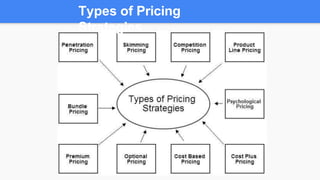
This document discusses various pricing strategies that companies can employ:
1. Penetration pricing sets prices artificially low to gain market share, then prices are increased once market share is achieved. Price skimming charges high initial prices for products with substantial advantages.
2. Competitive pricing matches competitors' prices to avoid trial and error. Product line pricing reflects quality differences between a company's product range. Psychological pricing uses odd prices like $1.99 to increase demand.
3. Premium pricing charges high prices for unique brands to signal quality. Optional pricing sells accessories at higher prices. Bundle pricing offers package deals at lower combined prices to increase profits. Cost-based pricing adds a markup percentage to manufacturing costs