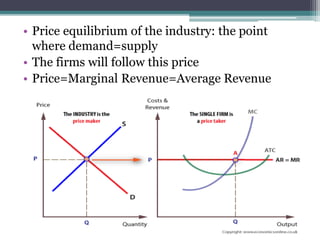
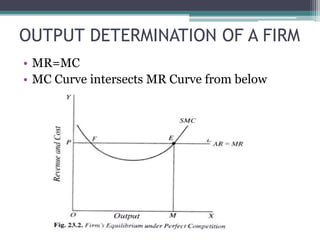
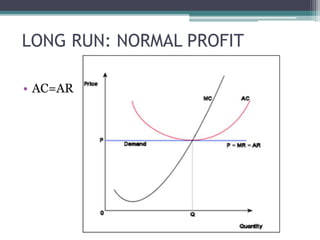
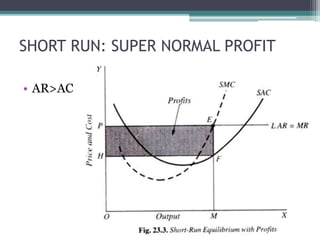
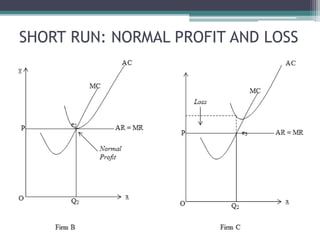
Under perfect competition, firms are price takers and cannot influence the market price. The market price is determined by the intersection of total industry demand and supply. In the short run, a firm can be in a situation of normal profit, super normal profit, or loss depending on the relationship between average revenue (AR) and average cost (AC). In the long run, all firms will earn only normal profits as inefficient firms exit the industry. The shutdown point occurs when a firm's average variable cost equals its average revenue.