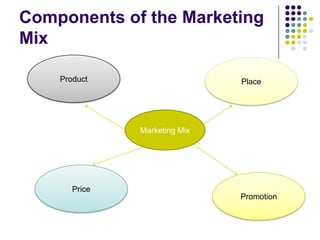
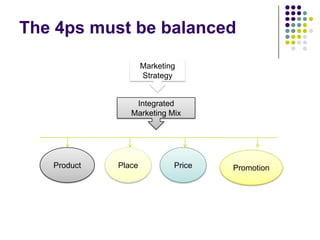
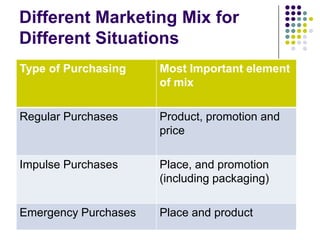
The marketing mix is a fundamental aspect of marketing that includes the 4Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. It is used by businesses to decide how to market products based on customer needs. Price is an important element that impacts revenue and market share. Common pricing strategies include cost plus, penetration pricing, price skimming, competitive pricing, promotional pricing, and loss leaders. The appropriate strategy depends on factors like market entry, increasing sales, and covering costs.