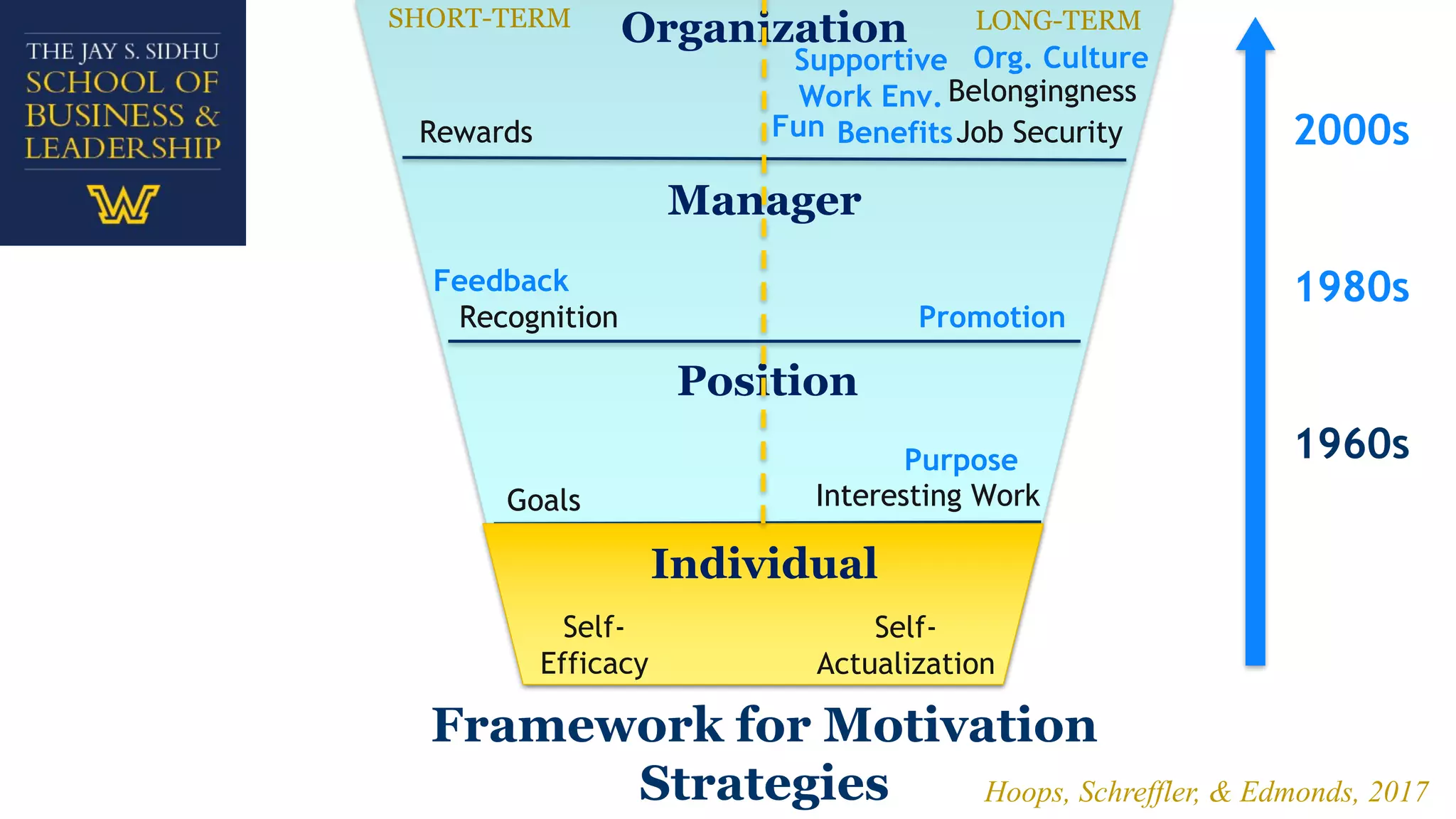
The document explores employee motivation, highlighting its significance in improving productivity and job performance, indicating that only 20% of employees feel adequately motivated. It reviews historical and contemporary trends in motivation strategies, focusing on intrinsic and extrinsic factors such as self-efficacy, recognition, and job security. A proposed framework suggests that effective motivation strategies balance short-term and long-term approaches to foster engagement and satisfaction among employees.