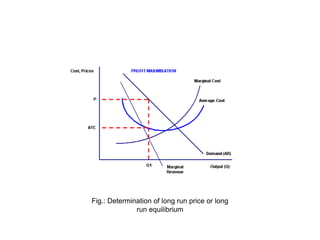
Monopoly is a market situation where there is only one seller of a product or service with no close substitutes. A monopoly firm is a price maker that can determine prices to maximize profits. Under monopoly, the demand curve is the average revenue curve, which slopes downward. Marginal revenue is also downward sloping. In the short run, a monopoly can earn super-normal profits, normal profits, or minimize losses. In the long run, monopoly equilibrium occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. A monopoly may also engage in price discrimination, charging different prices to different customers to increase total revenue and profits.