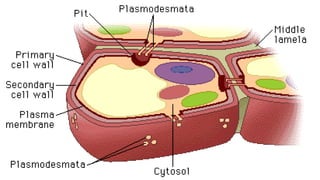
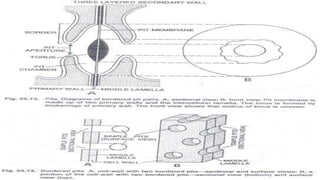
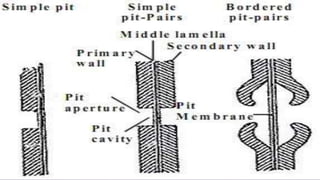
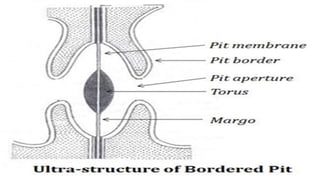
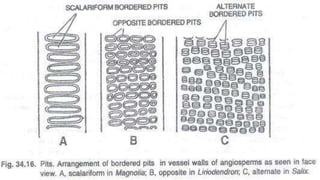
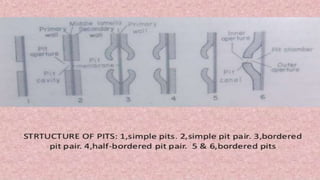
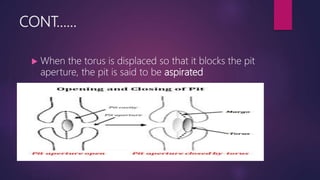
The document discusses the types and structures of pits in plant cell walls, which facilitate communication and transport between adjacent cells. It describes various types of pits, including simple, bordered, half-bordered, blind, compound, and vestured pits, along with their characteristics and functions. It also highlights the similarities between pits and plasmodesmata in enabling substance exchange within plant cells.