This document discusses different types of digital media channels that can be used for marketing communications. It provides details on six main channels:
1. Search engine marketing, including search engine optimization and paid search advertising. It discusses best practices for planning, managing SEM, and the advantages and disadvantages.
2. Online public relations, how it differs from traditional PR, and best practices for managing online PR.
3. Online partnerships like affiliate marketing, how different affiliate models work, and best practices for planning affiliate marketing programs.
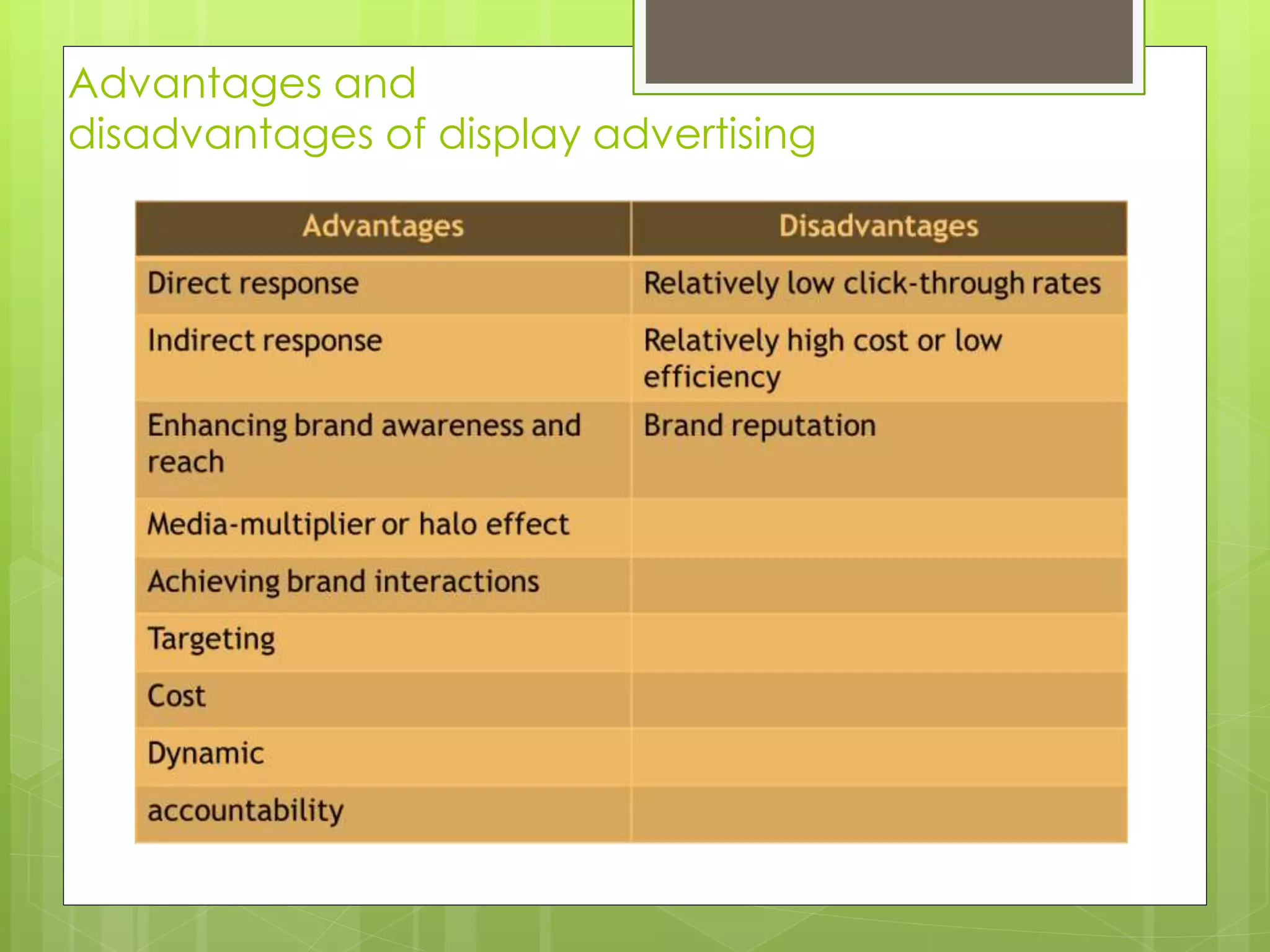
4. Interactive display advertising, how to purchase ad placements, and best practices for measuring and managing display ad campaigns.
5. Opt-in email marketing and best practices for list acquisition