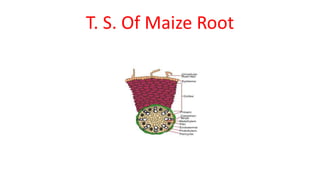
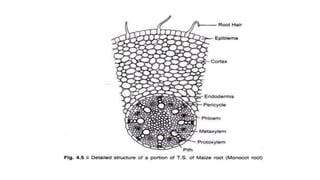
The document is a detailed study of monocot root anatomy, particularly focusing on maize roots. Key features discussed include the structure and function of the epiblema, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and vascular bundles, highlighting their roles in water absorption and mineral regulation. The document notes the absence of secondary growth and the distinct characteristics of various root tissues, including the arrangement of vascular bundles and the presence of casparian stripes.