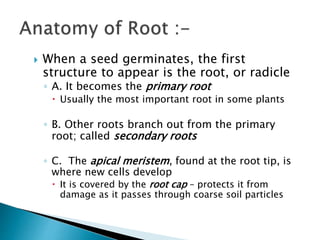
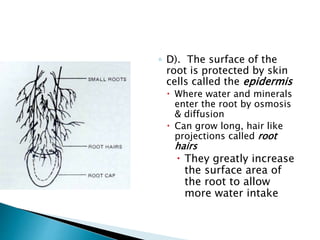
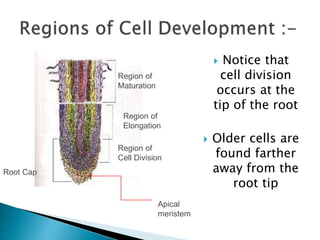
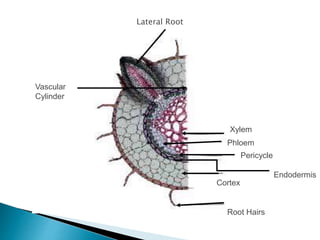
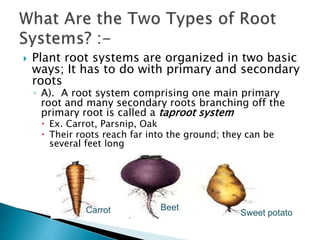
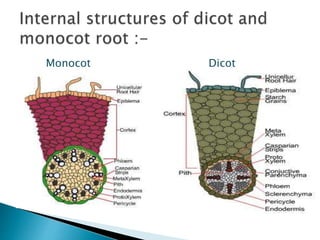
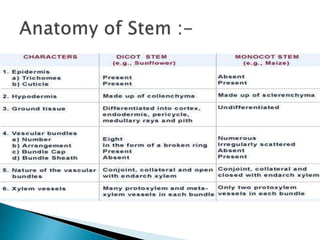
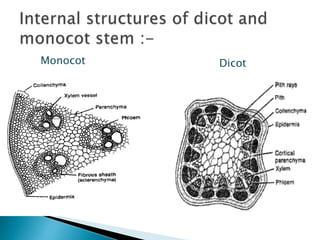
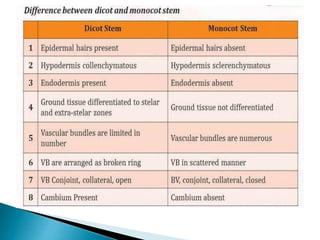
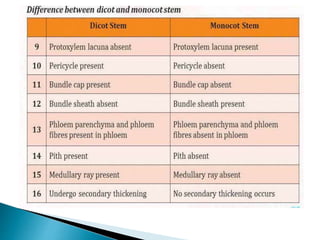
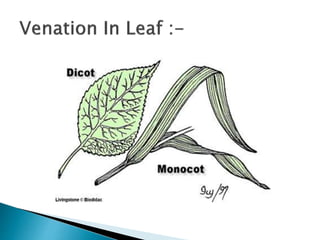
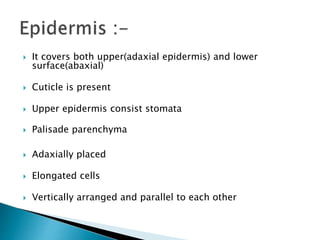
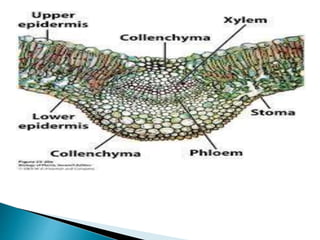
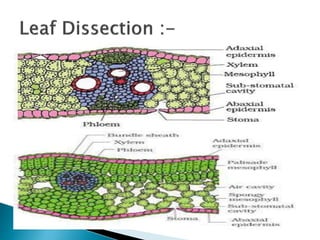
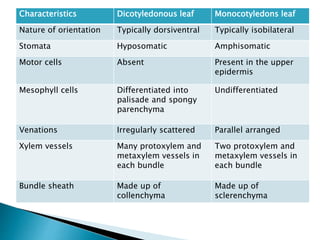
This document summarizes the histology of roots, stems, and leaves. It describes the key structures and tissues of plant roots including the root cap, epidermis, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, vascular cylinder, and root hairs. It also discusses the two main types of root systems - taproot and fibrous. For stems, it focuses on vascular bundles. Finally, it provides details on leaf anatomy like the epidermis, mesophyll, and vascular system. It compares the characteristics of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous leaves.