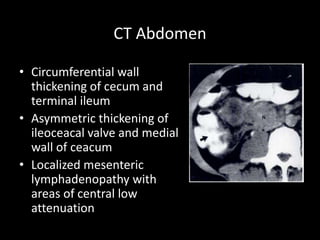
This document discusses intestinal tuberculosis, which can involve any part of the gastrointestinal tract. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is usually the causative pathogen. It can reach the intestines through ingestion, hematogenous spread from a lung infection, or direct spread from adjacent organs. Common sites of infection include the ileocecal region. Symptoms vary depending on the location but often include abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, and changes in bowel habits. Investigations include blood tests, imaging modalities like ultrasound and CT, and acid-fast bacilli testing of biopsy specimens. Treatment involves a standard antibiotic regimen over 6 months along with nutrition support. Surgery may be needed for complications like obstruction, hemorrhage, or perforation