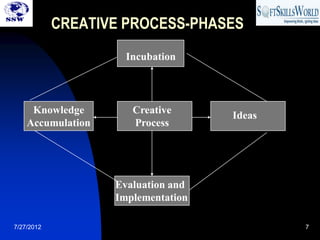
The document discusses innovation and creativity. It states that innovation is key for entrepreneurs and involves converting opportunities into marketable ideas through a creative and systematic process. Creativity generates new ideas that improve efficiency and involves both process and people. The creative process involves phases like knowledge accumulation, incubation, idea generation, and evaluation. Developing creativity requires recognizing relationships, having a functional perspective, using both sides of the brain, and eliminating limiting mindsets. Innovation often stems from addressing incongruities or needs and following principles like keeping ideas simple, customer-focused, and continually testing and revising.