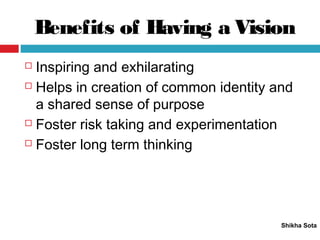
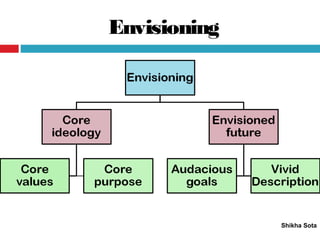
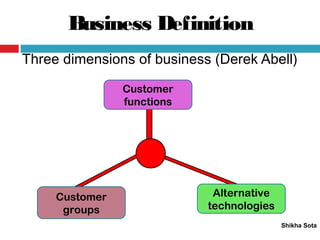
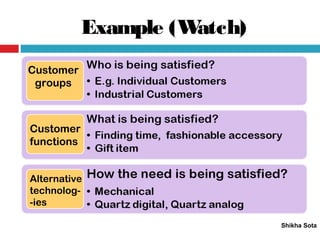
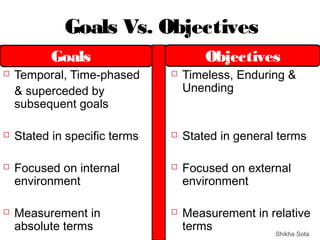
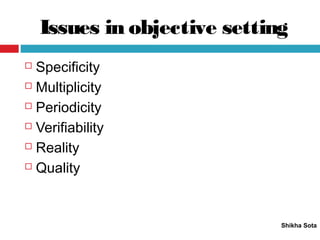
The document discusses various strategic planning concepts including strategic intent, vision, mission, business definition, goals, objectives, and critical success factors. Strategic intent refers to the long-term purpose of an organization. Vision describes what the organization would ultimately like to become. Mission answers questions about the organization's purpose and reason for existence. Business definition outlines the customer groups, functions, and technologies that define a company. Goals and objectives help operationalize the vision and mission, with objectives being more specific and measurable. Critical success factors are the key elements necessary for success in a given industry.