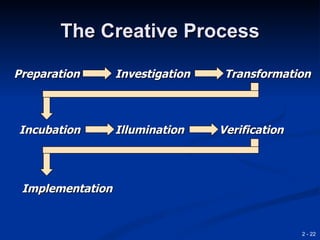
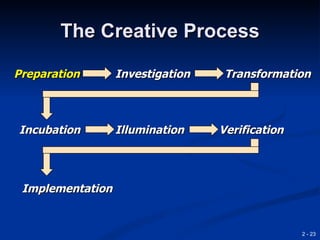
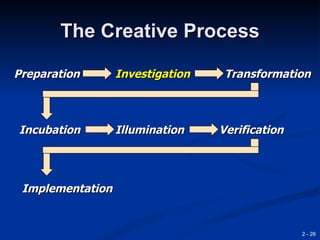
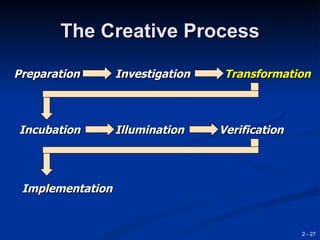
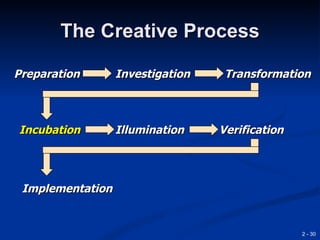
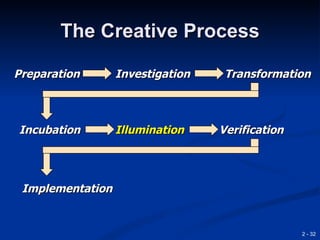
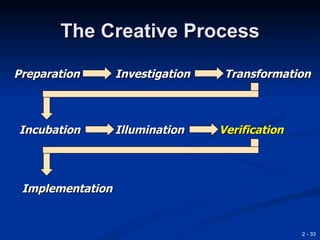
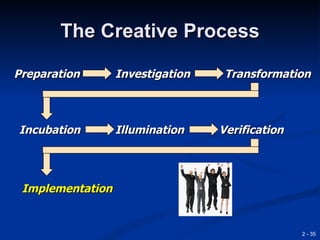
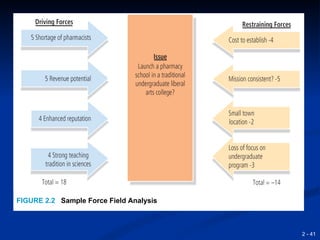
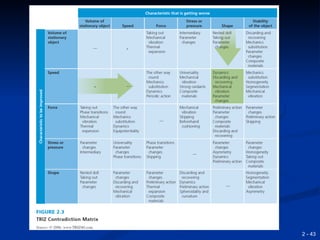
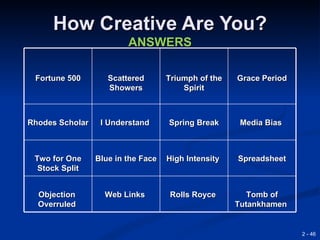
This document provides an overview of creativity and entrepreneurship. It discusses how creativity involves developing new ideas and looking at problems in new ways, while innovation applies creative solutions. Entrepreneurship combines creativity and innovation to identify marketplace needs and opportunities. The document then provides tips and techniques to enhance creativity at both the individual and organizational levels, including questioning assumptions, brainstorming, mind mapping and prototyping ideas.